With the active development of the credit industry in a rather unstable financial and economic situation in the country, more and more lenders (both individuals and legal entities) are faced with the problem of overdue debts from their borrowers. In order to repay the debt relatively quickly without resorting to legal proceedings, banks and other credit organizations use the procedure of assignment of the right of claim. In our article we will look in detail and in simple terms at what an assignment agreement is and how to conclude it correctly in a bankruptcy case.
- What is
- Legislative framework and principles
- Risks
- What demands can be ceded?
- Conclusion of contractual obligations of assignment
- When is an assignment agreement drawn up in the event of bankruptcy between a debtor and a creditor?
- Types of assignment agreement in case of insolvency of an enterprise
- Documents for drawing up an assignment agreement
- Step-by-step instructions for drawing up an assignment agreement in case of insolvency
- Challenging an assignment agreement in bankruptcy
- Peculiarities
- Termination of an agreement
What is
The essence of this financial and legal transaction is the change of one of the parties' obligations. That is, the assignor (creditor), on a clearly regulated basis by law, cedes the opportunity to claim debts from the borrower to a third party (assignee). In fact, this is a procedure for resale of debt to another organization, which will bear all the difficulties in collecting loan funds.
From Latin, this term is literally translated as the transfer of authority over something (for example, securities, property, etc.), which is documented according to the letter of the law. An assignment agreement is a document that formalizes a voluntary agreement between the original lender and a third party. It confirms the legality of the transaction and also regulates the terms of the assignment.

There are three parties involved in the procedure:
- a legal owner who cedes the opportunity to collect a debt to another person and, in the course of the transaction, acquires the status of an assignor;
- an organization that repurchases the debt on favorable terms and gets the opportunity to demand full repayment from the borrower, called the assignee (usually a collection agency);
- debtor - nothing changes with him, except for the name and details of the creditor (the amounts and terms of return of funds remain the same).
The document clearly reflects the terms of imprisonment, measures of responsibility and responsibilities of all participants.
Bankruptcy of individuals
from 5000 rub/month
Read more
Services of a credit lawyer
from 3000 rubles
Read more
Legal assistance to debtors
from 3000 rubles
more
Write-off of loan debts
from 5000 rub/month
More details

Legislative framework and principles
The change of actors in the obligation occurs in accordance with the legal framework of the Russian Federation, namely on the basis of Articles 382-390 of the Civil Code. A financial and legal transaction can be recognized as legal even without the consent of the borrower. However, he must be notified (in writing) about the procedure for changing the credit institution. If this condition is not met, then the debtor has every right not to reimburse the new lender.
According to Article 384 of the Criminal Code, the amount of debt that is transferred from the assignor to the assignee cannot change. In practice, this means that the amount of debt, taking into account the interest rate, remains at the same level. Penalties, penalties and other additional charges are illegal. If the borrower considers the demands of the updated creditor to be unlawful, then, on the basis of Art. 386 may raise a legitimate objection.
Today, the assignment operation is additionally regulated by the new law on the activities of collection organizations. In the “strengthened” edition of the latter, control over their work has been significantly tightened. Now, for the legality of the procedure, collectors must be registered in a special state register. If the debtor has a precedent with collectors, then he has the right to demand their state registration number. The updated bill makes the debt collection process more legal.
Regulation by laws
The assignment agreement is becoming widespread every day. Its popularity currently exceeds the frequency of use of supplies. It is especially often used by people working in the credit field.
Organizations of various sizes use assignment of debt claims against borrowers. This is one of the most effective methods for stimulating the payment of monetary debts.
The term sale of debt is used only colloquially; the term is not correct from the point of view of legal structures and is not present in the civil code today. This form allows you to make a threatening impression on borrowers.
This trick is considered an effective psychological technique. The correct wording of the described action is the transfer of the right to claim under an obligation. It can be found in codes. The role of the latter can be played by various documents regulating certain responsibilities of clients.
First of all, clients who have not dealt with credit institutions before are interested in the question of whether it is possible to transfer the right of claim to third parties. Its transfer to collection agencies is possible if the corresponding column was indicated in the agreement.
If it is missing, then users will have grounds to file a claim in the courts. This risk is not practical for banks, since the plaintiff most often wins during the proceedings.
