Purpose of a common house heating meter
After the Housing Code determined that the common property of an apartment building is the property of the residents, their area of responsibility expanded significantly. Responsibilities for the maintenance and servicing of common property fell on the shoulders of apartment owners.
Since it is impossible to refuse to pay for general house needs, it makes sense to reduce the cost of heating residential and non-residential premises and pay only for the heat actually received.
To measure the amount of energy consumed, a common house heat metering device (CDMU) is installed. By paying for heating in an apartment building by meter, you will be able to control energy consumption and keep track of expenses. This is not the only purpose of installing ODPU.
Another goal pursued by the management company is to encourage residents to save heat outside their own apartments and take care of common property.
If the doors and windows in the entrance are tightly closed, the heat will be retained, and residents will receive the service in full.
It should be immediately mentioned that ODPU itself does not save anything. This is just a metering device that provides more accurate data for determining the final amount of payment for heating than the standards.
Purpose, pros and cons
According to the Housing Code, the common property of an apartment building is considered the property of the residents, which increases their responsibility. The owners of living space are responsible for the maintenance and maintenance of common property.
Since it is impossible to refuse regular payments for general house needs, the best option is to reduce the cost of heating non-residential and residential premises by paying for the heat actually received.
To measure the actual volume of heat energy consumed in apartment buildings, a common building heat meter is installed.
Property owners not only have the opportunity to pay for heating in an apartment building by meter, they can control energy consumption and keep track of utility costs. This is an important advantage of installing ODPU.
When installing heating devices in apartment buildings, the management company pursues several goals. One of them is to encourage owners to save heat outside their apartments and treat common property responsibly. If the entrance doors to the front door and the windows in the entrance are tightly closed in winter, the heat will remain in the building, and residents will receive utilities in full.
ATTENTION! It is worth considering that a common house heat meter does not save heat. This is an energy metering device that allows you to obtain accurate data for calculating heating bills.
The main advantages of using a common house heat meter in an apartment building:
- You can save on installation costs, since self-installation is expensive. The cost of installing communal equipment is shared among residents.
- All residents will try to keep warm. Therefore, they will begin to take a more responsible approach to the problem of an open door or window structure in a common entrance.
An important disadvantage is the high cost of the electrical appliance. Moreover, if the devices fail, the residents of the multi-story building will have to pay for the repair work. The main disadvantage of a common house heat meter is the inability to save on heating living space due to lower consumption of thermal energy.
Installing a communal heat meter is legal
People first started talking about public meters back in 2009, when Federal Law No. 261-FZ “On Energy Saving and Increasing Energy Efficiency” was published. In the original version, the law prescribed the mandatory installation of ODPU in multi-storey buildings before January 1, 2012. Later this period was extended several times.
The last change in the period until January 1, 2019 and until January 1, 2021 (for Crimea and Sevastopol) was fixed on July 26, 2017.
Thus, the law on communal heating meters clearly confirms the need for their installation in apartment buildings. An exception is allowed only for dilapidated, unsafe and subject to demolition houses, as well as objects where installing a meter is technically impossible due to the non-compliance of the parameters of the utility network with the installation conditions of the device.
Rules for installing communal heat meters in an apartment building
The process of accounting for the consumption of utility resources must comply with the law. For these purposes, communal heat meters are installed in an apartment building, which provide reliable monitoring and recording of readings. Installation of ODPU is a mandatory procedure performed in compliance with current rules. There are reasons to avoid placing a common flow meter.
Installation procedure for a collective heat meter
If the centralized heat supply system has the technical ability to install a common house heat meter, it must be installed.
In newly built houses, energy meters are installed before the facility is put into operation. This requirement is contained in the law on the installation of a common house meter dated November 23, 2009 in paragraphs 7-8 of Article 11, and paragraph 9 of Article 13 defines the area of responsibility for installing a public meter in houses where it is not available.
In order for a common house meter to appear in your home, you must go through several stages of its installation procedure.
- A meeting of owners of an apartment building (MKD) is the basis for the installation of heat meters for heating in an apartment building.
