The system of arbitration courts was created to resolve economic disputes arising from business activities. The main document defining the work of Arbitration Courts is the Arbitration Procedural Code (APC RF), adopted in 2002. The Code is regularly updated; at the time of writing, the latest changes related to the peculiarities of broadcasting meetings on radio and on the Internet were made in July 2021.
Arbitration courts hear cases in which the parties are: individual entrepreneurs, legal entities, government bodies (a more complete list is in Article 2 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
Levels of Arbitration Courts
The first instance is the Arbitration Courts of the constituent entities of the federation. In St. Petersburg this is the Arbitration Court of the City of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region, located at Suvorovsky Prospekt 50/52
Appellate instance – 20 appellate courts. In St. Petersburg this is the Thirteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal at Suvorovsky Prospekt, 65.
Cassation instance – Arbitration court of the cassation instance.
The highest arbitration court is the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, located in Moscow (until 2014, this function was performed by the Supreme Arbitration Court). Certain categories of arbitration cases are submitted to a higher authority.
The process of considering a case in an arbitration court has a clear sequence of actions prescribed in the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation (procedural form of the arbitration process).
Article 267 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. Time limit for consideration of an appeal (current version)
1. The arbitration court of appeal shall consider an appeal against the decision of the arbitration court of first instance within a period not exceeding two months from the date of receipt of the appeal along with the case by the arbitration court of appeal, including the period for preparing the case for trial and for the adoption of a judicial act, unless otherwise provided by this Code. If the appeal was received by the arbitration court of the appellate instance before the expiration of the deadline for filing it, the period for consideration of the appeal is calculated from the date of expiration of the deadline for filing the appeal.
This is important to know: Time limits for consideration of a complaint by bailiffs
2. The period established by part 1 of this article may be extended on the basis of a reasoned statement from the judge hearing the case by the chairman of the arbitration court up to six months due to the particular complexity of the case, with a significant number of participants in the arbitration process.
- URL
- HTML
- BB code
- Text
Stages of the arbitration process
Stage 0. Pre-trial work
At the preliminary, zero stage, the plaintiff sends the defendant a pre-trial claim drawn up in a certain way. The specific list of categories of cases for which pre-trial work is mandatory changes periodically, so we will not provide it in this article.
Stage 1. Initiation of proceedings in the case
After pre-trial work is completed, a statement of claim is filed with the arbitration court. Before initiating legal proceedings, within 5 days the judge alone checks the application and attached documents (Article 127 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). The statement of claim must comply with the current requirements:
- be subordinate to the arbitration court in accordance with the requirements for jurisdiction
- have the necessary documents as attachments
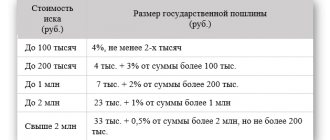
- must be accompanied by paid state duty
- contain the circumstances of the case and requirements for the defendant with references to legislative norms
If the statement of claim is accepted, the arbitration court issues a ruling on the initiation of proceedings in the case. In addition to the actions that must be performed by the persons participating in the case, it must also contain the address of the Internet site, telephone numbers, and e-mail by which you can obtain information about the case under consideration. Copies of the ruling on acceptance of the claim by the arbitration court on this or the next day are sent to the parties to the case.
The statement of claim is not always accepted for consideration. If there are grounds, the judge may also:
- refuse to accept a claim
- leave the claim without progress
- return the statement of claim
Stage 2. Interview and preliminary meeting
The main court hearing on the merits of the dispute is not scheduled immediately. Before this, the court carries out preparatory actions:
- interview (Article 135 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
- preliminary meeting (Article 136 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
Preparing the case for trial
After reading the statement of claim, the judge calls the parties to clarify the circumstances of the case:
- offers to confirm demands/objections
- proposes to more fully disclose the evidence, provide additional confirmation
- resolves issues about the need for examination, witnesses, translators, new evidence at the request of the parties, etc.
- explains the rights and obligations of the parties, the consequences of actions
- resolves the issue of securing a claim
- sets the deadline for the submission of new documents and the date for the subsequent preliminary meeting
The preliminary work of the court is aimed at ensuring the correct and timely consideration of all circumstances at the subsequent main hearing.
