What are the categories of land?
The composition of lands on the territory of Russia is regulated by Art. 7 of the Land Code. According to the law, there are seven categories of land:
- Land intended for agricultural needs.
- Lands of populated areas.
- Land plots for special purposes (intended for the purposes of industry, transport, communications, defense, security, etc.).
- Lands of specially protected areas and objects.
- Forest fund lands.
- Water fund lands.
- Reserve lands (areas that are currently unused and are in the country’s reserves).
The legal regime of certain categories of land may provide for special conditions. This is necessary to preserve the natural characteristics inherent in the territory (for example, areas of national parks).
Each category has several types of permissible use of land. Read on to find out what “permitted use of land” is.
Zones
The conditionally permitted use of a land plot can be any from a possible list. Moreover, depending on the functionality of the zone and the decision of the authorities, one territory may have one list of types of uses, and another - different from it.
Conditionally permitted for residential sectors in terms of land development will be the construction within their boundaries of free-standing buildings:
- for retail spaces, shopping and entertainment centers;
- Catering;
- office and administrative;
- medical, etc.
In the area designated for business and public use, residential buildings of a private and multi-apartment nature are classified as conditionally permitted uses. For production zones, all of the listed species will become conditionally permitted.
Zoning of the territory from the point of view of urban planning is carried out in accordance with the fourth chapter of the Civil Code. The Code establishes the need for the development and approval by the head of the territorial administration of Land Use and Development Rules, including:
- general provisions (the procedure for their application and amendments);
- zoning map for possible development purposes;
- town planning regulations.
The draft Rules are required for public discussion. After approval at all stages, they are approved by the head of local government. Changes can be made at the initiative of an interested party (for example, when planning a development). But this requires coordination with the competent structures, passing the stage of public hearings and approval by the municipal authority.
Types of permitted use of land plots
The permitted use of a land plot is a clarifying characteristic showing the purpose of the territory. You can use the site, even if it is owned, only in accordance with its belonging to a certain type of permitted use.
There are more than 3,000 possible types of permitted use. All of them are listed in the classifier, which was established by order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated September 1, 2014 No. 540 “On approval of the classifier of types of permitted use of land plots.”
Using a land plot for other than its intended purpose is grounds for bringing the violator to administrative liability.
The fine for using land for other purposes is quite significant - up to 1% of the cadastral value, but not less than 10,000 rubles. Penalties are imposed in accordance with Art. 8.8 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In addition, if the owner has placed a retail outlet on a site whose permitted use is the construction of a residential building, he will have to not only pay a fine, but also demolish the non-purpose structure.
Before purchasing a plot of land, it is worth clarifying the type of permitted use. As a rule, it is registered in the cadastral passport.
Mainly two categories of land are involved in active turnover: agricultural land and residential land. Despite the fact that forest areas can also be registered as private property, citizens rarely use this.
What is a conditionally permitted use?
Conditionally permitted use of land (hereinafter referred to as URVI) is additional to the main one. This is an opportunity to expand the classifier when it is quite difficult to provide for all situations. It is possible to apply the URVI only after agreement with the local administration and public hearings, with the condition that such expansions are provided for in the Urban Development Plan of the territory.
The main uses of the allotment may in some cases be insufficient. This, for example, is the possibility of developing a low-rise residential building (according to code 2.1.1) and the need to build individual garages. The classifier allows the construction of garages only within the framework of the conditionally permitted use of land. Then the owner of the site will need to declare in writing to the local administration that he wants to use it in accordance with the conditional permit. Note that the URVI must be listed in the Land Use and Development Rules (LRU), which are approved by the administration of the locality.
Let's look at the example of the city of Omsk, which, in accordance with the Development Rules, is divided into 10 residential zones. They can be used in accordance with the main type for residential buildings and kindergartens. Conditionally permitted use will be for:
- low-rise residential construction with no adjacent land;
- construction of consumer service buildings, including hotels (including motels and hostels), hairdressers, workshops that repair household appliances, etc., cultural and art institutions, museums;
- construction of administrative, business and utility buildings;
- public catering (restaurants, bars, canteens), pharmacies, baths, shops, temporary trade facilities;
- garages.
Lands of settlements: types of permitted use
The lands of settlements have a clear boundary. Such areas are intended for the residence of citizens and the placement of the necessary infrastructure.
All land in settlements is divided into zones. They are listed in Art. 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. There are nine such territorial zones of settlement lands:
- Residential areas.
- Social and business.
- Production.
- Engineering and transport infrastructures.
- Recreational areas.
- Areas of agricultural use.
- Special purpose zones.
- Military facilities.
- Other land plots.
Each zone has its own types of permitted use. Citizens are only interested in residential and agricultural zones, since they can be transferred into ownership.
Land plots located in residential zones have the following types of permitted use:
- Individual housing construction (individual housing construction);
- Private household plot (personal subsidiary plot);
- DNP (dacha development).