- The meeting may be initiated by the Management Company. In HOAs, housing cooperatives, and residential complexes, the meeting is held on the basis of an application from the owners; 10% of the signatures of the total number of votes is sufficient.
- Technical conditions for the installation of an ODPU, in accordance with which its design and installation will be carried out, are issued by the heat supply organization.
- The installation project and the estimate for the work are prepared by the design organization, taking into account the specific installation location and indicating the device model.
- Coordination of the project with the heat supply organization that issued the technical specifications.
- Purchasing a project-approved ODPU, mandatory with a verification stamp.
- Installation of ODPU and putting the meter into operation.
Find out in more detail how to install communal metering devices in apartment buildings.
Organizations responsible for installing ODPU
According to Law No. 261-FZ, the responsibility for installing a collective heat meter is assigned to the owners of apartments in a multi-storey building, who must carry out this activity independently, choosing an equipment supplier and a contractor for the work.
Assuming that there will be houses that are not equipped with ODPU, legislators determined who should install heat meters in this case. So, if on July 1, 2012, houses did not have a heat meter, the responsibility for installing it was transferred to the resource supply organization (RSO).
In addition, the RSO is obliged to prepare proposals for equipping apartment buildings with metering devices and carry out the corresponding work, which is confirmed in the letter of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia dated December 8, 2011 No. AG/45584.
Thus, the widespread information that the management company installs heating meters is erroneous. The task of the management company is only to:
- bring to the attention of the owners of apartments in apartment buildings the need to install a collective heat meter;
- organize a meeting;
- draw up a protocol of consent.
Activities for installing the device can be carried out by heat energy supply organizations or specialized companies that have:
- Qualified specialists on staff of the company.
- Permission to perform the relevant type of work, issued by SRO.
House-wide heating meters in an apartment building
Owners of apartments living in apartment buildings have the right to resolve the situation with high heat consumption by installing an IPU instead of a common building meter. However, this is not the most economical method, since the price of the equipment is high. The total cost should be divided among all owners and then the amount will be acceptable.
Readings from a common meter are taken monthly by employees of the management company or HOA. Payment is made in accordance with the square footage of each living space. Additionally, the rule of subsidies and recalculation applies. The latter option involves a refund if the temperature of the batteries and the ambient air in the apartment does not meet the standards.
Who installs
A heat meter is installed based on the decision of the residents of the apartment building. To do this, a meeting is initiated where installation is discussed. Additionally, they determine who will inspect the ODI element, take readings, and also generate invoices for payment.
The decision is recorded in the protocol, then a statement of consent to install the equipment is sent to the management company. The main purpose of installing a common house appliance is low price. But as a result, economic feasibility may not have the expected effect. For example, in old houses there is insufficient thermal insulation, which leads to increased resource consumption.
Formula for calculating heating using a common house meter
Pi = (Vi + (Si x (Vd - ∑Vi)) / Sob) x Tt,
Where:
- Pi – the amount of heating contribution for one property, obtained based on the calculation results (rubles);
- Si – square footage of an apartment or non-residential premises;
- Sob – total m2 of apartment building;
- Vd is an indicator of energy consumption based on TDPU, if calculated within a season or from the average volume for 12 months;
- Tt – the current tariff in the region for the resource;
- Vi – individual heat consumption;
- ∑Vi – total volume throughout the house.
How much does a communal heating meter cost?
Since heat meters for heating, in accordance with Law No. 261-FZ, are the property of the residents of an apartment building and they bear all the costs of their purchase and installation, the issue of the cost of ODPU is very important. Let's look at what expense items make up the cost of installing a collective meter.
- Cost of the device. The price of a heat meter directly depends on its type and manufacturer. There are several types of heat meters:
- tachometer - the cheapest models (6-10 thousand rubles) with a service life of 2 to 4 years;
- vortex - a more expensive option, the average price of which is 15 thousand rubles;
- electromagnetic - costing 15-17 thousand rubles;
- ultrasonic - depending on the model, the price from the manufacturer ranges from 15,000 to 50,000 rubles.
- The cost of preparing a document containing the technical conditions of the heat supply system and developing design documentation for the equipment of the metering unit.
