Home / Government procurement / Federal Law 223
Back
Published: September 19, 2018
Reading time: 9 min
0
520
Request for proposals is one of the most popular procurement methods under 223-FZ, along with request for price quotes. This is a competitive procurement, which is carried out in an open form and does not imply restrictions on the number of participants.
- Request for Quotation and Request for Proposals: Differences
- Legislative regulation
- Types of request for proposals
- Order of conduct
- Documentation
- Dates
- Grounds for cancellation
Its peculiarity is that the customer evaluates applications received from participants according to a set of criteria, including price and non-price parameters.
Commercial offer
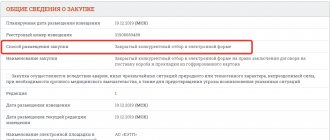
A request for proposals under 223-FZ is a form of procurement, which some people confuse with a request for proposals of a commercial type, carried out in the process of monitoring the current market by the customer.
In the second case, the applicant determines the initial maximum price, which will subsequently be reflected in the procurement documentation. According to the rules of the request for proposals under 223-FZ, the customer does not have the right to independently increase the declared price.
When determining the upper limit of the amount, customers use different methods. Most often, parties to transactions use the comparable market prices method. The essence of this method is that the buyer finds out prices from several sellers of the required product or service. After the analysis, a weighted average is calculated or the highest proposed price is set.
It should be remembered that the mere presentation of a price list for goods or services does not yet constitute an offer and does not oblige the participant to immediately enter into an agreement on the terms that were offered to him. This is due to the fact that the purpose of the analysis procedure is to select the most beneficial conditions for the implementation of the contract for the customer within the framework of the received application.
Request for Quotation and Request for Proposals: Differences
A request for proposals as a form of procurement should be distinguished from a request for commercial proposals as part of market monitoring by the customer. A request for commercial proposals is required for the customer to determine the initial maximum contract price, which will be indicated by him in the procurement documentation. This is the price above which the customer does not plan to enter into a contract on the given terms.
To determine the maximum contract price, the customer can use different methods. The most popular method is the comparable market prices method. Based on this methodology, the customer requests prices from several suppliers of the product or service he needs . It then determines a weighted average or takes the highest bid price as the NMCC.
The response to the customer’s request and the provision of a price proposal will not be considered an offer and will not force the participant to further enter into an agreement on the terms proposed by him.
The purpose of the request for proposals as a procurement procedure is to select the best conditions for the execution of the contract among the received applications.
When requesting proposals as a form of procurement, the participant confirms with his application his readiness to sign an agreement in the future . If he refuses or evades signing the contract, information about the participant is transferred to the register of unscrupulous suppliers, which can create certain difficulties with the company’s participation in procurement.
Request for proposals
In the process of drawing up a request for proposals (under Federal Law No. 223) as a procurement form, by submitting an application, the participant confirms his readiness to conclude a deal in the future. If he subsequently refuses to conclude an agreement or avoids doing so in every possible way, he will be entered into a special register where all unscrupulous suppliers are recorded.

In the future, being in this group may negatively affect the desire of other customers to enter into contracts with such a seller. This is due to the fact that before concluding transactions, the parties very carefully study their counterparties to identify more profitable and reliable partners.
The legislative framework
The main regulatory legal act governing the procurement of services and goods by the customer, as well as the process of conducting a request for proposals, is 223-FZ of July 18, 2011. Each customer organization must, based on this document, develop a Procurement Regulation that is relevant for this legal entity.
According to Federal Law No. 223, the general rules for requests for proposals determine that the customer must prescribe what procedures he uses in the process of selecting suppliers who provide the services and goods he needs.

The Regulations also stipulate the conditions for selecting a request for proposals. According to the legislation, there are three procurement options:
- contest;
- auction;
- request for various proposals.
The last method is not the main one, unlike the first two. Legislative norms establish the customer’s right to use the comparative method of prices. Once the method for determining the supplier has been selected, it must be recorded in the procurement plan.