Construction is possible on each of these sites. However, there are significant differences.
Land plots intended for residential development and private household plots imply the possibility of development, regardless of the required dimensions. But there is a significant disadvantage - it is very difficult to register in such areas.
Buildings on individual housing construction lands are maintained in the same way as buildings in urban settlements. The owner has the right to register here freely. Although there are no restrictions on the dimensions of buildings, the construction project will need to be agreed upon with the municipality. The disadvantage of individual housing construction plots is the increased tax rate relative to DNP lands.
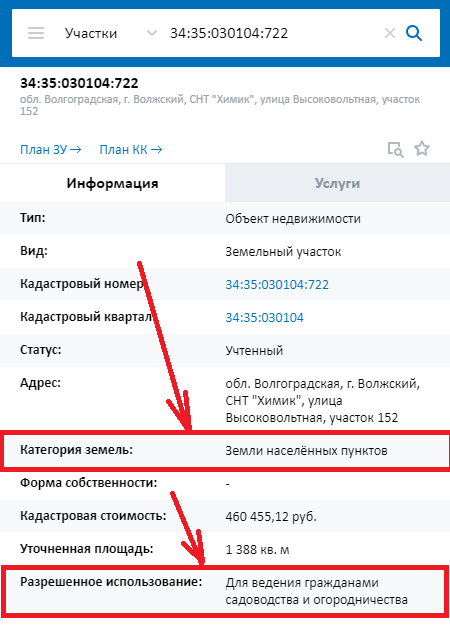
We look at the public cadastral map of Rosreestr
- Follow the link - Public cadastral map of Rosreestr . The site often slows down, please wait for it to load.
- You can find the desired area in 3 ways:
- 1. Using the cadastral number of the plot. At the top left, enter the cadastral number of the plot and below click on the proposed number.
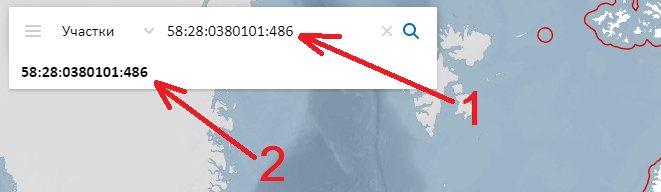
- 2. Using the address. Enter the site address and click on the suggested address below.
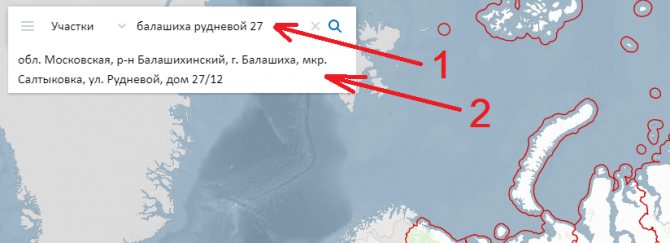
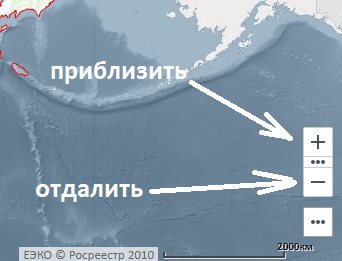
- 3. On the map itself using navigation. You can zoom in and out of the map using the buttons at the bottom right of the screen or the “wheel” on the mouse. The “+” button brings the map closer, the “-” button zooms out. Once you find the area you want, click on it. If the plot is not displayed on the map, most likely: 1) it is not in the cadastral register or 2) it is in the cadastral register, but its boundaries are not defined. In this case, the VRI and category of land can be found in the documents.
- Scroll down VRI is shown in the “Permitted use” line.
If you need free legal advice, write online to the lawyer on the right or call (24 hours a day, 7 days a week): 8 (Moscow and region); 8 (St. Petersburg and region); (all regions of the Russian Federation).
Types of permitted use of agricultural land
Agricultural lands are located outside the boundaries of settlements. Hayfields, pastures, gardens, arable lands and buildings can be located here.
The intended purpose of agricultural land for citizens may be as follows:
- Personal farming. Installed with or without a building permit.
- Country construction. The construction of a suburban residential building is allowed here. Unlike development on settlement lands, the construction project does not need to be approved.
- Horticulture, animal husbandry, crop production, etc.
A significant disadvantage of acquiring ownership of agricultural plots is the almost complete impossibility of registering in a constructed residential building.
Where are URVI indicated?
The main document of the municipality regulating urban development within its boundaries is the Land Use and Development Rules. Therefore, for construction on a specific site, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with them in advance in order to avoid unpleasant situations later.
Often such rules are called a “land construction passport”, which contains information about the allotment. They include all permissible types of its use (including conditionally permitted), as well as restrictions on the land. There is also a topographical diagram with construction zones, red lines, etc.
