Currently, the register of unscrupulous suppliers is maintained on the basis of:
Federal Law No. 44-FZ of April 5, 2013 “On the contract system in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 44-FZ); Federal Law of July 18, 2011 No. 223-FZ “On the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 223-FZ); Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 25, 2013 No. 1062 “On the procedure for maintaining a register of unscrupulous suppliers (contractors, performers)” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1062); Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 22, 2012 No. 1211 “On maintaining a register of unscrupulous suppliers, provided for by the Federal Law “On the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1211); Order of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia dated August 27, 2007 No. 267 “On maintaining a register of unscrupulous suppliers, including and excluding information from the register of unscrupulous suppliers, conducting inspections of facts of evasion of a procurement participant from concluding a state or municipal contract, carrying out unscheduled inspections when considering information about unscrupulous suppliers "(hereinafter referred to as Order of the FAS of Russia No. 267); letters of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia dated March 28, 2014 No. IA/11604/14 “On the consideration of requests for inclusion in the register of unscrupulous suppliers of information about unscrupulous suppliers (contractors, performers), contracts with which were terminated in the event of a unilateral refusal of the customer to fulfill the contract due to with a significant violation of the terms of the contracts" and dated December 8, 2014 No. ATs/50130/14 "On clarification of the legislation on the contract system regarding the issue of the customer sending information to the register of unscrupulous suppliers about the participant recognized as the winner of the procurement, who subsequently evaded concluding a contract in the event , if the second participant evaded concluding a contract” and other acts.
It should be noted that in these documents, including Art. 3 of Law No. 44-FZ, there are no definitions of the concepts “register of unscrupulous suppliers” and “unscrupulous supplier”. In this regard, in theory and practice, researchers and lawyers have discussions on this issue.
Why was the registry created?
In order to ensure that a person fulfills the obligations assumed within the framework of the procedure for placing state and municipal orders, as well as orders of certain types of legal entities, to protect fair competition and to prevent abuse in the field of placing orders by dishonest actions of suppliers (performers, contractors) in the above legal acts it was envisaged to create a register of unscrupulous suppliers (Determination of the RF Armed Forces dated August 12, 2016 No. 310-KG16-5426).
As stated in the decision of the Thirteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated March 23, 2015 No. 13AP-2095/2015, the register of unscrupulous suppliers is a special measure of liability, a kind of sanction for a violation in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs and procurement by certain types of legal entities.
Reasons for inclusion in the register of unscrupulous suppliers
In accordance with part 2 of Art.
104 of Law No. 44-FZ, part 2 of Art. 5 of Law No. 223-FZ and sections I and III of Letter No. IA/11604/14 of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia, the register of unscrupulous suppliers includes information about the following procurement participants: 1) those who evaded concluding contracts (agreements), including when:
failure of the participant recognized as the winner of the auction to comply with the requirement to provide appropriate information; failure to provide adequate security by the winner of the competition within the prescribed period; failure to sign the contract within the prescribed period by the winning procurement participant.
The term “evasion from concluding a contract” implies not only a formal violation of legal requirements, but also the absence of a real intention to conclude and fulfill a contract, therefore, in order to be included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers on this basis, in addition to the fact of violation, it is necessary to establish the direction of the will and the dishonest nature of the behavior of the auction winner (p 12 Final information on current issues of application of Federal laws dated July 18, 2011 No. 223-FZ “On the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities”, dated April 5, 2013 No. 44-FZ “On the contract system in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs”, approved by the presidium of the AS of the Ural District on June 24, 2016);
2) suppliers (contractors, performers) with whom contracts (agreements) were terminated by a court decision (including due to their significant violation of the terms of contracts (agreements));
3) in case of unilateral refusal of the customer to fulfill the contract due to a significant violation by the supplier (contractor, performer) of the terms of the contracts (except for the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities).
