General provisions
The Labor Code does not clearly define the concept of moral harm.
It is more focused in the Civil Code, which is worth paying special attention to. And many other areas of law can use this concept because of its universality. In general, it concerns the violation of non-property rights of a personal nature, which entailed not only moral, but even physical suffering. If cases of compensation are provided for by law, then they must be compulsorily satisfied by the court. The amount and amounts for compensation vary. But they all proceed from numerous principles, which form the basis for them.
- The guilt of the offender, its degree, other circumstances that should be taken into account.
- The nature of any suffering caused. They must also take into account the characteristics of the individual.
- Justice and reasonableness.
- Facts and events in which everything happened.
There are times when moral damages must be compensated regardless of the employer’s fault. This mainly concerns harm to human health when the cause was a source of increased danger. In each individual case, everything must be considered individually, since there can be no talk of universality here.
Legal regulation
All persons who were discriminated against while performing work have the right to receive compensation for damage to morals. This is provided for by the third article of the Labor Code. This regulatory act, namely Article 21, states that the employee has the right to request an amount for moral damage, and the employer must compensate in the prescribed amount.
When dismissal occurs not according to the law, as well as when a transfer occurs in violation of the law, you can demand payment of moral damages. This is stated in Article 394. But still, the basis for moral damage is Article 237 of the Labor Code, which states that compensation occurs only in monetary terms. If the parties cannot resolve the dispute on their own, they should go to court, providing all the necessary reasons and grounds.
Even if the employer delays wages, you can apply for compensation for moral damage. The law does not prohibit this. The employer's inaction may also have certain consequences.
Moral damage in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The Labor Code does not consider the concept of moral harm to an employee. Therefore, if a corresponding situation arises, you must be guided by the legal norms that apply in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
However, in the text of the articles there are references to this concept:
- Article 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that discrimination of any kind in hiring gives him the right to go to court to receive compensation for moral damage caused.
- Article 394 of the Labor Code regulates the possibility of complaining about an illegal transfer or dismissal and demanding compensation for this.
- Article 237 states that if a manager causes moral damage, he is obliged to pay an amount determined by the terms of the employment contract signed by the parties.
It should be noted that such lawsuits have a special limitation period. As is known, in the field of labor disputes it is short, and courts often decide that when compensating for moral damage, this period should have the same duration.
However, Article 208 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation directly states that when protecting personal non-property rights, the concept of limitation of actions does not apply in all cases, except those provided for by law.
Statement of claim to recover moral damages from the employer
The civil procedural period stipulates not only the procedure for writing an application, but also its content. This document must consist of established and mandatory parts:
- Introductory. It specifies the authority to which the appeal is made (name of the judicial authority), information about the applicant (full name, place of residence and place of registration, if they differ, the price of the claim). As for the cost of the claim, it includes not only material damage, but also moral damage.
- Motivational. Referring to the legislation, the violated rights of the employee are indicated, all existing claims are listed, that is, the essence of what happened is described. It is very important to describe the harm caused to the applicant by the employer.
- Supplementary. The applicant asks the court authorities that his claims against the employer were satisfied to the extent that he claims.
- If necessary and available, additional documents are attached that will confirm the fact of harm to the employee, as well as the resulting consequences, treatment costs, etc.
Documents of evidence
To prove his case, an employee of an enterprise can provide certain documents to the court, which will serve as the basis for compensation for moral damage. Only a statement is provided in case of moral torment of the employee, since other documents here in terms of proof will be in question.
Of particular importance are medical documents, which include certificates, sick leave certificates, reports of doctors and forensic experts. They are studied in detail by the judicial authorities when there has been a direct physical impact on the employee’s health. This applies to work-related injuries.
But they will play a mediocre role in the case where the health impairment was a consequence of poor sleep or mental state due to the actions of the employer. In this case, the court will independently and at its own discretion take them into account. The main thing is that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the resulting consequences and the actions (inaction) of the employer. It will not be amiss to provide receipts (receipts) from pharmacies for the purchase of necessary medications.
When harm to health is associated with a source of increased danger, then compensation for moral damage to the employee is mandatory, regardless of whether the employer is at fault. This is provided for by the Civil Code, namely Article 1100.