Like the Procurement Regulations, the plan must be drawn up taking into account all the requirements of Federal Law No. 223 and Resolution No. 908, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, which reflects the rules for posting information about ongoing procurement in the Unified Information System.
When posting information, it is important to indicate in the appropriate column of the procurement plan (purchase method) the option for conducting the procurement procedure: auction, tender or request for proposals.
The concept of request for technical and commercial proposals
From a legal point of view, a request for technical and commercial proposals is a special procedure that is carried out by a state or municipal customer in order to establish not only the existing indicators of the price market, but also in order to prepare a justification for the initial maximum price of a contract or agreement at subsequent implementation of any procurement procedure.
However, it should be noted that based on the provisions of Federal Law No. 223-FZ “On the procurement of goods, works, services by certain types of legal entities,” a request for technical and commercial proposals is a market monitoring procedure that does not oblige the customer to make such a purchase in the future - this procedure may be used only to determine the price level, including for the purpose of budgeting certain types of expenses for future financial periods.
At the same time, in all existing federal and regional regulations governing the scope of procurement to meet state and municipal needs, there is a rule that the customer’s request for technical and commercial proposals is not a mandatory condition for further procurement or concluding a contract with the person who provided the most advantageous offer for such a customer. The specified request does not oblige the customer to anything in terms of mandatory procurement procedures.
The customer can conduct a request for technical and commercial proposals at any time when, in his opinion, there is a need for this, or when the need for such monitoring arises.
Benefits of various offers
Carrying out the request for proposals procedure (under 223-FZ) in a closed or open form is the most preferable procurement option for the following reasons:
- It differs from auctions, and therefore is not regulated by articles 447-449 of the Civil Code. Thus, the customer is not obliged to sign an agreement with the supplier who offered the most favorable conditions, becoming the winner in the request for proposals based on the procurement results.
- The customer has the right to establish regulations for the procurement procedure in the Regulations.
- The customer has the right to refuse the purchase at any time. At the same time, he is not subject to the obligation to pay compensation to procurement participants (for example, to reimburse postage costs for sending proposals).
- By requesting translations, the customer can quickly select the most suitable supplier for himself due to the fact that the period for submitting written applications is determined by him.
Deadlines for request for quotations
223-FZ does not in any way regulate the timing of requests for prices. Usually they are indicated by the customer himself in the Procurement Regulations. The standard time frame for requesting quotes is 5-10 business days.
The deadline for requesting prices is no more than 20 days. The participant is given no more than 7 days to form and submit an application.
Therefore, customers usually prefer to request price quotes if they are limited in time and price is a determining factor in choosing a supplier or contractor.
Algorithm for the procedure
When participating in a tender on an electronic trading platform, according to 223-FZ, it is very important that the Procurement Regulations from a particular customer are posted on the website there. This document should record the entire algorithm for implementing the procedure for familiarizing with suppliers’ proposals, as well as the requirements for the procurement.
The Regulations reflect the following points:
- submission of written applications;
- proposal form;
- application requirements;
- refusal to purchase;
- securing applications;
- procedure for accepting proposals from suppliers;
- criteria for evaluating and determining the winner;
- consequences of registration of the purchase as failed;
- deadlines for concluding a deal with the winner;
- other conditions.
In the process of preparing the Procurement Regulations and the regulations for conducting a request for proposals, according to Federal Law No. 223, in open or closed form, the customer must remember that in addition to the requirements of the specified regulatory legal act, he must also comply with the rules of Federal Law No. 135 in the field of antimonopoly policy.
When choosing a request for proposals in an open form as an option, the customer independently determines the criteria for selecting participants. An open request is considered the most convenient option in cases where the customer is interested not only in the price criteria offered by the supplier.