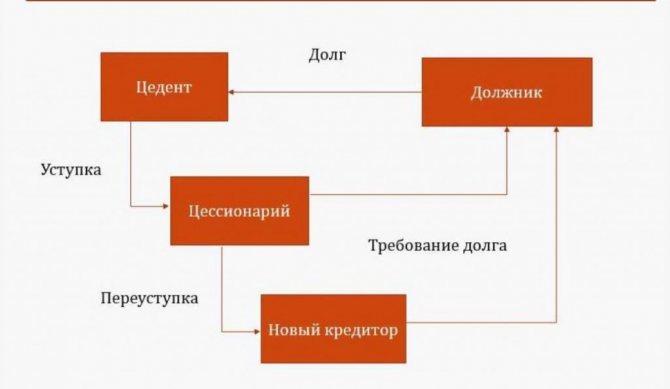
Scheme of assignment agreement with the bank.
There are several legal norms regulating the activities of parties in the economic sphere. The Russian Civil Code contains an article describing and regulating the relationship between the parties.
Part 1 of Article 382 states that the ability to recover, which belongs to the creditor on the basis of the debtor’s obligations, may be transferred to third organizations by law or by a concluded transaction.
Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 382. Grounds and procedure for transferring the creditor’s rights to another person
1. The right (claim) belonging to the creditor on the basis of an obligation may be transferred by him to another person under a transaction (assignment of the claim) or may be transferred to another person on the basis of law.
2. To transfer the rights of a creditor to another person, the consent of the debtor is not required, unless otherwise provided by law or agreement.
If the contract provided for a prohibition of assignment, the assignment transaction may be declared invalid at the request of the debtor only if it is proven that the other party to the transaction knew or should have known about the specified prohibition.
The prohibition of the transfer of the creditor's rights to another person provided for in the contract does not prevent the sale of such rights in the manner established by the legislation on enforcement proceedings and the legislation on insolvency (bankruptcy).
3. If the debtor was not notified in writing about the transfer of the creditor's rights to another person, the new creditor bears the risk of the resulting unfavorable consequences for him. The debtor's obligation is terminated by its performance to the original creditor, made before receiving notification of the transfer of rights to another person.
4. The original creditor and the new creditor are jointly obliged to compensate the debtor - an individual for the necessary expenses caused by the transfer of the right, if the assignment, which entailed such expenses, was made without the consent of the debtor. Different reimbursement rules may be required under securities laws.
What does the assignment agreement include?
The primary step for this action is signing a loan agreement. It involves the transfer of the bank and the client in the role of lender and borrower. The assignment agreement has the following content. A sample agreement can be downloaded below.
A bank that has lent money to a civilian decides to transfer the right to repay the debt to a collection agency. The client, as a rule, has financial difficulties that do not allow him to fulfill the prescribed obligations.
A third party who has successfully collected the debt provides funds to the bank. Their volume may be lower than stipulated in the contract. However, claims of this kind against the borrower are finally closed and incentive actions towards him are suspended.
The Civil Code does not regulate restrictions on the activities of third parties. Therefore, collectors often use harsh methods. The Federal Law on Banks and Their Activities calls a bank a legal entity that has a wide range of rights along with the ability to issue loans.
The assignment agreement confirms that the third party involved in the debt collection process acquires rights similar to the bank.
Debt repayment methods
People exposed to sewers experience a logical inconsistency. To whom and how to repay the debt, if the loan was issued by a banking institution that has received a license from the Central Bank of Russia for a long time, and it is required by an enterprise, the registration of which does not require the same hassle.
The features of the assignment agreement with the bank are discussed in this video:
A collection agency can be easily created and registered in the state registry within a week by selecting a suitable legal status. The regulated scope of activity of a given organization may differ from its practical scope. The contract may specify trade or supplies.
This clash of opinions is a consequence of vague legal norms that do not have a clear outline. The lack of consistency in government acts and regulations often serves as a cell for the actions of attackers.
Citizens who have a low level of legal literacy and have not fully studied the list of basic and special rights unknowingly contribute to unscrupulous companies. There are countless different nuances that can nullify the rules provided for in the assignment agreement.
In this case, the document will not have legal force during legal proceedings. A lawyer with extensive experience is able to regulate the activities of the parties in accordance with the law.