No limit on refunds
On Tuesday, the Russian Tripartite Commission is considering a bill from the Ministry of Labor (RG has it) establishing a deadline for going to court to demand compensation for moral damage caused by violation of labor rights. Now any employee who believes that he was illegally fired, underpaid, etc., can demand compensation from the employer for moral damage caused.
“Now, if the employee and the employer do not come to an agreement on the restoration of violated rights and payment of compensation for moral damage, the employee has to go to court,” the Ministry of Labor explained to Rossiyskaya Gazeta. “But when the rights themselves have already been restored through the court, it is difficult for the employee to receive compensation for moral damage, since at the legislative level there are no deadlines for filing a claim with the court for compensation for moral damage for these violations.” Therefore, the Ministry of Labor proposes to establish the same deadlines for applying to court for compensation for moral damage as are currently in effect for claims to resolve labor disputes. If a person is dissatisfied with the actions of the employer and considers his rights to be violated, but the employer does not admit guilt, then a claim can be filed within three months. And if an employee believes that he was illegally fired, then he must file a claim with his superiors within a month.
“Despite the fact that the judicial system, as a rule, protects the rights of the employee, decisions on compensation for moral damage are strikingly diverse. In the absence of gross violations of labor legislation that led to serious consequences and significant violation of rights, the amount of moral compensation rarely exceeds 50-100 thousand rubles. As a rule, people are sued for illegal dismissals, refusals to provide vacations and rest days, due benefits and compensation. The adoption of the bill will expand the practice of filing claims for compensation for moral damage to an employee and will stimulate the courts to award the citizen amounts that are truly adequate to the moral suffering suffered,” says Honored Lawyer of Russia Ivan Solovyov.
As lawyer Vadim Tkachenko adds, any violations of labor laws imply compensation for moral damage. “Employee rights can be violated by orders and various local acts. Another question: it is necessary not only to demand a certain amount, but to justify its expediency in court. But our courts are not ready to recover really serious amounts. In our practice, there was a case when an amount of 1 million rubles was declared, and the court of first instance collected only a thousand rubles from the defendant in labor disputes, but the appellate instance “raised” this amount, but not by much - up to 10 thousand rubles,” he clarified lawyer.
Grounds and conditions
In order for amounts for moral damage to be approved by the court, there must be grounds. These include not only physical, but also moral suffering as a result of non-compliance with the established rights of an employee of the enterprise, the emergence of infringements in the field of industrial relations, as well as in the event of injury, damage to health, and the formation of certain injuries.
Article 233 of the Labor Code states that compensation for moral damage is possible only in the form of material obligations of the employer. In this case, there must be conditions so that everything is in accordance with the law. The conditions include existing damage to the employee, expressed in actions or inactions that are necessarily illegal, as well as a cause-and-effect relationship between the damage caused and the employer’s actions.
Among the grounds for payment of moral damage are relocation to another job with non-compliance with labor rights, holding anyone accountable for no reason, failure to pay wages on time, and other issues. In each of these cases, compensation for moral damage to the employee is provided.
Payment amount
Judicial practice suggests that an employee will not be able to receive a large amount of compensation for moral damage. Most often, compensation amounts to several thousand rubles. Only in exceptional cases, when harm is caused to the life and ability of an employee, are payments increased. When considering the case, all circumstances affecting the amount of compensation must be taken into account:
- the degree of involvement of the employer in causing the damage;
- what is the harm?
- requirements of reasonableness and fairness;
- circumstances of the damage.
There is no pre-approved amount of compensation, since all cases are considered in court strictly individually.
There are also no established restrictions on the amount of payment. But it should be noted that often the amount requested by the plaintiff is reduced. In some cases, during the performance of work duties, the moral health of employees of organizations is damaged. Most often this is expressed in moral suffering due to delayed wages and unacceptable working conditions.
Russian legislation gives citizens the right to recover compensation for such damage from their employer. To do this, you must either enter into a payment agreement with the employer or file a claim in court.
