Given the difficult economic situation in the country, staff reductions are not a rare occurrence. Even highly qualified employees are not immune from it, but some have preferential rights. From this article you will find out who gets laid off first, who is given preference at equal skill levels, and who cannot be fired at all on this basis.
What is an abbreviation
There are 2 concepts - downsizing and downsizing. In Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not spell out the differences between them. In practice, the difference is also insignificant. When staffing is reduced, the position remains on the staff list, but the number of people occupying it decreases. When staffing is reduced, the position is eliminated.
The reasons for downsizing at an enterprise are:
- Difficult economic situation in the country.
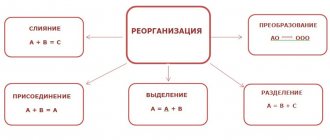
- Merger, reorganization or accession of companies.
- Internal optimization.
If any positions are excluded from the staffing table, a position reduction procedure is carried out. Learn more about the procedure for job reduction and employee notification.
What is downsizing?
Sometimes managers are forced to resort to reducing the number of their employees. Their right is completely legal and can be justified by many reasons: a decrease in income or production volumes, a change in the staffing structure, or the economic unjustification of some work units.
Article 81. Labor Code of the Russian Federation
. Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer
“An employment contract may be terminated by the employer in the following cases:
- reduction of the number or staff of employees of an organization, individual entrepreneur;”
However, there are special categories of citizens
who are under
state protection
and cannot be dismissed at the initiative of the employer. Often, many employees who are wrongfully dismissed are not familiar with the law and do not know that they are among those who are not subject to layoffs. In such cases, issues are resolved in court and end with forced restoration of the workplace.
Who gets laid off first and why?
Interesting information
Not only specific positions, but also entire divisions, divisions, and departments may be subject to staff reductions. The employer has every right to do this. However, in both cases, during layoffs, respect for the rights of workers is mandatory, and those who are not allowed to be fired must remain at the enterprise. If entire departments are going to be cut, then employees who have “special” rights should be transferred to other departments.
Let's look at who gets laid off first at work and on what basis. The employer determines preferential rights, and a certain algorithm is provided for this:
- Employees who are prohibited by law from being laid off are excluded from all candidates for dismissal. According to Art. 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, these include pregnant workers, mothers of children under 3 years of age, single parents with children under 14 years of age or disabled children under 18 years of age, as well as some others. It is prohibited to dismiss employees on maternity leave due to layoffs (Part 4 of Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Part 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The remaining workers are assessed on their skill levels and productivity. The comparison is made between employees who occupy the same positions created within the same structural unit. Correctly evaluate the qualifications of two leading accountants working in the same department. It is incorrect to compare a leading specialist and a category 2 accountant - this is indicated in the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court No. 33-27711/2015 dated 08/06/2015. Similar rules apply to the assessment of labor productivity.
- If the comparison reveals equal levels of qualifications and labor productivity, then family circumstances and other advantages are taken into account when the employee is laid off. There is one exception. If a position is abolished or all staff positions in one position are reduced, then preferential rights are not taken into account. This is indicated in the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court No. 33-1708 dated January 22, 2015.
The law establishes certain rules regarding the dismissal of an employee. We read about the regulations of the Labor Code on reducing the number or staff of employees.
We determine the circle of people who cannot be reduced
Before downsizing, the employer must find out which employees cannot be dismissed on its initiative. In Part 4 of Art. 261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation and paragraphs. 28, 29 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1 lists categories of employees, including part-time workers, whom the employer does not have the right to dismiss due to staff reduction.
These include:
- pregnant women;
- women raising children under 3 years of age;
- single parents (legal representatives) with a child under 14 years of age or a disabled child under 18 years of age;
- a parent (another legal representative of a child) is the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under 18 years of age or a child under 3 years of age in a large family with young children, if the other parent does not work.
Note! If there is a reduction in the position occupied by an employee from the listed categories, the employer is obliged to transfer such employee to another vacant position.
Important! Persons who are guaranteed job retention during the period of their absence, namely: women on maternity leave (Part 4 of Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), other employees on leave (educational, primary, additional, at their own expense ) and on sick leave - cannot be reduced during their absence from work.
What are preemptive rights and who has them?
Given equal levels of qualifications and labor productivity of employees, preference is given to those who have advantages in the reduction of staff. According to Art. 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the following categories of workers can apply for job retention:
- family people who have two or more dependents (minor children, other disabled family members who are fully supported by the employee or regularly receive assistance from him, representing their permanent and main source of livelihood);
- the only “breadwinners” in the family are employees whose families do not have other people with a regular income;
- employees with injuries and occupational diseases received while working in this organization;
- employees who are currently improving their qualifications in the direction of the employer.
If you were illegally fired due to layoffs, you need to contact several authorities. First, send a written application to the organization's trade union. The union must consider the complaint within a week. This case may also be considered by the Federal Labor Inspectorate and the prosecutor's office. If the trade union and the labor inspectorate do not reveal any violations, then a lawsuit must be filed.