The main requirement for procurement in the form of a request is compliance with deadlines. The customer is given only twenty days to place a notice on the website of his desire to conclude an agreement before signing it with the selected supplier.
Most often, a request for proposal options is used in cases where the initial contract price does not exceed ten million rubles. In addition, this method is especially popular among customers who want to be able to cancel the purchase at any time without any burden.
When choosing a method for carrying out a procurement activity, customers should be guided by the recommendations of the Federal Antimonopoly Service published on the website. FAS specialists point out that this option for concluding transactions is most relevant when purchasing goods for urgent and urgent needs, if the initial price of the contract is small.
Step-by-step algorithm
The timing of the request for prices is not regulated by law. Usually they are 5-10 days. This is why customers prefer requesting quotes if they are limited in terms of identifying a supplier. The customer must specify the specified time frame in the Procurement Regulations under 223-FZ.
The customer should indicate the following deadlines in the procurement documentation:
- Start date for accepting proposals.
- Closing date for proposals.
- Deadlines for consideration of received price quotations by the procurement commission.
- Deadline for signing a contract based on procurement results.
Document requirements
The customer’s responsibilities include posting the procurement notice and procurement documentation in the Unified Information System.
The UIS does not contain information about procurements that constitute a state secret, as well as those on which a government decision was made. The latter include procurements that do not contain any signs of state secrets, but the Government may consider that information about such procurements does not need to be placed in the Unified Information System.
In the procurement documentation, the customer must specify the basic requirements for the purchased goods, works and services. The required quality of products, the conditions for the implementation of the future contract, as well as requirements for procurement participants, including requirements for subcontractors and contractors, are indicated here.
When preparing documentation for a request for quotations, the customer must specify the NMCC, including its justification, and the requirements for the amount of security for the execution of the application for participation and the contract.
In addition to the procurement documentation, a draft of the future contract is publicly available. Typically, customers attach an application form for participation in the request for prices, which is recommended for participants. In addition, instructions for filling out the participation form are attached.
During the procurement process, the customer places in the Unified Information System changes made to the documentation and protocols for considering applications for participation and determining the winner. The protocols indicate the results of consideration of applications and voting on them. If, as a result of submitting applications for participation, only one application is submitted, then data on recognizing the procurement as failed is entered into the protocol.
To participate in the price request, the supplier must present:
- A completed application for participation in the procurement.
- Documents that confirm the participant’s compliance with the established requirements.
Today, RFPs are not sent in a paper envelope: only in the form of an electronic document.
To demonstrate compliance with established requirements, the supplier may be required to:
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
- An extract from the SME register (if the purchase is carried out exclusively among representatives of small and medium-sized businesses).
- Statutory documents for the organization.
- Information about the founders and their passports, TIN.
- Accounting and financial reporting.
- Certificate from the Federal Tax Service confirming the absence of debts on taxes and fees.
- Documents confirming the compliance of the goods with established requirements : certificates, invoices, etc.
The participant also submits a declaration of its compliance with the established procurement requirements. This, in particular, is the absence of unscrupulous suppliers in the register, not being at the stage of recognition of financial insolvency or liquidation, the absence of decisions to suspend the company’s activities administratively, etc.
Carrying out step by step
The procedure for selecting a supplier through a request for quotations involves going through the following stages:
- Identifying needs for goods, works and services.
- Determination of the procurement method taking into account the Procurement Regulations . The customer must understand whether he has the right to carry out this purchase in the format of a request for quotation.
- Procurement planning taking into account financial and other indicators of the supplier.
- Determining requirements for the upcoming tender.
- Formation of procurement documentation , specification of requirements for the procurement object.
- Publication of a notice of order in the Unified Information System.
- Clarification of the terms of procurement documentation upon receipt of a request from procurement participants . If necessary, based on received requests, the customer makes amendments to the provisions of the procurement documentation in accordance with 223-FZ.