Types of consequences
Compensation for moral damage to an employee is provided in the case when a person was fired from work without reasonable grounds. The size is set in accordance with the concluded employment contract. But necessarily in monetary terms. Material damage does not count here. When these norms are not reflected in the contract, then everything is decided in court and it is the judicial authorities who make the final decision.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Reduction of a position in the staffing table: procedure, documents
An industrial injury occurs not only during the direct performance of work duties, but also while traveling to work, as well as during non-working hours, if at the same time he worked on the territory of the enterprise and performed established duties under the contract. When a person receives any injury, a commission is created to investigate what happened.
There is also the concept of an occupational disease, which is associated with the fact that it was formed as a result of temporary or permanent action of factors located at the place of work. They can be chronic or acute. If an employee develops an illness, he is paid a specified amount of temporary disability benefits.
In this case, you can write a statement for compensation for moral damage caused. In this case, the amount of payments is established by the court, and not by the current legislation. Even if the employer is not at fault here, the mental damage to a person must be compensated in the event of an occupational disease, if, for example, he worked on a vehicle (a source of increased danger).
As soon as a person has not received his wages on time, he has three months to receive, in addition to the wages itself, compensation for moral damage. A statement must be written here in which it is necessary to reflect all the emotional losses that are expressed in insomnia, a ruined weekend or holiday, a trip or excursion that did not take place, or experiences.
Compensation for moral damage to an employee – All about personnel
The employer and employee can independently agree on the amount of compensation, which must necessarily be in monetary value. To protect themselves, each party must insist that an appropriate agreement be entered into. Payment is made on the basis of an order issued by the employer. But if the size does not satisfy the employee, he has the right to go to court.
When considering an application to the court, all factors relating to the case are taken into account. Each moment is approached individually. Of no small importance is the degree of guilt of the employer, the amount of suffering caused, the nature of the harm, and the identity of the parties. In any case, this provides for fairness in decision-making, as well as the reasonableness of establishing the amount of compensation.
Now a little about timing. When an employee finds out that his rights have been violated or should have known about it, from that moment he is given exactly three months to go to court by writing a corresponding statement. If we are talking about dismissal of an employee without grounds provided for by labor legislation, then only one month from the moment the employee is familiar with the relevant order.
The same period is established after receiving the work book from the place of work. When legal relations have not yet been completed, wages have been accrued, but payments have not been made, then missing this deadline will not serve as grounds for refusing to consider the application. This offense will be deemed to be a continuing offense.
The deadlines can be restored, but for this there must be clear and justified valid reasons that the court will take into account.
All violations by the employer should not go unnoticed by the judicial authorities. But for this it is important to write a high-quality statement of claim, where the essence of the problem is stated. This will help somehow teach the employer a lesson and force him to subsequently act in accordance with the rules of law. Compensation for moral damage should be compensated only in monetary terms, which is established by a concluded agreement or a court decision.
Save
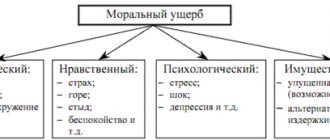
Moral harm is the infliction of moral and physical suffering on a citizen as a result of the actions of other citizens or legal entities.
This type of compensation is also provided for employees whose rights are violated by the employer. In accordance with labor legislation, they are a type of financial liability of the employer to the employee.
From the point of view of civil law, moral damage includes:
- Violation of a citizen's property rights;
- Violation of his personal non-property rights;
- Encroachment on intangible benefits belonging to a citizen by birth or by force of law.
Thus, moral damage can be caused:
- If you lose your job;
- When revealing a family secret;
- When disclosing medical confidentiality;
- When distributing information discrediting the dignity of a citizen or business reputation;
- For moral experiences associated with the loss of relatives;
- In case of temporary restriction or deprivation of any rights;
- When causing physical pain as a result of injury or other damage to health;
- In case of illness suffered as a result of moral suffering, etc.
It is possible to recover compensation for moral damage in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation only in court.
The amount of compensation is determined taking into account all the circumstances of the case.
Note: one of the prerequisites for the recovery of moral damage is the guilt of the perpetrator.
According to labor law, moral damage is harm caused by unlawful actions or inaction of the employer.
This includes:
- Discrimination;
- Delay in payment of wages;
- Unlawful dismissal;
- Illegal transfer, etc.