Preliminary hearing
The parties to the case are notified of a subsequent preliminary hearing, where the case is heard by a single judge.
The parties have the right to participate in a preliminary hearing via video link (Article 153.1 of the Arbitration Procedure Code). If the plaintiff or defendant has been duly notified but fails to appear, the hearing will be held in their absence.
At a preliminary meeting, the sufficiency of the evidence presented is decided, the parties present their arguments, and the other party may require new evidence.
Stage 3. Main sessions
After presenting the necessary evidence and holding a preliminary hearing, the main meeting of the arbitration court is scheduled (Article 153 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation), at which the case is considered on the merits.
The parties to the trial are required to be notified of the time and place of the hearing.
The procedure for holding a court hearing is strictly recorded (Article 154 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation), and persons who do not comply with it may be removed from the hearing, as well as subject to a court fine (Chapter 11 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
When judges enter the courtroom, everyone present in the courtroom stands up. All persons present in the courtroom shall listen to the decision of the arbitration court while standing. Persons participating in the case and other participants in the arbitration process address the arbitration court with the words: “Dear court!” They give their explanations and testimony to the court, questions to other persons participating in the case, and answers to questions while standing. Deviations from this rule may only be permitted with the permission of the court. The actions of persons present in the courtroom and carrying out filming, photography, video recording, and broadcasting of the court hearing on radio, television and the Internet, permitted by the court, must not interfere with order in the court hearing. These actions may be limited by the court in time and must be carried out in places specified by the court in the courtroom and taking into account the opinions of the persons participating in the case.
The judge or the presiding judge at the court hearing during a collegial hearing observes the following procedure (Article 153 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation):
- opens the court session and announces which case is to be considered
- checks the appearance at the court hearing of persons participating in the case, their representatives and other participants in the arbitration process, establishes their identity and verifies their credentials
- establishes whether persons who failed to appear at the court hearing were properly notified and what information is available about the reasons for their failure to appear
- clarifies the question of the possibility of hearing the case
- announces the composition of the arbitration court, informs who keeps the minutes of the court session, who participates as an expert, translator, and explains to the persons participating in the case their right to challenge
- explains to the persons participating in the case and other participants in the arbitration process their procedural rights and obligations
- removes witnesses who have appeared from the courtroom before the start of their interrogation
- warns the translator of criminal liability for knowingly incorrect translation, the expert for giving a knowingly false conclusion, witnesses (immediately before their interrogation) for giving knowingly false testimony and refusal to testify
- determines, taking into account the opinions of persons participating in the case, the sequence of procedural actions
- finds out whether the plaintiff supports the claim, whether the defendant acknowledges the claim, whether the parties want to end the case with a settlement agreement or apply the mediation procedure, about which appropriate entries are made in the minutes of the court session
- leads the court hearing, provides conditions for a comprehensive and complete study of evidence and circumstances of the case, ensures consideration of statements and petitions of persons participating in the case
- takes measures to ensure proper order at the court hearing
Participants in the arbitration process can not only attend the meeting in person, but also use video communication (Article 153.1 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation) if the court satisfies the previously filed petition.
A request to use video communication will not be granted if:
- the court does not have the technical capacity to carry it out
- the trial is held in closed court
After considering the dispute, the court makes a decision that either fully or partially satisfies the stated requirements, or refuses to satisfy them.
Stage 4. Review by the appellate court
If at least one of the parties does not agree with the decision made by the first instance, and this decision has not yet entered into legal force, it can file an application with the appellate authority (Chapter 34 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). The appeal is filed through the arbitration court that made the decision in the first instance, which is obliged to send it along with the case to the appropriate arbitration court of appeal within three days from the date the complaint was received by the court. An appeal cannot contain new claims that have not been previously considered in the arbitration court of first instance.
Similar to the consideration of a claim in the first instance, an appeal is filed with the Arbitration Court, where within 5 days the issue of its acceptance for proceedings is considered (Article 261 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation) by the arbitration court of appeal.