An urban development plan is issued to the land owner only on the basis of an application submitted to the local government body. Preparation takes 20 working days, calculated from the date of application, and is issued free of charge (Article 57 3 of the Town Planning Code).
Types of land use for individual housing construction, vegetable gardens and business according to the classifier
For the purposes of individual development and personal farming, plots with codes 2.0 – 2.7 in section 2 of the classifier are suitable. These numbers mean that the land can be used for the following purposes:
- construction of low-rise residential buildings (up to 3 floors, not implying apartment division);
- growing fruits, berries, vegetables and other agricultural crops (gardening and horticulture);
- ancillary buildings (construction of sheds, garages, etc.);
- construction of garden buildings;
- maintaining personal subsidiary plots and organizing a plot;
- construction of temporary mobile structures with the ability to connect to general technical networks (trailers, campsites, etc.).
When planning business activities, a land plot that has the type of permitted use provided for in section 4 of the classifier (codes 4.0-4.9) is suitable. The intended purpose of such sites allows for the placement of capital construction projects built for trade, transport services, recreation, entertainment, etc.
What it is?
This type of permitted use is a list of types of capital construction projects permitted for construction on a specific site, which is distinguished by the following features:
- determined in relation to each land plot, depending on its location in a particular territorial zone;
- the right to construct for these types of uses arises from a person only if he goes through a certain procedure and fulfills the conditions;
- permission for this type of use is obtained in the form of an act of the head of local government.
Important! If the conditions for the construction of an object from conditionally permitted types are not met, official permission to grant the right to such use is not obtained, the construction of such an object will be illegal, and the already constructed object may be demolished.
The need to go through official procedures provided for by the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation and local regulations is the peculiarity of this type of land use. For main and auxiliary types, no preliminary approvals are required.
What other types of permitted land use are there?
The Town Planning Code establishes three options for the types of permitted land use. According to Art. 37 Civil Code of the Russian Federation exist:
- main types of permitted use;
- conditionally permitted types of land use;
- auxiliary types.
The main types of permitted use of land plots are listed in the classifier. They are not subject to additional approval from authorities. This means that the owner has the right to dispose of the site at his own discretion within the framework of the law and the classifier.
It is impossible to provide for everything with a classifier. Therefore, there are conditionally permitted types of land use. This provides an opportunity to expand legal uses of the land if necessary. The list of conditionally permitted species is established at the local level.
To establish an additional type of permissible use on your site, you must go through the approval procedure with the municipality and the Land Use and Development Commission. This may be required, for example, if you plan to build a retail outlet for selling small retail goods on your site intended for individual housing construction.
Auxiliary types of permitted use are used to clarify the existing intended purpose. Such an addition may be required if the owner wants to build a fence, garage or other small object on his property.
Possible problems
For example, there is no category for residential buildings built on land for farming purposes.
But, since the Classifier only works for the main VRI, it makes sense to refer to the Land Use and Development Rules established in the area where the land plot is located.
It is quite possible that the construction of a residential building on agricultural land will be classified as conditionally permitted VRI.
In order for the land to be fully used in this case, it is necessary to contact the commission for land use protection and write an application to change the type of permitted use. After the hearing, the owner will receive a building permit.
If the site initially had a conditionally permitted VRI, then the owner will receive a decision that he needs to apply for a use permit. This is another way to determine what kind of VRI a territory has: basic or conditionally permitted.
When is it possible to transfer land for individual housing construction to another category?
To understand what type of permitted use an existing one can be changed to, you need to refer to the territorial Development and Land Use Rules:
- We open the section of town planning regulations;
- We find the item “For individual housing construction (Zh-4)”;
- We receive a list of types of permitted use of land plots that are possible in a given territory.
For example, in Moscow alone there are about 40 types of permitted use of land plots for individual housing construction: hotels, restaurants, shops, banks, schools, fitness centers, pharmacies, etc.
Territorial zone of agricultural use CX-2
Gardening and vegetable gardening area
CX-2 is designed to accommodate summer cottages and garden plots where residential buildings can be erected. In them, land owners will be able to relax and grow crops. In addition, greenhouses and conservatories are located in zone CX-2.
Type of permitted use / Code (numerical designation VRI):
- Water features 11.0
- Land plots (territories) for public use 12.0
- Vegetable gardening 13.1
- Gardening 13.2
- Country farming 13.3
- Vegetable gardening 13.1
Conditionally permitted types of use: food, trade and consumer services facilities.
Separately located retail facilities or catering or consumer services establishments should receive a small flow of customers. No more than 250 square meters of total area is allocated for them. The company’s lawyers will help you avoid violations when placing objects in this zone, suggesting how to use such lands more efficiently.
Auxiliary types of permitted use: private household plots, educational facilities, religious use, business management, entertainment, sports.