- The price of an additional set of equipment and related materials.
- Installation cost: installation, electrical installation, as well as commissioning.
All costs result in a fairly high amount: from 150 to 300 thousand rubles. This is what the residents of the house have to pay. You can do this in several ways:
- one-time payment (required for legal entities);
- installment payment, which is provided for a period of up to 60 months and is paid in equal installments. The interest rate depends on the refinancing rate set by the Central Bank.
- using funds from the overhaul fund, provided that this service is included in the list of works on overhaul of common property in the apartment building in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, in accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation (Part 2 of Article 166).
The payment mechanism is regulated by law: the amount is distributed among all apartment owners depending on the area of housing and the timing of deposits.
Legislation on heating meters in apartments
Rules for the installation and use of heat meters are set out in various regulatory documents. For example, Federal Law No. 261 (with the latest amendments in 2021) indicates that residential properties and other buildings to which the resource is supplied should be equipped with metering devices, including individual devices. The responsibilities of premises owners include ensuring the safety of equipment, monitoring its working condition, as well as carrying out verification and replacement.
Additionally, the use of heating meters is regulated by Federal Law No. 190 (current version 2021). Article No. 4 states that commissioning and connecting new consumers is impossible without preliminary installation of metering devices.
The responsibility for installing IPU and common house devices lies with the owners of apartment buildings, who independently regulate their safety or enter into an agreement with management organizations.
Please note: at the stage of construction of an apartment building, the developer must install metering devices before receiving permission to hand over the apartment building.
Watch the video: “Innovations in legislation on the installation of individual heat meters in apartments and their varieties.”
Standards for heating consumption in apartment buildings without a meter from 2020
The tables show heating consumption rates based on a season lasting nine months. The unit is Gcal per 1 m2 of all premises in an apartment building:
Buildings erected up to and including 1999:
Table 1.
| Floor | No coefficient | With coefficient frequency |
| 1, 3, 4 | 0,025 | 0,01875 |
| 2 | 0,023 | 0,01725 |
| 5-9 | 0,021 | 0,01575 |
| from 10 | 0,02 | 0,015 |
MKDs built after 99:
Table 2.
| Floor | No coefficient | With coefficient frequency |
| 1 | 0,02 | 0,015 |
| 2, 6, 7 | 0,018 | 0,0135 |
| 3-5, 8, 9 | 0,019 | 0,01425 |
| from 10 | 0,016 | 0,012 |
Since 07/01/16, the formula by which charges for utility resources are calculated for buildings that are not equipped with metering devices, Government Decree No. 603 has introduced an adjustment factor.
The size is calculated by dividing the duration of the heating season by the total number of months in the year (PP No. 354, Appendix No. 2, clause No. 2). In other words, if the authorities of the subject issued an order to calculate the standard for 9 months, but with distribution for a year, then the frequency ratio will be 9/12.
Maintenance of common house heat metering devices
Maintenance of the meter involves maintaining it in working condition. This is achieved as a result of preventive work, such as:
- inspection and elimination of causes affecting wear and breakdown of the control and measuring unit;
- checking the operation of additional equipment;
- operational maintenance and control of metrological accuracy of measurements of the metering device;
- weekly readings for analysis and development of recommendations for maintaining the required temperature.
If a malfunction is detected during the inspection, the device is dismantled, the damage is repaired and reinstalled.
To get a complete picture of maintaining the ODPU in working condition, find out how the MKD heating system is maintained.
Classification of common house heat meters
Heat metering equipment, although it performs the same function, uses different operating principles, has its own design features, and requires compliance with certain specific installation and maintenance requirements.
Therefore, you not only cannot select a common house meter yourself, but also have no right. Only competent specialists from the relevant organizations will be able to accurately determine which type of devices is optimal in specific conditions, recommend a trusted supplier, and calculate the required amount of additional equipment.
It is useful to know that the following types of meters are used in housing and communal services:
- tachometer;
- electromagnetic;
- vortex;
- ultrasonic.