In most banks, employees are aware of the flaw in the laws, so before the assignment agreement is actually executed, they will most likely try to repay the debt by any means.
Methods of influencing debtors
Managers often use psychological pressure. They regularly call with demands, send text messages and try to make contact in real life, threatening with legal proceedings and criminal penalties.
Your loan case will be assigned to an individual curator or manager who is part of the security service. The bank also has the right to transfer the right of claim to collectors. The effect of this contract does not change the focus of the lender.
It will apply the same measures, enhanced by the influence of collection agencies. The latter receive a clear percentage of the total amount of debt in case of successful collection.
If the bank does not get the desired result, then it is faced with the following choice: to enter into an assignment agreement with collectors, which is associated with great risk, or to file a claim in the courts.
If the first option is used, the bank will not receive the desired funds in the primary amount, but will protect itself from tedious negotiations with the borrower. In another situation, the duration of the payment procedure increases significantly.
There is also the possibility of reducing previously accrued fines and penalties. They may be considered unfounded or the borrower may not have the necessary financial capacity to pay. The administration of the banking institution is faced with a choice.
Risks
The assignee risks the following:
- Failure by the borrower to fulfill its direct obligations - violation of the terms of repayment of funds is most often associated with the difficult financial situation of the defendant or his unreliability. Another common reason for non-repayment is simple ignorance that the creditor and, accordingly, his details have changed. To avoid such problems, the party acquiring the right to claim the debt must make sure that the debtor is aware of the assignment procedure. If inaccuracies were made during the execution of the initial papers, the borrower can challenge the current agreement.
- Features of taxation - everything is relatively simple here. If the collection fee exceeds the amount of the debt obligation, then the collector is obliged to pay income tax. When the assignment payment is less than the debt, the assignment is written off as a loss. When preparing such documents, it is important to take into account the deadlines - if an overdue debt is reissued, then the process of writing it off will be much more difficult.
- Invalidation of the contract. Such a decision is made by the court when the transaction is fictitious or carried out in violation of current legislation.
Read Affiliated Interested Parties in a Bankruptcy Case: Who is and is included in the group, how to prove and rights under the law

In legal practice, there are also cases when the original agreement clearly stated a ban on the sale of obligations or the debtor simply does not agree to change the credit institution. Many nuances may arise with the registration of a cession for property that is pledged. Such precedents are resolved with the help of highly qualified lawyers in the manner prescribed by law. You can get professional legal assistance at.
Purpose of the assignment
The essence of this operation is to change the party to the obligation. In other words, the creditor (assignor) cedes to a third party (assignee) the right to demand the debt from the debtor, who will repay the overdue debt to the assignee. The creditor must notify the debtor of the assignment. If there is no notice, then the debtor has the right to make payments to the old creditor, and the debtor will not be responsible for partial or complete non-payment. And also a creditor who has his own obligations can pay them off by transferring to his creditor the right of claim against someone.
What demands can be ceded?
The assignor under the agreement has the right to assign to the successor any recovery, if this does not contradict the norms of current legislation, the agreement of the parties or the essence of the debt obligations. In fact, you cannot transfer only such debts as:
- payment of moral damages;
- alimony;
- debts related to divorce proceedings.

When is an assignment agreement drawn up in the event of bankruptcy between a debtor and a creditor?
The assignment of claims is one of the ways to clear the balance sheet of receivables in the Russian realities of doing business. The procedure, with the right approach, makes it possible to quickly stabilize financial indicators in the event of bankruptcy of a company, as well as return a considerable part of the money.
The procedure for using the assignment in the event of the borrower's insolvency is regulated by Art. 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The agreement can be signed without the participation of the debtor. A third party buys the right to claim tangible and intangible assets in full. That is, the debt from one organization is transferred to another - the original creditor sells the debt (usually for a smaller amount) and is guaranteed to receive funds, and the assignee himself tries to take the money due to him from the defendant.

Assignment in bankruptcy proceedings can be used for a variety of purposes, the most common of which are:
- the borrower uses his insolvency as a lever for the prompt withdrawal of funds before starting a fictitious operation to declare insolvency (in such a situation, the debt becomes the property of a third party);
- a debtor who is experiencing financial difficulties tries to obtain financing in such a way as not to lose business;
- a reseller company buys up the debts of a specific legal entity in order to specifically bankrupt it;
- a change of creditor for the debt obligations of a bankrupt company or individual is carried out to minimize losses caused by a long wait for debt repayment;
- the procedure for assigning rights of claims is necessary to increase the bankruptcy estate at a meeting of lenders, etc.