To recover moral damages, the following conditions must be met:
- Causing physical and (or) moral suffering to an employee;
- The employer commits culpable unlawful acts or omissions;
- The presence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the unlawful culpable actions (inaction) of the employer and the physical and (or) moral suffering of the employee.
Note: in some cases, moral damage must be compensated even in the absence of the employer’s fault (for example, if the harm was caused to the employee by a source of increased danger).
Moral damage is compensated in monetary form, the amount of which is determined by agreement of the parties.
This agreement must be concluded in writing in 2 copies. The agreement specifies the procedure, amount and date of payment of compensation. One of the copies is given to the employee against signature.
Example
Agreement on compensation for moral damage
01/18/2017 Moscow
State government institution "Moscow Roads" (GKU "Moscow Roads" hereinafter referred to as "Employer", represented by the head
Novikov Andrey Genadyevich, acting on the basis of the Charter, with
on the one hand, and design engineer Andrey Petrovich Goritsky,
We invite you to read: Is furlough possible during layoffs? || Is the employer obliged to provide vacation first and then make layoffs?
hereinafter referred to as “No. Employee”, on the other hand, collectively referred to as
The “Parties” have entered into this Agreement as follows:
- The parties agreed that in connection with injury to the Employee
When performing labor duties, the Employee is paid compensation
for moral damage in the amount of 240,000 (two hundred forty thousand) rubles.
- Compensation for moral damage is paid to the Employee by
transfer of the amount specified in clause 1 of this Agreement to the settlement
Employee's account no later than the next working day after signing
present agreement.
- This Agreement is drawn up in two copies, containing
equal legal force, one for each Party.
EMPLOYER EMPLOYEE
Novikov / A.G. Novikov/ Goritsky / A.P. Goritsky/
I received a copy of the agreement. Goritsky Date
The conclusion of the above agreement does not deprive the employee of the right to go to court to seek compensation for moral damage caused from the employer.
The amount of claims (the amount of compensation collected) is determined by the employee independently. However, the final amount of compensation is determined by the court based on the specific circumstances of the case.
If the employer refuses to pay compensation, or if the employee disagrees with the amount of compensation, he may go to court.
When considering a case in court, the following nuances should be taken into account:
- The employee must prove that the employer caused him moral or physical suffering. It is not always necessary to confirm them with documents, because... a sufficient basis for compensation for moral damage is the fact of violation of the employee’s labor rights.
- If an employee receives an injury or other damage to health or illness suffered as a result of moral suffering, the court will also consider documents drawn up during the investigation of the accident or occupational disease, medical reports, etc. In addition, the employer’s guilt in the incident is determined.
- When determining the amount of compensation for moral damage, the court also takes into account the financial situation of the victim, the presence of disabled dependents, state of health, size and sources of income, etc.
Note: when resolving individual labor disputes, the employee must go to court no later than 3 months from the moment he learned or should have learned about the violation of his rights.
In case of labor disputes related to dismissal, you must go to court no later than 1 month from the date of delivery of the work record book or a copy of the dismissal order.
If there are good reasons for missing the deadline for filing a claim, it may be reinstated by the court. To do this, you must submit a corresponding application.
Labor legislation obliges the employer to provide the employee with safe working conditions (Part 1 of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If an employee receives an injury or injury from a source of increased danger (use of vehicles, machinery, high-voltage electrical energy, nuclear energy, explosives, potent poisons, etc.
, carrying out construction and other related activities, etc.), the employer is obliged to compensate him for moral damages, regardless of whether the employer is at fault.
Unless he proves that the harm was caused as a result of force majeure or the intent of the victim.
When determining the amount of compensation, the court also takes into account the actions of the victim himself in the accident. For example, if there was gross negligence on the part of the employee, the amount of compensation will be reduced.
Work injury
Each of us, one way or another, fears for our lives at work. Someone dislocates their jaw with the next yawn, someone strains their lower back, reaching out to the cooler, and someone even becomes a veteran of office warfare, injuring their fingers on the knife-sharp edges of paper. But not everyone hardened by office work knows that there are injuries for which they can demand compensation from the employer for moral damage caused to them. Of course, fingers pierced by a stapler do not fall into this category, but in other cases such a requirement will be completely legitimate.
