Article on the topic: Divorce
A marriage registered in accordance with the procedure established by law is recognized as valid. But there are cases provided for by law when a marriage can be annulled. Divorce and annulment are different procedures with different consequences. Only a court can declare a marriage invalid. Apart from him, no government body will be able to make a decision on this issue. The procedure for declaring a marriage invalid occurs on the basis of an application from one of the spouses, his guardian or prosecutor.
The concept of limitation of actions
What is a statute of limitations in family law? The concept of limitation of actions established by the RF IC
is a requirement that is relevant for a number of branches of law. In the traditional sense, it is a legal term, a unique legal fact that has a number of characteristics unique to it.
Considering the concept of limitation of actions in family law as a legal fact, we can note the moment of its occurrence, change or termination.
From a practical point of view, the statute of limitations in family law is the period during which violated rights can be protected by government agencies, which means a person can apply to the justice authorities for protection of their rights through litigation.
The imperative nature of the definition of “limitation period in family law” speaks of a clearly established time frame, the expiration of which does not allow obtaining judicial protection of rights and, in fact, excludes the guilt of the act of the second party.
Statute of limitations in family law
Family relationships are ongoing. They cannot be precisely limited in time. At the same time, in family law there are legal processes that require precise determination of deadlines, including the limitation period. Such processes consist in the emergence, change and termination of those rights and obligations that are vested in an industry entity.
The procedure for applying the provisions on the limitation period in family law is determined by the provisions of Art. 9 RF IC. The specificity of family relations, which is associated with the existence of a large volume of personal non-property rights, does not allow the legislator to establish clearly defined terms for their protection. Thus, the limitation period in family law cannot be applied to legal relations arising upon divorce or determination of paternity. Personal non-property rights of subjects of family law are protected by the state beyond the statute of limitations.
The statute of limitations in family law can only be applied to those family relationships that are based on the existence of property rights, that is, to those legal relationships that can be subordinated to a single economic turnover.
Do you need help from a family law specialist?
Sign up for a consultation with the practice manager
+7
Application of statute of limitations in family relationships
As a general rule, the statute of limitations in family law is the period during which a person can protect his violated rights.
Family Code in Art. 9 clearly defines that the use of a statute of limitations in family legal relations is unacceptable. Exceptions to this rule are provided for by the code itself; the list of exceptions is exhaustive. The fact that it is impossible to apply the concept of “limitation period in family law” to family relationships suggests that the protection of rights by the state is carried out regardless of the time frame, the moment of their violation or the time when the person learned about such a violation. The reason for this is the predominant nature of personal non-property interests connecting the subjects of family law.
As an exception, the statute of limitations in family law is applicable to those claims that are of a property nature and are expressed in the form of its division, or the parties’ disagreement to conclude property transactions. In addition, the statute of limitations applies to those disputes that arise when considering cases of recognition of the invalidity of a marriage, the reason for which was the presence of a legal relationship with the other party, venereological diseases or HIV infection, which the latter party knew about before the marriage.
The application of the limitation period to family relations is carried out in accordance with the norms provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Conditions for the invalidity of marriage
The following conditions are grounds for declaring a marriage invalid:
- violation of the voluntariness of marriage and reaching marriageable age;
- concealing the presence of a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection;
- a marriage entered into without the intention of starting a family (fictitious marriage);
- marriage between persons, at least one of whom is already in another registered marriage;
- marriage between close relatives, adoptive parents and adopted children;
- marriage between persons, at least one of whom has been declared incompetent by a court due to a mental disorder.
One of the main conditions for marriage is the mutual voluntary consent of the man and woman entering into marriage and their reaching marriageable age. The age of marriage in the Russian Federation is set at 18 years.
Expert opinion
Kozlov Pavel Vyacheslavovich
Practicing lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in defense in court.
Marriage is a voluntary agreement between two equal people; coercion, threats, deception, and violence are unacceptable, otherwise the marriage may be declared invalid in a claim for the invalidity of a marriage entered into without the consent of the spouse.
Signs of a fictitious marriage include:
- lack of communication between spouses;
- lack of intimate relationships, moral support of the spouse;
- ignorance of obvious facts from the life of the spouse;
- lack of cohabitation or a short period of cohabitation without good reason;
- lack of common things, joint budget;
- the presence of goals other than creating a family for the spouse at the time of marriage (examples of such goals include avoiding military service, obtaining citizenship, obtaining a meeting with a prisoner, acquiring a euphonious surname).
It is not permitted to enter into a marriage between persons, at least one of whom is already in another registered marriage. Such a prohibition is based on the recognition of the principle of monogamy, which, in turn, is a reflection of the moral and religious views prevailing in our society.
Please note that this only refers to a registered marriage; actual marital relations (cohabitation) are not taken into account.
Marriages between close relatives are prohibited, by which we mean relatives in a direct ascending and descending line (parents and children, grandparents, grandchildren; full and half-siblings (brothers and sisters having a common father (half-blood) or mother (half-brothers). Half-brothers and sisters should be distinguished from half-siblings.