Assignment in legislation
The possibility of transferring claims to another person is regulated by Art. 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the transfer of such claims from one creditor to another does not require coordination with the debtor, but notification of the latter is necessary. Guided by Art. 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the debtor has the right not to fulfill obligations to the new collector until he is presented with evidence of the transfer of the debt to a third party.
The exception is cases where the debtor has received notice from the original claimant. The transfer of powers to carry out collection from one person to another occurs through the conclusion of a written agreement.
The parties to such an agreement are called assignor and assignee:
- Assignor is the party who transfers the right of claim.
- The assignee is the new creditor under the agreement.
When concluding such an agreement, according to Art. 390 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the assignor is responsible for the invalidity of information regarding the debt transmitted to the assignee, but the original creditor does not bear any responsibility for the debtor’s failure to fulfill the legal demands of the new collector.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides the following conditions for an assignment agreement:
- the transferred claims exist at the time of assignment (or will occur in the future);
- the assignor has the appropriate authority to complete the transaction;
- the assignor has not previously concluded a similar agreement with another person;
- the original creditor did not commit actions that could become the basis for objections to the assignment of rights of claim on the part of the debtor.
With the assignment of rights, the original claims do not change, only the creditor changes.
Types of assignment agreement in case of insolvency of an enterprise
In legal practice, there are several types of agreements in case of insolvency of a legal entity:
- Free and compensated - in the first case, cases from one credit organization are transferred to another without compensation, in the second - for a certain fee. According to the norms of the Civil Code, official agreements to change the creditor between legal entities on a free basis are illegal, since they have no economic benefit.
- Tripartite – here it is necessary to obtain the borrower’s consent to resell his debt obligations. A standard agreement has a bilateral nature (between the assignor and the assignee), where the defendant does not influence its signing in any way, but is only notified of the fact of conclusion by a special letter.
- According to writs of execution, a similar situation is allowed by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, but if the court decision has already gained force, then the court must be notified of this type of transaction.
- Free and paid - often debt obligations are sold for less than the amount of the original debt. This covers the risks and inconveniences of the receiving credit institution.
Read Features of bankruptcy of individual entrepreneurs

Assignment restrictions
The law prohibits the transfer of an obligation in cases where it is inextricably linked with the personality of the debtor. Can not be transferred:
• Child support debt.
• Compensation for moral damage.
• Payments during divorce.
• Compensation for harm caused to human health or life.
The debt under the writ of execution is transferred only after applying to the court with an agreement on procedural succession and receiving the appropriate court ruling.
Documents for drawing up an assignment agreement
The package of papers that must be prepared to conclude a transaction on the assignment of rights of claim in the event of insolvency is individual. Standardly it contains the following:
- The initial agreement between the lender and the borrower as the basis for the formation of debt. This includes documentation for the provision of services, delivery of products, obtaining a bank loan, etc.
- Additional information on contractual obligations. The presence of a legally formalized transaction does not mean the appearance of debt. That is why you will need direct evidence that services were provided or goods were shipped (reconciliation reports, invoices, payment scheme, etc.).
- A general set of data about the original creditor and the defendant - copies of charter papers, extracts from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, etc.
- Additional agreements, annexes to existing agreements.
- A court ruling on the appointment of a responsible person (who initiates the assignment).
- A power of attorney to represent certain interests of a specific party.
The difference between assignment and assignment
Assignment and assignment are often confused. An assignment is a transfer or sale of a right of claim to a third party without incurring obligations on the former creditor. An assignment, according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is a transaction under which a third party acquires not only the right to demand the return and repayment of obligations, but also acquires certain obligations along with debt obligations.
A simple example is the assignment of a lease. The new lessor received not only the right, but also new obligations - to make periodic payments for the leased item.
The assignment of rights under the DDU is also not an assignment, although some developers call this the transaction of the sale of their rights by the shareholder to a third party. Such an agreement is called the assignment of the right to demand the transfer of ownership of an apartment to a citizen within a specified time frame.