So when can you claim compensation for moral damages in case of a work injury? What is generally considered a work injury? Is the employer presumed to be at fault when an employee is injured?
What is moral damage and in what cases is an employee entitled to compensation? How to establish the employer's guilt? What documents are needed for the court?
What is moral damage and in what cases is an employee entitled to compensation?
The concept of moral harm is enshrined in paragraph 2 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 20, 1994 No. 10, and moral harm is understood as moral or physical suffering caused by actions (inaction) encroaching on intangible benefits belonging by birth or by force of law (life, health and etc.), or violating his personal non-property rights or violating the property rights of a citizen.
In this case, as indicated below, moral harm, in particular, may consist of physical pain associated with causing damage or other damage to health.
It is necessary to understand: the right to life and health are rights guaranteed to everyone by the Constitution, and therefore every worker injured at work has the right to compensation for moral damage.
This is also indicated by the Labor Code, which enshrines in Article 22 the employer’s obligation to compensate for harm caused to an employee at work, as well as to pay compensation for moral damage in cases established by the Code.
How to establish the employer's guilt?
The culpability of the employer is one of the most pressing issues in this topic. As follows from the provisions of the law “On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases”, the inflictor of harm is obliged to compensate the victim for moral damage.
At the same time, the Labor Code, among other things, establishes that moral damage that was caused to an employee by unlawful actions or inaction of the employer is compensated in the amount established in the agreement between the parties, and in the absence of such an agreement or in the presence of a dispute, the amount is established by the court, while the amount of possible property damage will not play any role.
Thus, if the employer’s guilt is proven, the employee has the right to claim compensation for moral damage. Moreover, such guilt can be expressed in various forms.
Thus, in the case considered on October 27, 2016 by the Fokinsky City Court No. 2-678/2016, the employer’s fault was that he did not carry out a special assessment of working conditions on time, which directly prevented the employer from performing the main function - providing workers labor safety and conditions that meet labor protection requirements, that is, to create such working conditions under which harm to the life and health of the employee would be excluded. The plaintiff's claims for compensation for moral damage were satisfied, and the defendant was found guilty.
As can be seen from the provisions of paragraph 32 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court dated No. 1 of February 26, 2010, compensation for moral damage without the employer’s fault is possible only if the injury was caused by a source of increased danger. In all other cases, it is the employer’s fault that is the main condition allowing the employee to demand compensation for moral damage from him.
It is also possible to demand compensation for moral damage when the employee did not survive as a result of the work-related injury. Thus, in case No. 2-1529/2017, considered on August 23, 2017 by the Khabarovsk District Court, the plaintiff, acting in the interests of a minor - the daughter of a deceased employee - demanded compensation for moral damage.
The court sided with the plaintiff and, in addition to a one-time compensation for moral damages, ordered the defendant to pay a monthly fixed sum of money with the necessary indexation until the girl comes of age.
What documents are needed for the court?
To begin with, it should be discussed that the courts are unanimous on the issue of when moral damage is, in principle, present. Thus, when determining the amount of compensation for moral damage, the court, taking into account the requirements of reasonableness and fairness, should proceed from the degree of moral or physical suffering associated with the individual characteristics of the person who suffered harm.
The degree of guilt of the offender and other noteworthy circumstances of each case also influence. The amount of compensation for harm may be reduced if the occurrence or increase of harm was caused by the gross negligence of the victim himself. The guilt of the victim is established at a certain percentage.
Gross negligence of the victim cannot serve as a basis for refusal to compensate for the harm caused to his health; this is possible only if the victim intended, and simple negligence is not taken into account and, accordingly, does not affect the amount of compensation.
From here it becomes obvious that even if there is your fault, expressed in the form of negligence, this does not exclude the employer’s obligation to compensate for the moral suffering caused to you.
Industrial injuries are a force majeure event, which, unfortunately, often happens in the workplace. Remember - if this happens to you, in one hundred percent of cases you have the right to compensation for moral damage. The amount of compensation depends on the severity of the injury, as well as on many other factors.
According to labor law: compensation for moral damage caused to an employee
Moral damage according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is any moral and physical suffering that a person experiences due to the illegal actions (or inaction) of other persons (in particular the employer) encroaching on his intangible benefits:
- dignity;
- life;
- personal secret;
- business reputation.