The arbitration court of the appellate instance issues a ruling on the acceptance of the appeal, which initiates proceedings on the appeal. The ruling shall indicate the time and place of the court hearing to consider the appeal. In this case, the time for the first court hearing to consider the appeal is determined taking into account the fact that it cannot be scheduled earlier than the expiration of the period established by the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation for appealing the relevant decision of the arbitration court.
Copies of the ruling are sent to the persons participating in the case within five days from the date of receipt of the complaint by the arbitration court of appeal.
If the appeal was not accepted for consideration, it may be:
- left motionless
- returned
- the appeal may be terminated
How the case is considered by the arbitration court of appeal
In general, the rules for considering a case by the appellate court coincide with the rules for considering a case by the first instance of the arbitration court with several features.
For example, an appellate court always considers a case not individually, but in a collegial manner. To avoid confusion, only one decision is considered in the appellate court:
- multiple requirements cannot be connected or disconnected
- the subject or basis of the claim cannot be changed
- the amount of claims cannot be changed
- counterclaim cannot be considered
- the responder cannot be changed
- new third parties cannot be involved
Stage 5. Consideration in the cassation instance
The next possible stage of arbitration proceedings is the cassation instance. A cassation appeal can be filed in the following cases:
- disagreement with the decision of the arbitration court of first instance that has already entered into force
- disagreement with the decision received in the appellate instance
- if the appellate court refused to restore the missed deadline for filing an appeal
A cassation appeal can also be filed with the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, see stage 6.
How to file a cassation appeal (Article 275 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
A cassation appeal is not filed directly with the cassation court, but through the arbitration court, which heard the case and made a decision.
Next, within 3 days, the cassation appeal with the attached materials is transferred to the arbitration court of the cassation instance.
Acceptance of a cassation appeal for proceedings by the arbitration court (Article 278 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
After a concerning complaint is received by the arbitration court, the judge, within 5 days, makes a decision on the possibility of accepting the complaint for proceedings. If the requirements for form and content have been met, the court will issue a ruling to accept the complaint and initiate cassation proceedings. Copies of the ruling, including the place and time of the meeting, are sent to the parties to the case.
If the cassation appeal was not accepted for consideration, it may be:
- left motionless
- returned
- the cassation appeal was terminated
The procedure for considering a case by an arbitration court of cassation (Article 284 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
In general, the arbitration court of cassation considers the case similarly to the arbitration court of first instance. The failure of one of the parties to appear upon proper notice is also not an obstacle to the consideration of the case. The main difference is the collegial composition of the judges.
Stage 6. Consideration of a cassation appeal in the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
A cassation appeal can also be filed directly with the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. The basis is disagreement with the following decisions:
- decisions and rulings of arbitration courts of constituent entities of the Russian Federation that have entered into legal force
- decisions and rulings of arbitration courts of appeal
- decisions and rulings of district arbitration courts adopted by them in the first instance
- rulings of arbitration courts of districts issued by them in the process of cassation proceedings, if judicial acts in respect of which the possibility of appeal to the arbitration court of cassation are provided for were appealed in the specified order
- resolutions and rulings of district arbitration courts adopted based on the results of consideration of the cassation appeal
That is, when one of the parties did not agree with the decisions of the first, appellate and cassation instances, it can fully or partially appeal them to the Supreme Court. Received judicial acts are contested if, in the opinion of a party, they contain significant violations of substantive law, or the procedure for consideration has been violated, which has led to a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of a party to the case in business or economic activity.
A cassation appeal is filed directly with the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and may contain demands for the award of compensation.
The procedure for considering a cassation appeal submitted to the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (Article 291.6 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
The judge of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation examines the cassation appeal, presentation based on the materials attached to them, or on the materials of the requested case.
The person filing a cassation appeal may petition to suspend the execution of the appealed judicial acts. Within 3 days, the judge makes a decision on suspension or refusal to suspend, then copies of the relevant decision are sent to the persons participating in the case.
For how long is the execution of a judicial act suspended?