In addition to the categories of employees listed in the Labor Code, certain other persons also have benefits during layoffs in accordance with federal laws:
- military spouses;
- military personnel transferred to the reserve;
- authors of inventions;
- disabled people of the Second World War and combat operations;
- persons affected by radiation;
- and some others.
Preferential rights to remain at work may also be provided for by internal collective agreements in the company.
About dismissal due to staff reduction and the required payments here.
Persons who have a preferential right to remain at work
Note! If there is a reduction in one of the similar positions, the employer must conduct an analysis of the advantages of each employee in order to retain his job, taking into account the provisions of Art. 179 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
With the same labor productivity and qualifications, the following have the right to retain their place:
- family employees with two or more dependents;
- persons in whose family there are no other independent workers;
- employees who were injured or become ill at work;
- disabled people of the Second World War and combat operations to defend the Fatherland;
- employees who improve their qualifications at the direction of the employer without interruption from work;
- other categories of employees specified in the company’s collective agreement, who also have the right to count on maintaining their jobs.
If several employees have preferential rights at once, the one who has more such advantages will be able to keep their job.
How employees are compared
Some facts
Upon termination of an employment contract due to the liquidation of an enterprise, or a reduction in the number or staff of a company's employees, the dismissed employee must be paid severance pay in accordance with the average monthly salary. For a dismissed employee, the average monthly salary is recorded for the duration of the job search for 2 months from the date of dismissal.
The law does not describe specific requirements for the procedure for identifying the preferential rights of employees. Practice shows that courts place more trust in the decisions of commissions when recording the results in writing. Here are the main nuances that should be taken into account when comparing candidates for reduction:
- It is recommended that the commission include heads of departments where staff reductions are planned, as well as members of the trade union organization and specialists from other structural divisions (lawyers, personnel officers, those responsible for quality control, etc.).
- An order should be issued to organize the commission, defining the competence of each of its members. Personnel officers may be responsible for providing information about penalties and incentives imposed. Department heads should be entrusted with the generation of work reports, compilation of characteristics, etc.
- It is advisable to draw up summary tables that reflect the results of comparing the qualifications and labor productivity of workers according to a number of criteria.
- The commission's findings should be recorded in the official minutes of the meetings.
- The commission must make its conclusions based on the results of comparing the labor productivity of each employee, taking into account the entire set of criteria. The decision that one employee has higher qualifications because the second has less experience is considered illegal by the court.
- If candidates for layoff are registered in a trade union and regularly pay membership dues, the employer is obliged to take into account the opinion of this organization on the advisability of dismissing a particular employee. This is the requirement of Part 2 of Art. 82 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Watch a video that will tell you about the categories of workers who are prohibited from being laid off
Who gets fired first during downsizing?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not indicate who is the first to be laid off. The prerogative to consider this issue is decided exclusively by the manager with the involvement of the head of the personnel department. Previously, there was a trend in which persons who did not have sufficient experience were subject to dismissal.
Experts note that the following categories of employees receive notice of upcoming dismissal more often than not: 1) those hired less than a year ago and who do not have an impact on the direct receipt of profit; 2) persons who, at the time of the revision of the staffing table, receive state support (pension) or are preparing to receive it.
If a specialized department at an enterprise closes and there is nowhere to transfer an employee with the appropriate qualifications, then no amount of merit to the company will help to stay in place.
It should be noted that the law provides for compensation in connection with the imminent loss of employment. The Labor Code clearly states how dismissal that took place due to the liquidation of a workplace is paid.
Important! The rules on staff reductions do not apply to positions in budgetary organizations when it comes to the dismissal of civil servants. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not apply to them.
From the point of view of personnel policy
The head of the HR department monitors the behavior of personnel in the workplace. At an enterprise where a collective agreement is in force and a trade union body has been formed, they are additionally concerned about the rights of the employee. Therefore, when deciding on candidates for redundancy, a whole board meets. When reviewing the personal files of employees, personnel officers pay attention to:
- the number of sick days, days off, absenteeism, vacation pay, namely the number of days worked over a certain period of time;
- compliance with labor discipline;
- the presence of personal records (for example, sales) or other indicators of high labor efficiency;
- absence of grounds for including an employee in the group not subject to dismissal.
List of persons who cannot be dismissed due to reduction
The list of those who cannot be laid off by law includes the following categories of workers:
- temporarily disabled persons;
- employees on leave (including student leave and unpaid leave);
- mothers of small children under 3 years of age;
- women and men raising alone a child under 14 years of age or a minor child with a disability;
- members of the trade union organization.
Those who cannot be laid off from work also include pregnant employees and women on maternity leave. If an employee from the “untouchable” category is nevertheless fired due to staff reduction, he will be reinstated at work automatically by court decision.
We are ready to answer any questions you may have - ask them in the comments