Step-by-step instructions for drawing up an assignment agreement in case of insolvency
Signing a document on the transfer of rights of claim involves the following steps:
- Preliminary preparation - here all documentation is studied, evidence is requested about the existence of receivables, etc.
- Direct conclusion of a transaction between the assignee and the assignor. The borrower, as a rule, does not participate in this process. The document must clearly indicate the parties to the contractual relationship, the date, responsibility and liability of each of them, cost and other nuances. If a document is related to real estate transactions, then it must undergo the registration procedure with Rosreestr.
- Transfer of monetary reward to the assignor (in cash or by crediting to a specific current account).
- Collection of funds from the borrower by a new lender.
Challenging an assignment agreement in bankruptcy
Sometimes such agreements can be challenged in accordance with the procedure established by law. The basis for the paperwork is evidence that the assignor deliberately worsened his financial situation. In order to collect indisputable evidence, the arbitration manager must scrupulously examine the solvency of the borrower and the fact of possible collection of funds from him. The court has the right to annul contractual relations that were concluded in anticipation of the legal entity being declared insolvent, which, in turn, led to the satisfaction of obligations to the credit institution.
There are other reasons for recognizing an assignment agreement as invalid in bankruptcy. For example, if the existence of a debt was not properly proven or the initial agreement with the borrower clearly prohibited the assignment of debt. Also, errors made during paperwork may serve as a reason for challenging.
Bankruptcy of individuals
from 5000 rub/month
Read more
Services of a credit lawyer
from 3000 rubles
Read more
Legal assistance to debtors
from 3000 rubles
more
Write-off of loan debts
from 5000 rub/month
More details

What claims can be assigned under an assignment agreement?
Under an assignment agreement, rights of obligation are assigned. Since obligations can arise from contracts and other transactions, torts (causing harm), unjust enrichment, then with the help of an assignment it is possible to transfer both the right to demand the repayment of a loan, and the claim for payment of the cost of a broken display case in a store, as well as a claim for the return of funds, transferred by mistake to the bank account of an unknown person.
You can assign both the right to claim the fulfillment of an obligation as a whole, and individual rights to claim. For example, you can assign a claim to repay a loan, but not assign a claim to pay interest. In most cases, it is also permissible to assign individual rights of claim from a contract to different persons. Contingent claims and future claims can be assigned.
You can assign both a direct claim from the contract (for the fulfillment of obligations) and a claim that arises in connection with its violation. For this reason, assignment of claims for damages or penalties is permitted.
For assignment, with a number of exceptions, it is not necessary to obtain the consent of the debtor. Based on the norm of paragraph 1 of Art. 388 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the possibility of assignment, as a general rule, is provided for all rights of obligation. But the same article of the code provides a number of exceptions to this rule. In addition to this norm, a ban on the assignment of a number of claims is established in Article 383 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- Firstly, claims that are inextricably linked with the identity of the creditor cannot be assigned. Article 383 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation includes among such requirements alimony claims and claims for compensation for harm to life and health. The list of such rights of claim is not closed, the main thing is that they meet the criterion of an inextricable connection with the personality of the creditor - for example, a claim for compensation for moral damage meets this criterion.
- Secondly, without the consent of the debtor, other obligatory claims from obligations in which the identity of the creditor is of significant importance for the debtor cannot be assigned. The list of such situations is extensive, and as the Supreme Court points out, in order to assess this importance of the identity of the creditor, it is necessary to proceed from the essence of the obligation (Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2017 N 54 “On some issues of application of the provisions of Chapter 24 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the change of persons in obligation based on the transaction"). Among such obligations, undoubtedly, it is worth including various types of gratuitous agreements concluded due to special trust relationships between the parties. For example, if I agreed to let my friend use my car for free (loan agreement), then he cannot assign the right from this agreement to a third party, unless I myself approve of this.
- Thirdly, the contract itself can prohibit the assignment of rights without the consent of the debtor. If there is such a prohibition, the debtor may recognize the assignment as invalid under Article 173.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation if his consent is not obtained. The transaction will be invalid if the assignee knew about the prohibition. But how can one not know about the prohibition if the assignee will certainly check the contract from which the transferred claim arises? But in any case, the debtor can hold the assignor who violated the contractual prohibition liable for failure to fulfill obligations and, for example, collect from him the penalty provided for in the contract. However, the contractual prohibition does not apply to cases of assignment of claims under monetary obligations. In other words, the assignment on the request to receive funds will be valid even if the prohibition is violated. But the assignor will still be liable for violating the prohibition and a penalty can be collected from him.