Please note that the grounds for including information about an unscrupulous supplier (contractor, performer) in the appropriate register in the event of a unilateral refusal by the customer to fulfill obligations under the contract are documented circumstances:
failure by the supplier (contractor, performer) to fulfill obligations under the contract; improper performance by the supplier (contractor, performer) of obligations under the contract; identification by the customer during the execution of the contract of non-compliance of the supplier (contractor, performer) with the requirements specified in the procurement documentation; establishment by the customer during the execution of the contract of the fact that the supplier (contractor, performer) provided unreliable information about its compliance with the requirements specified in the procurement documentation.
Let us note that the customer has the right to decide on a unilateral refusal to fulfill the contract on the grounds provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation for unilateral refusal to fulfill certain types of obligations, provided that this was provided for by the contract (Part 9 of Article 95 of Law No. 44-FZ).
One of the reasons for entering information about a procurement participant into the register of unscrupulous suppliers is the participant’s carelessness and failure to take appropriate measures in order to exclude the possibility of adverse consequences for him (resolution of the Thirteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal No. 13AP-2095/2015).
Government procurement: consequences of being included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers (RNP). How not to get there?
“Supplier to the Imperial Court” - this title, soothing to the ears of any businessman, was once received by merchants and entrepreneurs who provided goods for royalty. The title was very prestigious, because the quality of the brand, appreciated by the emperor himself, was beyond doubt, as was the impeccable reputation of the supplier. A businessman could not imagine a better advertisement of goods and services. True, in order to achieve the right to supply goods, the applicant had to confirm the high quality of his products for a good ten years, participate in industrial exhibitions, have no complaints from buyers, etc.
A modern analogue of this procedure described above can be considered government procurement, in which everyone can take part, subject to compliance with the relevant requirements.
Purchasing is a lucrative business, but it comes with certain risks. For example, if a company or entrepreneur gets included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers , this can have very disastrous consequences for their business. How to avoid such a situation, says Valery Ovechkin, consultant, business coach on government procurement.
– Valery, what is RNP in general terms?
– This register includes companies that have not signed or failed to fulfill a government contract (violated its terms). In other words, this is a publicly available blacklist of suppliers.
– What sanctions are entailed by being included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers?
– Companies from this list will no longer be able to participate in government tenders for two years. In addition, if you are the founder of an LLC and your TIN is included in the RNP, then you, being in the status of an individual entrepreneur or founder in other companies, will also not be able to participate in the auction. And accordingly, companies of which you are the founder cannot participate in procurement.
There are no other negative consequences, but this sanction is fatal for many companies and literally closes the way to business, because first of all, damage is caused to its business reputation, and the entrepreneur cannot, for example, establish a new company to participate in government procurement.
– Is it possible not to end up in the RNP, even if there have been specific violations?
– First of all, you need to know that when adding to the RNP for non-signing or non-fulfillment of a contract, customers, in accordance with Part 12 of Article 95 of Federal Law 44, must adhere to the rules clearly stated in the law and follow certain procedures. If at least one of these rules is violated, then the FAS, if you point it out to it, will decide that you do not need to be included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers.
The Federal Antimonopoly Service is interested in preserving competition, and a company has every chance of avoiding a blacklist if there is any reasonable doubt about its guilt.
The second thing to consider is the circumstances of the case. If we are talking about an electronic auction and you had contract security in your current account, or a bank guarantee was issued, or you intended to sign this contract, but were unable to do so for reasons beyond your control (the digital signature did not work, the Internet was turned off, etc.) etc.), this is also not a reason for inclusion in the RNP.
It is important to consider one more point. Inclusion in the RNP is a lengthy process, it takes at least 40 days, and during this period you can participate in government procurement. Finally, if we are talking about an auction, request for quotation, or some other format of bidding under Federal Law 44, you may not sign the contract without any sanctions if you prove that there were violations in the terms of reference on the part of the customer. I will give examples from personal experience. The company won the tender for the demolition of the house, but part of the demolition work was already carried out in violation of the technical specifications, or the supplier won the request for quotations and was unable to sign the contract because it did not receive the draft contract on time. In both cases, no punishment was imposed by the FAS.