Step brothers and sisters are children of spouses who had children from their first marriage and entered into a new marriage. One of them is a parent for the children, and the other is a stepfather or stepmother.
This prohibition is due to both moral considerations and concern for the offspring, since as a result of such marriages, incest occurs and defective children are born.
Marriages between adoptive parents and adopted children are prohibited. This prohibition is based on the fact that although in this case there is no consanguinity, in its legal consequences adoption is generally equated to consanguinity. Therefore, allowing marriage between the adoptive parent and the adopted child would be contrary to the rules of ethics.
An obstacle to marriage is the incapacity of one of the persons entering into marriage (incompetent is a citizen who, due to a mental disorder, cannot understand the meaning of his actions or manage them). The ban is based on the fact that such a citizen cannot fully demonstrate conscious will when entering into marriage.
If one of the spouses has a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, provided that he knows about it and hid it from the other, the affected spouse has the right to demand that such a marriage be declared invalid. In addition, an unscrupulous spouse may be brought to criminal liability; the conclusion of such a marriage constitutes a criminal offense.
Limitation period in family law during divorce
Both marriage and its dissolution refer to actions that are the execution of personal non-property rights of the subject of family legal relations. The legislator did not in any way limit the parties wishing to dissolve the marriage to a time frame. They can use this right throughout their entire family life.
The fact of divorce and its timing are important for those subjects who have joint property and wish to divide it.
Provisions of Art. 38 of the RF IC determines the general statute of limitations applicable to claims for the division of property that is jointly owned. The date of divorce is considered the day when the court decision or the fact of termination of the marriage relationship in the registry office came into force.
For example, the countdown of the statute of limitations in family law regarding joint property that former spouses continue to use begins from the date when one of the parties committed actions that did not allow the other to use this property within the same limits.
Limitation period for division of property after divorce
Divorce is often accompanied by legal proceedings related to the division of property, determination of the amount of alimony payments, etc.
The limitation period in family law, which applies to an exclusive list of family legal relations, is determined by the norms of the Family and Civil Codes of the Russian Federation. Thus, the division of jointly acquired property of spouses can be carried out by the justice authorities within three years from the date. This period may, for example, be associated with the day when one of the parties created obstacles in the use of joint property by the other party. The statute of limitations for the division of property after divorce applies to any legal relationship that arises in the family on the basis of a property interest.
Personal non-property rights, as well as the collection of alimony payments for the maintenance of children, do not have a statute of limitations, because these rights are subject to state protection throughout the entire period of their existence. The right to alimony ends when the child reaches adulthood, which means that the statute of limitations in family law is limited only by this date.
Fictitious marriage
It is customary to call fictitious marriages that are registered without the intention of starting a family. Their goal is to take advantage of the benefits and rights that marriage provides, and the benefit does not have to be material. In practice, most often the benefit consists of obtaining the right to register at the spouse’s place of residence, the right to his living space, and the right to property after the death of one of the spouses. One of the above circumstances is sufficient to invalidate the marriage.
The difficulty in recognizing a fictitious marriage as invalid lies in the need to provide the court with evidence that the marriage was registered without the intention of starting a family. An experienced divorce and family law lawyer will help you collect evidence and present it competently in court. The court evaluates the duration of the marriage and the presence of children in it, the presence of a common household, witness testimony
Limitation period for division of marital property
Property acquired by spouses during marriage is recognized under family law as their joint property. The termination of marriage and family relations often leads to the need for legal division.
Legislators have determined that property that is common to former spouses can be divided by the court within three years. In cases where the former spouses continued to share property, the statute of limitations begins to expire from the date when one of the parties created obstacles in the use of joint property by the other party.
The statute of limitations for the division of marital property is enforced by the court when one or both parties make a statement about the need to apply it in resolving the dispute.
General provisions
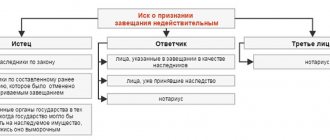
The main legal difference between the termination of a marital relationship through divorce proceedings and its recognition as invalid is the fact that the latter procedure does not give rise to mutual rights and obligations between the parties, but completely terminates them, which does not happen in a divorce. Family relationships can be declared invalid only in court. Reasons:
- fictitious nature of marriage relations. The most common phenomenon in practice, the concept of which is worth considering in more detail;
A marriage may be declared invalid if one of the parties concealed facts that could have a significant impact on the nature of the family relationship - the presence of elements of coercive, fraudulent, misleading actions in relation to both or one of the parties. If everything is more or less clear with coercion and deception, then with the concept of delusion it is rather ambiguous. Thus, this criterion includes situations where one of the parties did not know certain information, which it became aware of after registration of the relationship, and the other party did not notify about its existence or did not attach importance to it. This information must relate to the facts: that are present to the other party; which can have a significant impact on the nature of family relationships; in which the value of such marriages is questioned (inability to have children, serious medical pathologies, chronic alcoholism, drug addiction, criminal lifestyle). Inconsistency with the state of affairs in material, social, professional, national terms cannot be recognized as a delusion;
- husband and wife are close relatives to each other (full and half-siblings, children and their parents, grandchildren, grandparents). The purpose of the restriction is clear: social rejection of such actions, as well as the negative impact of incest on the health of future generations;
- The parties to the procedure are the adoptive parents and the adoptees. They are considered by law to be close blood relatives. It is also contrary to the nature and nature of adoption;
- the age limits for the possibility of entering into a marriage relationship have been violated (the established number of years has not been reached);
- having the status of an official marital relationship with a third party. Living within the framework of civil relations without their registration in the competent institutions is not taken into account. This provision enshrines and confirms the constitutional principle of monogamy in our country;
Concealment by one of the parties of the known fact of HIV infection or sexually transmitted disease - concealment at the time of the procedure by one of the parties of the known fact of HIV infection or venereal disease. If the party who has such a disease did not hide its presence and notified his future family partner about it, such conditions cannot become the basis for invalidating the official relationship. Concealment is the key basis for these circumstances; such action is subject to liability under criminal law. The presence of only two categories of diseases causes great controversy; many specialists and experts argue for the need to expand this list;
- status of incapacity caused by mental disorders of one of the parties.