Tachometer meters are the simplest budget option. They are equipped with mechanical water meters and a heat meter. Their cost is significantly lower than other metering devices. The main disadvantage of such equipment is problematic operation in conditions of increased water hardness. The filter will often become clogged, and this will naturally weaken the pressure of the coolant: a dubious benefit is obvious. Therefore, tachometer meters are usually chosen for private sector houses and apartments. A huge advantage of mechanics is the absence of all kinds of electronic components, which allows the device to function even for a long time in unfavorable conditions (humidity, dampness).

The correct operation of a common house heat meter is influenced by factors such as the purity of the liquid in the system, pressure uniformity, and the microclimate of the room in which the measuring device is installed.
Electromagnetic devices are an affordable solution that guarantees high-quality measurement accuracy with high-quality installation and periodic qualified maintenance. Suitable for areas with good water quality, since metal impurities in it can distort the reliability of the device's readings - upward.
Vortex meters can be easily mounted on both horizontal and vertical sections of a pipeline, display correct readings under any conditions, and have a radio interface that helps identify faults and take readings remotely - this is probably why service organizations speak very positively about them and recommend them, for the most part , to install them.
Although ultrasonic metering devices are highly accurate and modern, in practice they do not demonstrate particularly high reliability - due to poor water quality, they often quickly fail. In addition, this equipment is very sensitive to welding currents.

Like any other measuring device, a common house heat meter is subject to mandatory periodic verification. Both the service life of the equipment and the objectivity of the figures in housing and communal services bills depend on the quality of service
Reconciliation of readings from a common house heat meter
To calculate monthly payments, accurate and timely readings are needed, which are taken from the general building meter. In accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 06.05.11 No. 354, responsibility for heat metering lies with the utility service provider, which can be:
- Management Company;
- HOA;
- Housing cooperative;
- resource supply organization.
Meter readings are taken monthly from the 23rd to the 25th of the current month. The ODPU service agreement may contain a clause on the presence of a representative of the residents when readings are taken.
If there is no such condition, then, at the consumer’s request, the contractor is obliged, within one working day, to acquaint him with the instrument readings recorded in the ODPU reading log. This document is a kind of reporting to consumers and answers the question of how to check the readings of a common building heating meter.
Data storage period is 3 years. In cases where meter data is transmitted remotely in electronic form, the consumer has the right to request a screenshot of the readings recorded by the modem.
Household heat metering device in an apartment building: benefit or punishment
Heating is one of the most expensive items on your utility bill. The calculation is based on standards and tariffs - indicators established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation by the executive authorities of the subject in the field of state regulation of prices. Also, the payment structure may include the volume of thermal energy consumption if a common house heat meter is installed in an apartment building. Let's find out in what cases installation is required, how to do it correctly and what benefits residents will receive.

Calculation of heat energy consumption using a collective meter
Compared to the standards, the installation of ODPU provides more accurate accounting of thermal energy consumption. The calculation is based solely on meter readings, taking into account the difference between them at the end and beginning of the calculated period. This value is required to calculate the amount payable for heating.
The formula for calculating the cost of heating is as follows:
P = Qtot x S / Stot x T.
In other words, the volume of heat according to the meter (Qtotal) is multiplied by the area of the house (S), divided by the area of the apartment (Stotal) and multiplied by the tariff (T). (RUB/Gcal), approved by local governments for each region separately.
Find out more about how heating is calculated for an apartment.
Responsibility for lack of meters
The absence of ODPU is considered a violation of the law, which threatens the management company and the HOA with fines, and residents with an increased coefficient. Currently, this value is 1.6 of the heat supply tariff. The increasing factor does not apply to houses where it is not technically possible to install meters.
A resource-saving organization may be fined on several grounds:
- non-compliance with the requirements for submitting proposals for equipping apartment buildings with heat metering devices. The fine will be from 20 to 30 thousand rubles for officials and from 100 to 150 thousand for legal entities (clause 6 of article 9.16);
- Unreasonable refusal or evasion from concluding an agreement for the installation of ODPU and/or its execution is subject to a fine of 20-30 thousand rubles for officials and from 50 to 100 thousand for legal entities (Clause 12 of Article 9.16 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
The management company can be fined for failure to comply with notification measures, because its function is to encourage residents to install a meter, justifying the need for this measure. The fine will range from 5 to 10 thousand rubles for officials and from 20 to 30 thousand for legal entities (clauses 4-5 of Article 9.16 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Read more about how the responsibility of the management company manifests itself.