There is only one rule: if you feel that the customer is wrong in something, or you can prove that you were unable to sign or fulfill the contract for some reason beyond your control, notify the FAS about this when you are invited to the meeting. As a last resort, you can contact specialists who, during the procedure for entering into the RNP, will help to avoid this in 80% of cases. The cost of such a service is about 20–25 thousand rubles, which is often incomparable to the losses that you will incur if you are included in this register.
Program for searching tenders (regularly) - AuSe scanner
AuSe robot for winning tenders and auctions.
The material is written based on documents from open sources.
Grounds and terms for inclusion in the register
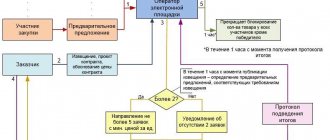
As established in part 7 of Art.
104 of Law No. 44-FZ, the federal executive body authorized to exercise control in the field of procurement, includes information about the procurement participant in the register of unscrupulous suppliers within three working days from the date of confirmation of the existing facts, whereas according to paragraph 13 of Resolution No. 1062 information about an unscrupulous supplier (contractor, performer) is entered into the register within 3 working days from the date the authorized body makes the relevant decision. In this regard, the question arises: is the fact of the supplier’s dishonesty confirmed (exclusively) by a decision of the FAS Russia (its territorial body) or in another way? At the same time, as follows from paragraphs. 6 and 7 of Order No. 267 of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia, information about procurement participants who evaded concluding state or municipal contracts, about suppliers (performers, contractors) with whom state or municipal contracts were terminated due to a significant violation of the terms of the contract by them, is included in the register unscrupulous suppliers on the basis of an order from the head of the FAS Russia.
As part of the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities, information on unscrupulous procurement participants, suppliers (performers, contractors) confirmed by the results of an audit is entered by the authorized body into the register within 3 working days (clause 9 of the Rules for maintaining the register of unscrupulous suppliers, approved by the Resolution No. 1211).
However, we draw special attention to the fact that neither Law No. 223-FZ nor Resolution No. 1211 establishes the procedure for consideration by the FAS of Russia of information about a procurement participant from the point of view of inclusion in the register of unscrupulous suppliers and the right to participation of representatives of the parties, which is provided for by analogy in paragraph 12 of Resolution No. 1062.
There is also no norm in the regulatory legal acts on the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities that contains the basis for the FAS Russia bodies to enter information about the procurement participant into the appropriate register (order, decision or other document of the authorized body).
In practice, there are often cases of untimely inclusion of information about a procurement participant in the register of unscrupulous suppliers. According to the Judicial Collegium for Economic Disputes of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, this is a violation by the authorized body of the established deadlines for performing these actions, which is inconsistent with both the goals and objectives of the provided procedure for protecting the rights of customers, and with the guarantees provided to unscrupulous suppliers included in the relevant register , since if the authorized bodies comply with certain deadlines, a person who has evaded concluding a state or municipal contract has the right to count on the timely exclusion of information about him from the register of unscrupulous suppliers, which will ensure the right of such a person to further possible participation in auctions and meets the requirements of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the corresponding principle legal equality (Definition of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2016 No. 310-KG16-556).
Deadlines for submitting an application and including the supplier in the RNP
If the supplier is recognized as having evaded, as well as in case of termination of the contract by a unilateral decision of the customer or a court decision, the customer within 3 working days from the date of evasion or termination of the contract.
Within 5 working days from the receipt of all necessary documents, the FAS begins to verify the provided facts about violations.
If all data is confirmed, then information about the supplier is entered into the register of unscrupulous suppliers within 3 working days from the moment this information is confirmed.
Responsibility of the founders of the procurement participant
In paragraph 2 of part 3 of Art.