The concept of moral harm caused to an employee by unlawful actions in the field of labor law twenty years ago was exotic; such cases were traditionally referred to the sphere of civil legal relations, considering, for example, illegal dismissal together with cases of compensation for harm under a contract.
Moral damage consists of the moral feelings of a person, for example, who is unable to continue his work activity due to illegal dismissal, to lead an active social life, due to the presence of information discrediting his reputation or injury received at work.
Moral damage in the field of labor relations can arise in the presence of circumstances, the range of which is specifically stipulated by law.
According to the rules set out in Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the moral suffering of an employee during his illegal dismissal must be compensated by the employer in cash in the amount provided for in the employment contract, regardless of compensation for material damage caused by the same dismissal.
If there is no such information in the contract or disputes arise in this regard, compensation for moral damages of a dismissed employee can only be appealed in court. It is important for a judge to determine the degree of moral suffering of a person.
To do this, the judge will take into account:
- the nature of the damage caused, both physically and morally;
- the circumstances under which the damage occurred;
- also the individual characteristics of the employee himself (for example, he is a person with a heart condition and his dismissal resulted in a month-long hospital stay (even after he was reinstated at work).
According to Art. 227 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an industrial accident is an incident as a result of which an employee was injured or injured while performing his work duties. Moreover, this injury resulted in disability, death, or temporary loss of ability to work.
The fact of an accident can be recognized by a court or a commission created specifically to investigate accidents at an enterprise (Article 229 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The commission recognizes the fact as having occurred due to the fault of the employee himself, for example, due to alcohol intoxication or use of work equipment for personal purposes.
In this case, the injury cannot be recognized as work-related, and the employer will have every right to leave the employee without compensation payments, including for moral damage.
Based on the documents, the employee will be paid temporary disability benefits and other payments from the Social Insurance Fund.
The amount of money for moral suffering is paid in addition to temporary disability benefits and does not replace it.
for occupational disease
An occupational disease is the result of short-term or systematic exposure to harmful production factors in the workplace.
According to Regulation No. 967 “On approval of the Regulations on the investigation and recording of occupational diseases” dated December 15, 2000, all occupational diseases are divided into two types: acute and chronic.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Amount of damage for initiating a criminal case: size, level
Just like damage caused as a result of an industrial injury, damage from an occupational disease is compensated by temporary disability benefits or a lump sum insurance payment paid on the basis of sick leave.
In the most tragic cases, family members of the employee have the right to receive compensation for death at work.
In accordance with Art. 1100 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, an employee’s right to compensation for mental damage due to an occupational disease at work occurs regardless of the employer’s fault, if the employee worked with a source of increased danger (for example, in a car).
The employer's liability for non-payment or untimely payment of wages to a subordinate is regulated by Articles 362, 419 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. A Art. 236 of the Labor Code establishes that the administration of the enterprise must pay interest on the unpaid amount of wages, calculated for each day of delay, not less than 1/300 of the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
How to justify the mental losses caused by delayed wages? What exactly ?
In this case, moral suffering can be expressed, for example:
- insomnia due to the fact that a person could not buy necessary things and products for his family;
- ruined vacation or weekend;
- a disrupted tour;
- experiences that resulted in documented deterioration in health, etc.
In accordance with Article 349 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, military personnel and police officers, in addition to the norms of federal laws regulating their activities (Federal Law of March 28, 1998 N 53-FZ “On Military Duty and Military Service”), are also subject to the norms of labor legislation .
Thus, this category of citizens can also file a claim for compensation for moral suffering caused to them as a result of:
- injuries;
- contusions;
- injuries;
- diseases acquired during service or within 24 months after dismissal.
In accordance with Article 131 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, a claim for compensation at work consists of several parts:
- introductory: name of the court, full name, address of the plaintiff and the price of the claim (moral damage and material damage);
- motivation: the plaintiff describes the essence of the case (harm to the employee caused by the employer) and lists his claims with references to the legislation;
- pleading: the plaintiff asks the court to satisfy his claims;
- At the end, an additional list of documents is attached to the claim.