- before the judge makes a ruling to refuse to transfer the cassation appeal
- before being presented for consideration at a court hearing by the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation
- for the period until the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation adopts a ruling based on the results of consideration of the cassation appeal, presentation along with the case
- deadline set by the judge
After considering the cassation appeal, the judge of the Supreme Court either refuses or transfers the complaint for consideration at a court hearing by the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court.
Powers of the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation based on the results of consideration of cassation appeals, presentations along with the case (Article 291.14 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
Based on the results of consideration of a cassation appeal or presentation along with the case, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation has the right to:
1) leave the decision of the court of first instance, resolution or ruling of the court of appeal or cassation without change, cassation appeal, presentation without satisfaction
2) cancel the decision of the court of first instance, resolution or ruling of the court of appeal or cassation in whole or in part and send the case for a new trial to the appropriate arbitration court. When sending a case for a new consideration, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation may indicate the need to consider the case by a different composition of judges;
3) cancel the decision of the court of first instance, resolution or ruling of the court of appeal or cassation in whole or in part and leave the application without consideration or terminate the proceedings ;
4) leave in force one of the judicial acts adopted in the case;
5) cancel or change the decision of the court of first instance, resolution or ruling of the court of appeal or cassation and adopt a new judicial act, without transferring the case for a new trial, if an error was made in the application and (or) interpretation of substantive law;
6) award compensation for violation of the right to trial within a reasonable time or refuse to award it;
7) leave the cassation appeal or presentation without consideration on the merits.
When considering a case in cassation proceedings, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation checks the correctness of the application and (or) interpretation of the norms of substantive law and (or) norms of procedural law by the arbitration courts that considered the case, within the limits of the arguments set out in the cassation appeal or presentation. In the interests of legality, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation has the right to go beyond the arguments set out in the cassation appeal or presentation. At the same time, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation does not have the right to check the legality of judicial acts in the part in which they are not appealed, as well as the legality of judicial acts that are not appealed.
When considering a case in cassation proceedings, the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation does not have the right to establish or consider as proven circumstances that were not established or were rejected by the court of first instance or appeal, or to prejudge questions about the reliability or unreliability of this or that evidence, the superiority of some evidence over others and determine what judicial act should be adopted upon a new consideration of the case.
The instructions of the Judicial Collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, including on the interpretation of the law, set out in the ruling on the annulment of a judicial act, are mandatory for the arbitration court re-hearing the case.
Stage 7. Revision due to newly discovered circumstances
Judicial acts that have entered into legal force can also be reviewed by the Arbitration Court based on new or newly discovered circumstances (Article 309 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
Arbitration courts reviewing judicial acts based on new or newly discovered circumstances (Article 310 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
A decision, court order, ruling that has entered into legal force and adopted by the arbitration court of first instance is reviewed based on new or newly discovered circumstances by the court that adopted this decision, court order, ruling. When a decision in a case was made by the appellate, cassation, or Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the review is carried out by the court that changed or adopted a new judicial act.
What circumstances are considered new or newly discovered (Article 311 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
The newly discovered circumstances existed at the time the judicial act was adopted. These include:
- significant circumstances of the case that were not known to the applicant
- detection and confirmation of falsification of evidence, false testimony of witnesses, expert opinions, incorrect translation
- unestablished criminal acts of a party to the case, a representative or a judge committed during the consideration of the case
New circumstances are also significant for the case, but arise after the adoption of a judicial act. These include:
- cancellation of the judicial act that served as the basis for the considered case
- recognition of the invalidity of a transaction that entailed the adoption of an illegal or unfounded judicial act in this case
- recognition by the Constitutional Court of the law applied in the case as inconsistent with the Constitution of the Russian Federation after the applicant’s appeal
- decision of the European Court of Human Rights after the applicant's appeal
- determination or change in the resolution of the Presidium or Plenum of the Supreme Court of the practice of applying a legal norm, indicating the possibility of revising judicial acts that have already entered into legal force
Consideration of an application for review of a judicial act based on new or newly discovered circumstances (Article 316 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
To review a court decision based on new or newly discovered circumstances, a party to the case submits a corresponding application to the Arbitration Court, which considers it in a court hearing within a month.