- Opening access to applications for participation in procurement from the ETP operator . The purchase is considered completed when at least 3 applications for participation are received. If less than 3 applications are received, then the further procedure is determined by the customer: he has the right to recognize the procurement procedure as failed and sign a contract with a single supplier, assign a new purchase, extend the deadline for accepting the application, or cancel the purchase and conduct it in another form.
- Evaluation and consideration of received applications for participation . When selecting applications received from participants, the customer most often evaluates the application’s compliance with the requirements of the documentation, the reliability of the information presented in the application, the compliance of the procurement participant himself with the requirements, etc.
- Rebidding . This stage is introduced at the discretion of the customer, and it is allowed only if rebidding has become possible or has been indicated as a mandatory stage in the procurement documentation. Only those participants who, based on the results of the qualifying stage, are found to comply with the provisions of the procurement documentation are allowed to re-auction. Rebidding is usually carried out in real time.
- Determination of the winner of the purchase . This becomes the person who made the offer with the lowest price and fully meets the customer’s requirements. Based on the results of selecting the winner, a final protocol is formed and posted in the Unified Information System.
- Conclusion of an agreement with the winning participants of the request for prices . The procurement notice usually clarifies that a request for prices is a non-commercial procedure; the customer is not obliged to sign a contract with the winner based on the results of this procedure (unlike, for example, a procurement in the form of a competition). But usually the request for prices ends with the signing of a contract. It is signed first by the supplier recognized as the winner, and then by the customer. The timing of signing the contract is determined by the customer in the Procurement Regulations, but usually the contract is signed no earlier than 10 days after the publication of the final protocol. During this period, those who do not agree with the procurement results have the right to appeal the customer’s actions to the FAS.
- Publication of information about the signed agreement in the UIS.
Varieties
According to Federal Law No. 223, when conducting a request for proposals, you can cover an unlimited number of suppliers. In this case, this form of procurement will be considered open and accessible to everyone.
Individuals and legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs who meet the requirements specified in the procurement documentation, can take part in open procurement.
The requirements for suppliers include the following conditions:
- Availability of a license, if required by law, or another option to meet the customer’s requests.
- The organization should not be at the liquidation stage.
- The supplier’s activities should not be suspended according to the rules of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
- The seller should not be on the register of unscrupulous suppliers.
If procurement is carried out in the form of a closed request, therefore, suppliers are invited separately. At the same time, data on the ongoing procurement is not posted in the Unified Information System.

Only those suppliers who have passed the pre-qualification selection can participate in closed inquiries. Most often, this option for concluding transactions is used if the customer needs to purchase a unique or technically complex product.
Recently, the most common procurement option is a request for proposals in electronic form. Federal Law No. 223 provides such an opportunity. In addition, in the near future this will be the only way to select a supplier for a contract. And the written version will be canceled in accordance with the provisions of Federal Law No. 503.
Requests for proposals in non-paper form are carried out through a tender on the electronic trading platform. 223-FZ determines that the list of sites may not be limited to a specific list, as is the case with procurement under Federal Law No. 44.
Conducting electronic procurement is more convenient for the customer due to the fact that it allows you to automate the entire procedure for selecting a counterparty and concluding a transaction.
Implementation procedure
Procurement mechanisms and stages of inquiries are not directly spelled out in Federal Law No. 223 and other regulatory legal acts. Each customer independently establishes the rules for concluding a contract, which is enshrined in the third part of the third article of the law in question.

There are six mandatory stages of the request procedure:
- The first stage is the development of conditions for the purchase of services and goods, as well as basic requirements for suppliers.
- The second stage is the preparation of procurement documentation, posting a notice of the opportunity to conclude contracts in the Unified Information System. The deadlines for sending applications, requirements for the seller and the supplied product (service), conditions for fulfilling the contract and other important points are also recorded here. The legislation allows for the possibility of sending additional messages to customers clarifying the specified requirements if some points are not clear. In this case, the customer must respond to all persons in writing. At the same stage, you can make changes to the notice, which are immediately published in the UIS.