Advantages and disadvantages
common house meter
When justifying the need to install ODPU, the Criminal Code usually gives the following arguments:
- payment for actually consumed heat energy. The presence of a meter allows you to accurately monitor heat consumption and reduce heat energy costs by up to 30%;
- recording leaks in the heating system in order to prevent overpayments for water losses from the central pipeline to the house;
- increasing responsibility for the common territory. By paying for losses from their own pockets, residents of the house are more attentive to the condition of the common property.
Along with the advantages, a heat meter for an apartment building also has disadvantages, which primarily relate to the financial burden on the owners of apartments in multi-apartment buildings. All costs associated with installation and repair of the meter are borne by the residents. The fewer apartments in the building, the higher the payments.
Individual heat meters
Installation of an individual heat meter is not necessary. It is installed at the request of the apartment owner, as stated in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 05/06/11 No. 354 (clause 3, article 33, section V).
According to the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development dated December 29, 2011 No. 627, individual meters are prohibited from being installed in apartments with vertical wiring.
In addition, in order for the calculations for heating to take into account the readings of apartment meters, they must be installed in each residential and non-residential premises of the apartment building along with a general heat energy meter.
More information about the types of individual heat meters and their purpose is contained in the material “Heat meters for heating in an apartment.”
Disadvantages of collective metering devices
The innovation in the form of communal heat meters also has a lot of disadvantages. The main one is the need to pay for them out of your own pocket. The cost of the meter, the costs of its installation and configuration are fully borne by the residents of the house. Moreover, we are talking about quite impressive sums: all this “pleasure” costs at least 150 thousand rubles. Fewer apartments in a building means more money will have to be shelled out.
In addition to purchasing the device, you must choose a reliable organization that will install it and register it; will carry out comprehensive maintenance and, if necessary, repair of the device. Cooperation with dubious companies can result in additional difficulties – primarily financial ones. But if you contact a reliable company and order the installation of a heat meter for your home on a turnkey basis, you can save yourself from a whole load of problems, because its specialists:
- will help in preparing and obtaining technical specifications;
- develop design and technical documentation;
- coordinate the project with the heat supply organization;
- will carry out installation and commissioning work.
Returning to the shortcomings of the equipment, it is also worth noting the lack of opportunity to save in each individual apartment. “Tightening” the battery to the minimum and paying “pennies” will not work. This requires individual metering devices. If the design of the heating system in the house allows the installation of the latter, then this is certainly an ideal option. With them, the principle “what you consume, how much you pay” is absolutely real and the savings can become very noticeable. True, an individual meter will require significant expenses - not everyone can afford it.
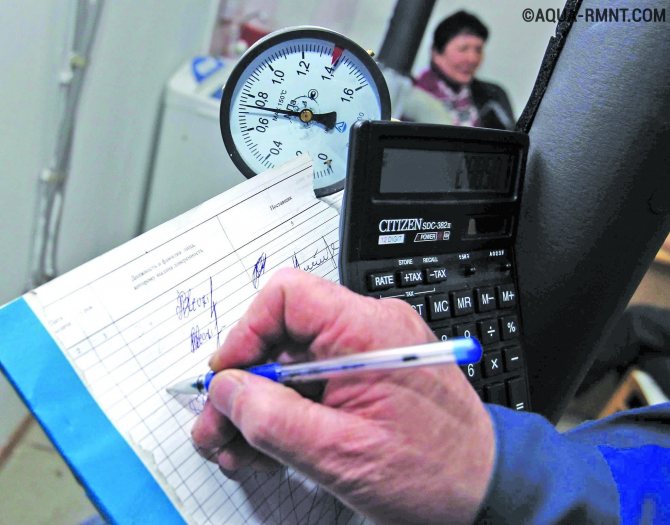

If your apartment is located in a building where the heating system is installed according to a horizontal scheme, you can install an individual heat meter. For buildings with vertical wiring, a common house meter is the only hope for savings
Results
The Energy Saving Law obliges residents of apartment buildings to install common heat energy meters at their own expense, with the exception of houses that do not meet the technical capabilities.