104 of Law No. 44-FZ establishes that the register of unscrupulous suppliers includes information, including the name, taxpayer identification number - a legal entity or, in relation to a foreign entity in accordance with the legislation of the relevant foreign state - an analogue of the taxpayer identification number, which is the founder of the legal entity specified in part 2 of this article, last names, first names, patronymics (if any) of the founders, members of collegial executive bodies, persons performing the functions of the sole executive body of legal entities, also named in part 2 of Art. 104 of Law No. 44-FZ. Within the meaning of this article, the founders of a legal entity are responsible for its actions as a procurement participant. Then the question arises of how this requirement of the procurement law relates to the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 56 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation that the founder (participant) of a legal entity or the owner of its property is not liable for the obligations of the legal entity, and a legal entity is not liable for the obligations of the founder (participant) or owner, except for cases provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation or other law.
In addition, another logically substantiated question arises, which the legislator left without attention: if the founder, information about whom is included in the register of unscrupulous suppliers, has a share (shares) of several legal entities, then this automatically suppresses the legal capacity of these legal entities to participate in procurement to ensure state and municipal needs?
For how long is information about the procurement participant (supplier) entered into the RNP and what are the consequences?
According to Part 9 of Article 104 of 44-FZ, information after 2 years from the date of its inclusion in the register of unscrupulous suppliers is excluded from the said register.
Those. within 2 years
procurement participants (suppliers) included in the “black list” are almost completely limited in their participation in state (municipal) tenders.
According to Part 1.1 of Article 31 of 44-FZ, the customer has the right to establish
requirement that the register of unscrupulous suppliers (contractors, performers) provided for by 44-FZ contains no information about the procurement participant, including information about the founders, members of the collegial executive body, the person performing the functions of the sole executive body of the procurement participant - a legal entity.
But, as practice shows, this requirement is included in almost every tender documentation. Even many commercial companies stipulate this requirement in their Procurement Regulations. Thus, it becomes obvious that the inclusion of information about the procurement participant (supplier, etc.) in the RNP imposes serious restrictions and can negatively affect the image and business reputation of the organization.
Exclusion of information about procurement participants from the register
Information about an unscrupulous supplier (contractor, performer) is excluded from the register after 2 years from the date of its inclusion in the register, and in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation - before the expiration of the specified period on the basis of a court decision (Part 9 of Article 104 of Law No. 44 -FZ, clause 16 of Decree No. 1062, part 5 of article 5 of Law No. 223-FZ and clause 10 of Decree No. 1211).
In accordance with paragraphs. “g” clause 20 of Resolution No. 1062 for the protection of information included in the register, it is provided, among other things, for the automatic exclusion from the register of information about unscrupulous suppliers (contractors, performers) after a 2-year period from the date of entering such information into the register with the preservation of the specified information in the archive.
We note that a similar requirement for the procurement of goods, works, and services by certain types of legal entities is not established in the relevant regulations. The question arises: on the basis of what document and who should exclude information about unscrupulous suppliers (contractors, performers), within the framework of Law No. 223-FZ, after a 2-year period from the date of entering such information into the register?
What could be the consequences of being included in the register?
When a company is included in the register of unscrupulous payers, it is prohibited from participating in state and municipal procurement. The blocking lasts for two years as long as information about it is listed in the RNP. Of course, if a service provider is blacklisted under 44-FZ, he can participate in bidding under 223-FZ without restrictions. And vice versa. While some companies can survive such “Tender Holidays” without any significant financial losses, for others this could be fatal.
Other unpleasant consequences for those included in the register may include termination of the contract by the customer.
If the mandatory requirements for participants state that information about them should not be included in the register, and the winner is a participant who, during the tender, fell into the ranks of unscrupulous suppliers, the customer has the right to terminate the contract with him. He can do this on the basis of the same 44-FZ (part 15, paragraph 1) unilaterally.