- Receiving and checking applications received from suppliers. Submitted proposals can be evaluated only according to the criteria specified in the procurement requirements placed by the customer. This is enshrined in the sixth part of the third article of the law in question.
- Selecting the winner. The supplier is determined by the criterion of optimality of the terms of the contract. If there are two applicants with the same indicators, the one who submitted the application earlier wins.
- Publication of the request for proposals protocol (this is regulated by 223-FZ) in the Unified Information System.
- Conclusion of an agreement with the winner.
Content:
1. The concept of a request for proposals 2. Request for proposals under 44-FZ
- The procedure for conducting a request for proposals under 44-FZ
- Cases of conducting a request for proposals
- Deadlines for the request for proposals
- Notice of request for proposals
- Amendments to the notice of a request for proposals
- Documentation of the request for proposals
- Criteria for evaluating applications during a request for proposals
- Securing the application and ensuring the execution of the contract during the request for proposals
- Recognition of the request for proposals as invalid
- Conclusion of a contract based on the results of a request for proposals
- Difference between request for proposals and other procurement procedures
3. Request for proposals under 223-FZ
Documentation
According to Federal Law No. 223, the documentation for the request for proposals includes the following papers drawn up by the customer:
- Notice of procurement planning.
- Documentation on the subject of the contract.
- Draft contract.
The procurement documentation must indicate all requirements for the design, content and composition of applications from potential suppliers. Contractors must provide the customer with the following documents:
- applicant's application form: name, details (TIN, OKPO, KPP, bank account number), registration date, etc.;
- copy of the Charter;
- extract from the relevant register;
- decision to complete or approve a large-scale transaction;
- power of attorney for the applicant's representative;
- information about consumer and functional characteristics of services and goods, conditions for fulfilling the terms of the contract, etc.;
- paper confirming the fact of making a deposit.
Dates
According to 223-FZ, a request for commercial proposals, along with the remaining stages of the procedure for accepting applications from suppliers, must be completed within twenty days. There is no specific time frame for submitting proposals in the legislation.

In practice, this period ranges from five to ten days from the date of publication of information about the purchase in the Unified Information System. The contract signing stage also does not exceed ten days. As a result, the entire procedure fits within a twenty-day framework.
Cases of conducting a request for proposals under 223-FZ
This type of procurement is regulated by a certain procedure; let’s briefly consider the procedure:
1. Drawing up documents in accordance with the Procurement Regulations, in accordance with parts:
- 9 part 3.2 of the article;
- 5, 9 and 10 parts 4 articles.
The documents also include:
- Notice
- Documents for the request for proposals
- Draft contract
These documents are subject to publication in the Unified Information System no later than 7 calendar days before the start of the procedure. These documents include information that is regulated:
- 23 part 3.2 of the article;
- 9 and 10 parts 4 articles;
2. Drawing up protocols and choosing the winner is regulated by:
- 13 and 14 parts 3.2 of article in Law No. 223-FZ.
After which the deal is signed in accordance with:
- 15 part 3.2 of article in Law No. 223-FZ.
Also, the organizer is prohibited from negotiating with the ETP operator if this entails advantages for one of the competitors in the request for proposals; this is regulated:
- 9 part 3.3 of article in Law No. 223-FZ.
Reasons for canceling a request for proposals
Federal Law No. 223 regulates this issue too. The customer has the right to cancel the transaction request at any time before selecting the winner. At the same time, he must immediately place this information in the Unified Information System and adjust the schedule for this purchase.
The list of reasons for cancellation is recorded in the Customer's Regulations. In addition, cancellation can be carried out by the Federal Antimonopoly Service if the purchase does not comply with legal requirements.
Request for proposals is the best option for those who want to purchase a specific product or service in a short time, without incurring responsibility for canceling the application at the last moment.