Both the management company and the RSO take part in the ODPU installation procedure, with the first organizing, and the second being responsible for installing the device. In case of failure to fulfill their obligations, companies will be fined, and residents will receive a receipt for heating payment with an increasing coefficient. Time will tell how expedient the forced installation of collective meters is, but the effect of using ODPU is undeniable: heating costs are reduced by up to 30%.
Central communal heating meter: who should install it and why?
The installation of communal meters is mandatory, which is stipulated in the articles of legislation. Heating meters in apartment buildings will not be installed in the following cases:
- the building is classified as dilapidated or in disrepair;
- the cost of equipment and its installation exceeds the amount of utility bills at home (for heating) for six months.
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation establishes that all property of a house is divided into personal and general. Personal property inside apartments and its safety falls solely on the shoulders of the homeowners. Common building amenities are located in shared areas (floors, elevators). Each owner and tenant of real estate (under a social or commercial tenancy agreement) undertakes to take care of the joint property and its safety.

The operation of communal heat meters performs a number of important functions, but does not guarantee large savings on utility bills.
Reducing costs depends on the owners and users of real estate themselves.
Purpose of a collective meter
Common house meters are installed in apartment buildings for the following purposes:
- management companies can control the actual consumption of resources;
- establishing fair payment based on resources used;
- developing a sense of economy among citizens (heat energy consumption and future payments will depend on the serviceability of doors and windows in the entrances).
The legislative framework
The design of the heating system, the procedure for taking readings, the rules for paying money for utilities are established by the articles of the following regulatory legal acts:
- Housing Code (fixes the distribution of common and individual property, and also obliges citizens to maintain both types of property equally);
- Federal Law “On Energy Saving” No. 261 (establishes the mandatory installation of communal meters in apartment buildings).
There are also local orders and acts that utility services and management organizations follow when forced to install numeric devices.
Who should install the device?
The procedure can be initiated by the owners of apartments in the building themselves or by the management company. Depending on the procedure, the algorithm will be as follows:
- organizing a house-wide meeting of owners and submitting for consideration the issue of installing heat meters;
- voting (to satisfy the decision you will have to collect the required percentage of positive votes);
- calculation of cash expenses (the management company can take money from the account for major repairs);
- if the available financial reserves are insufficient, then the meeting considers the issue of additional donation of funds for the installation of meters;
- The management company attracts third companies to the events that have a license to carry out work on installing public meters.

How much does installation cost?
The cost of communal heating meters is compensated by the apartment owners themselves. It can be:
- individuals who have received property rights on the basis of a legal agreement (purchase, gift, inheritance);
- legal entities, if the premises are used for business activities;
- IP;
- municipality, when the property is transferred to the temporary use of a family on the basis of a social rental agreement.
The cost of a common house appliance will vary between 50-500 thousand rubles per apartment building. The final price depends on the following factors:
- the locality in which the apartment building is located;
- competition;
- building area divided into private and shared squares;
- complexity of installation work;
- quality of materials used.
Maintenance of common house heat metering devices
Monitoring the serviceability of common house thermal energy metering devices is carried out:
- management company;
- housing and communal services inspector;
- representative of the company that installed the meters.
Expert opinion Mironova Anna Sergeevna Lawyer of a wide profile. Specializes in family issues, civil, criminal and housing law
The commissioning of a common house meter is impossible without the presence of a heating service provider in the house. A specialist from the provider must establish the serviceability of the meter, as well as seal it, recording the current readings. The utility provider does its own regular meter checks.

Maintenance includes a list of the following functions:
- regular inspection of the device for mechanical damage;
- monitoring the serviceability of mechanisms;
- no idle speed;
- recording readings from a common house meter.