- Fourthly, the assignment of a non-monetary claim requires the consent of the debtor if such an assignment makes the fulfillment of his obligations significantly more burdensome. For example, if a contract was concluded between the parties for the disinfection of premises, and the debtor carries out activities only on the territory of one constituent entity of the Russian Federation, then it is impossible to assign the requirement to carry out work on disinfection of premises to a person located at the other end of the country without seeking the consent of the debtor.
- Fifthly, in order to assign a claim under an obligation in which there are several joint and several creditors, each of them must obtain the consent of all other such creditors, unless they have agreed otherwise. Solidary plurality of creditors is a situation in which it is impossible to divide the execution between creditors. In other words, the execution is the same for everyone. This is easy to illustrate with an example when friends agreed to buy a car together so that they could use it in turns. In order for everyone, and not just one of them, to have a share in the ownership of the car, several people are included in the contract as buyers. But the debtor cannot transfer the car in parts and to each of the buyers in the corresponding part. Friends in this case are joint creditors and if one of them wants to give up his place to another person, he must seek the consent of the rest of his friends.
Finally, it is worth touching on such an important and pressing issue as the admissibility of assigning rights to collect fines provided for by consumer legislation. For consumers, unlike entrepreneurs, the law provides special rights to collect penalties (fines and penalties) from sellers, contractors and performers under consumer contracts, which are noticeably higher than for other persons. This issue has acquired particular relevance in the context of equity participation in construction - collection agencies have begun to buy up the claims of defrauded equity holders against developers. And when they began to pursue such claims, developers began to argue during the courts that since the right of claim is provided only for consumers, it means that it could not be assigned, since it is connected with the identity of the creditors (that is, their status as consumers). Initially, the courts supported the developers, which led to absurd results. Such a concession is undoubtedly beneficial to defrauded shareholders who want to get at least some money without wasting time and money on the court. But the rule of law that protects them has long been used against them. Recently, the courts have nevertheless sided with consumers and allowed legal entities to collect consumer fines from developers. In particular, this position has been established at the level of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (Determination of the Investigative Committee on economic disputes of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of May 28, 2021 N 306-ES17-12245).

Peculiarities
The assignment of claims is a consensual paid legal procedure. This financial and credit operation can be carried out without the consent of a third party, that is, the borrower. The basic laws of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation do not provide for any restrictions in terms of the legal status of participants in such contractual relations. The amount of remuneration for the assignor is determined individually, but it must be economically justified, otherwise the transaction may be declared invalid. One of the most important requirements of the assignment is a written form of its conclusion (depending on the initial agreement, it can be simple or certified by a notary office).

What are the features of an assignment agreement?
The assignment agreement (agreement on the assignment of rights) is the basis for the transfer of the right of claim from the assignor to the assignee. No more no less. Such an agreement is a disposition transaction - that is, it transfers rights from one person to another person. Such an agreement can only define the right being transferred and indicate to whom it is transferred.
But the agreement that stipulates the transfer of the assignment is not an assignment agreement. The rights of claim can be sold (sale agreement) or donated (donation agreement) - in such a case, a corresponding agreement is concluded. Despite the fact that often only one agreement is drawn up, it is formally worthwhile to separate the assignment agreement as an administrative transaction, which is the basis for the transfer of rights, and an obligatory transaction, regulating the relationship between the assignor and the assignee.
An assignment agreement is actually the equivalent of the transfer of a thing from the seller to the buyer under a purchase and sale agreement. But since the law of obligations, unlike a thing, does not exist in the objective world and we cannot see its transfer, therefore, in order to mark this transfer of law and make it publicly available, it is necessary to secure such a transfer in paper or indicate it by the actions or words of a person, and also comply with any other form prescribed by law.