Judicial acts adopted by the arbitration court based on the results of consideration of an application for review of a judicial act based on new or newly discovered circumstances (Article 317 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation)
After considering the application for reconsideration of the case, the court either refuses or grants it, accepting it for proceedings.
In case of cancellation of a judicial act due to new or newly discovered circumstances, the case is re-considered by the same arbitration court that canceled the previously adopted judicial act. After the judicial act is annulled, the arbitration court has the right to reconsider the case at the same meeting. A judicial act adopted as a result of a new consideration cannot be changed in the direction of worsening the position of the person held accountable for administrative or tax offenses, or public legal liability.
Stage 8. Enforcement proceedings
Execution of arbitration court decisions that have entered into legal force (Article 318 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). Typically, enforcement is carried out on the basis of a writ of execution issued by the court in an approved form.
0
0
0
0
0
Appeal in an arbitration case: the main nuances
The essence of the content of the appeal is to substantiate disagreement with the appealed decision of the arbitration court of first instance. “Arguments-facts-standards-time” - the lawyer’s possession of these components in a specific arbitration case is the key to success.
The filing of an appeal begins the appeal proceedings in the arbitration court. But before proceeding to an appeal, it is advisable to prepare for it while the case is being considered by the arbitration court of first instance. This applies to both sides. In our practice, regardless of the decision made, in 95% of cases it is appealed by the dissenting party. Accordingly, you need to be prepared either to prepare a response (objections) to the complaint, or to the appeal itself.
Court hearings of the arbitration court are audio , which will also be studied by the appellate court. If you did not timely exercise your right to declare the available evidence , then you must be prepared to argue why this was not the subject of consideration in the court of first instance? Why didn’t you appeal or file comments on the interim court decisions during the hearing of the arbitration case on the merits? In general, it will be difficult to convince an appellate court to consider new evidence, and there is little chance of choosing other methods of defense in an appeal. Only an experienced lawyer can calculate the possible options.
The procedure for filing an appeal, its form and content, the procedure and time frame for considering the complaint, the powers of the court considering the complaint, and other issues of proceedings in the appellate instance are determined by the norms of Chapter 34 of the Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation. The APC imposes certain requirements not only on the content of the appeal and its proper execution, but also on the list of documents attached to it, as well as the actions that the person filing the complaint must take.
You can find information on appeals on any of the websites of arbitration courts. If there is a need to familiarize yourself with it, then to save time we also provide a “standard set”.
An appeal must be submitted in writing and signed by a person who has the appropriate authority to do so.
Appeals must contain the following details:
- the name of the court to which it is filed;
- the name of the person filing the complaint and other persons participating in the case;
- the name of the court that made the appealed decision, in what case, indicating its number and the date of the decision.
This is important to know: How to sue noisy neighborsThe complaint shall indicate the subject of the dispute, as well as the submitted petitions.
It is recommended that the appeal contain other information from the participants in the trial that may be useful for the consideration of the case: telephone numbers, fax numbers, email addresses, etc. The list of attached documents is given in the complaint.
The appeals are accompanied by:
- a copy of the contested decision;
- documents relating to the payment of state duty (see clause 2, part 4, article 260);
- documents confirming the fulfillment by the person filing the appeal of the obligation to send to other persons participating in the case, copies of the filed complaint and documents attached to it that they do not have, by registered mail with return receipt requested or by other means (in particular, in person against signature );
- a document confirming the authority to sign the appeal.
If the complaint does not comply with the requirements of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation (Article 260), the court issues a ruling to leave it without progress and indicates the period during which the deficiencies must be eliminated. It is necessary to take into account that if the circumstances that served as the basis for leaving the appeal without progress are eliminated by submitting properly executed documents (on payment of the state fee, confirming the direction or delivery to other persons participating in the case, copies of the appeal and documents that they have there is no power of attorney or other document confirming the authority to sign the appeal, etc.), the documents must be submitted in such a way that by the deadline appointed by the court they arrive directly at the court, and are not sent by mail.In accordance with Part 2 of Art. 257 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, an appeal is filed with the court that made the decision.