Therefore, the assignment agreement must be concluded in the form in which the transaction from which the rights are assigned was concluded. If the agreement from which the transferred rights arise was concluded in notarial form, then the agreement on the assignment of the claim must also be certified by a notary. If the contract requires government registration, then the assignment also needs to be registered - a similar rule, for example, exists for preschool education. It is also worth saying that if rights are assigned outside of the transaction (for example, a claim for compensation for harm from the causer), then the rules on simple written form, prescribed by Article 161 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and providing for a requirement for written form for transactions, should be applied to the assignment agreement by the party of which a legal entity acts and transactions between citizens in an amount exceeding 10 thousand rubles. Failure to comply with such a written form entails the impossibility of referring to witness testimony to prove the fact of the conclusion of the agreement.

Termination of an agreement
This procedure is regulated by Articles 450 and 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and can be implemented either by mutual agreement of the parties or unilaterally. The following may serve as grounds for cancellation of contractual obligations between the assignor and the assignee:
- the transaction was concluded in relation to compensation for moral damages or alimony;
- the real estate or movable property that is the subject of the agreement is not properly registered in the relevant state register;
- for registration there are not enough official papers that will confirm the legality of the operation;
- the third party does not have the authority to collect the debt;
- When signing the initial agreement, the assignment procedure is not spelled out, and there are no clear conditions for interaction between the debtor and the credit institution-receiver.
Termination of a bankruptcy assignment unilaterally may take place if it is specified in the agreement or on the basis of a court decision, if the rights of one of the parties are infringed or the law is violated.
Video on assignment:
Key Basics of an Assignment Agreement
What are the main characteristics of an assignment contract?
At the legislative level, the concept of “cession” is used only in Article 197 of Part 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. There it is used as a synonym for the term “assignment of the right of claim”. An assignment of the right of claim is the replacement of a creditor in an obligation. The conditions for replacing the creditor in the obligation are determined by Chapter 47 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Article 510 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that the parties to an obligation are the creditor and the debtor. One of the parties to an obligation may be attended at the same time by not one, but two or more persons. But this is not always a regular circle of business partners: it often happens that the delivery is made to one person, and payment is made to another. In this situation, the contract may provide for the option of making payment to a third party. Based on the provisions of the third part of Article 512 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the creditor cannot be replaced in an obligation when such an impossibility is directly established by law. The Civil Code does not contain a separate provision on the contractual terms of the assignment agreement, which would directly regulate the relationships between the parties to such contracts. In the Civil Code, however, there is still an option to outline the legal basis of assignment contracts.
Article 515 of the Civil Code defines situations when replacing the creditor in obligations is impossible: if the obligations relate to the person of the creditor, if these are obligations to compensate for harm, expressed in injury, death or other damage to health. It is also prohibited to transfer obligations for alimony payments, compensation for moral damages for the fact that business reputation has been reduced, as well as much more.
It is worth noting an important point that it is possible to replace the creditor in an obligation even if the debtor does not agree (unless otherwise stated in the law - part 1, article 516 of the Civil Code). But the debtor in such a situation must be notified in writing, or the new creditor faces adverse consequences. In this situation, the debtor's fulfillment of his obligation to the original creditor is considered reliable performance. If such a situation arises, the parties must take measures and restore the original position (so-called bilateral restitution).
The assignment agreement stipulates that when assigning the right of claim in any situation, the debtor must be notified in writing (so that the interests of the new creditor are satisfied). Although this is not necessary.
[su_youtube url=”
«]
Upon assignment of the right of claim, the original creditor is obliged to transfer to the new creditor documents confirming the right of claim. They must also be provided with the information necessary for its execution. Until the debtor is provided with evidence of the transfer of rights to the new creditor in the obligation, the debtor has the right not to fulfill his obligation to the new creditor.
The obligation may be of a monetary nature (if we are talking about the purchase of goods for which payment has not yet been made), commodity (in the case of receiving an advance without making the delivery itself), non-commodity monetary (receiving repayable financial assistance without return).
Is compensation possible under an assignment agreement? Current legislation does not prohibit the establishment of remuneration when assigning a right of claim. It is possible to calculate fees for these services based on:
- Percentage ratio to the amount of transferred debt
- A fixed amount (the new creditor pays a smaller amount compared to the amount of the right to claim the debt, or the initial creditor pays the new creditor a regulated amount of funds for the service - this option is less common in practice).