The list of initiators of the procedure is strictly specified and limited by legal norms, depending on the following reasons and circumstances:
- if the issue is related to a minor: a person under the age of majority, authorized guardianship officers, parents of a minor, a prosecutor’s office employee;
- in case of violation of freedom of will when entering into a relationship: the victim or an employee of the prosecutor's office;
- in the presence of another official marriage or incapacity status: a bona fide party, a spouse in another marriage, a guardian of an incapacitated person, interested parties associated with other marital relations (children, relatives), an employee of the prosecutor's office or guardianship authorities;
- associated with serious diseases (HIV, sexually transmitted diseases): bona fide party.
A marriage declared invalid is valid for the entire duration of its validity, that is, from the moment of its registration, and not from the moment of recognition of invalidity.

A marriage declared invalid is valid for the entire duration of its validity.
The condition for the impossibility of recognizing official family relations as invalid is the fact of its termination. That is, a marriage can be recognized as such only if it is valid. The exception is if there is an established close degree of relationship or if one of the parties was in another official marriage.
Limitation period in family law when declaring a marriage invalid
Marriage relations relate to the personal non-property rights of the parties, to which, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the statute of limitations in family law is not applicable. This provision also applies to divorce. A marriage union can only be considered invalid after a court decision. Each of the grounds, except for concealing the fact of the presence of a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, established by paragraph 3 of Art. 15 of the RF IC, may cause the marriage to be declared invalid. Invalidity of marriage on the grounds specified in Art. 15 clause 3 of the RF IC, can be recognized only for 1 year, from the day when the second party was notified of such circumstances. The provisions of Art. are applicable to these legal relations. 181 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Procedure
The procedure for recognizing a marriage as invalid is established by the legislative and regulatory acts of the Russian Federation. The basis for starting consideration of a case on recognizing family relationships as invalid is receipt from the initiator of the claim, drawn up in the form of a written statement.
A statement of claim to declare a marriage invalid is filed together with the following official documents:
- a document indicating the existence of an officially formalized relationship;
- if there is a fact - documentation that is a birth certificate of children;
- in case of suspicion of fictitiousness - with papers confirming this fact (financial, banking documents, certificates from medical institutions, correspondence, written evidence of third parties).

. There are three options where a statement of claim for the invalidation of a marriage must be submitted with the appropriate package of documentation, depending on the specific circumstances:
- at the place of residence of the defendant;
- at the place of residence of the plaintiff, in a situation where a minor child lives with him or his health condition does not allow him to submit an application elsewhere;
- if the defendant’s place of residence is unknown - at his last known place of residence or at the place where he has property and property.
There are cases when an initially fictitious marriage develops into a serious relationship with the creation of a full-fledged family. Or an initially incapacitated person due to some illness, as a result of an amendment, receives full legal capacity. In such situations, legal norms cancel the invalidity of marriage.
The court makes a decision on the case based on the entire complex of available facts and evidence presented. After the verdict is rendered, if the claim is satisfied and the marriage is declared invalid, the necessary information is sent to the authorized registration authority, where appropriate adjustments are made to the documents and acts.

The court makes a decision on the case based on the entire complex of available facts
Limitation period in family law when drawing up a marriage contract
A prenuptial agreement is one of the main forms of regulating property relations that are established between the subjects of a marriage.
Challenging its conditions is provided for in Art. 44 of the IC, on the basis of which it can be declared invalid either in whole or in part. The most important circumstance for recognizing its invalidity is the placement of a party to the agreement in a too unfavorable position or the establishment of conditions in it that are clearly contrary to legal norms.
The fact that the agreement in question is a transaction gives grounds for applying to legal relations the statute of limitations in family law of three years, which is established by paragraph 3 of Art. 166 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. This is one of the opinions, in particular, with which the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation currently agrees. There is an opinion that the statute of limitations does not apply here.
The party that intends to appeal the consequences of the execution of the agreement must present its demands within one year, as defined in paragraph 1 of Art. 179 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Author of the article
Consequences of invalid marriage
A marriage can be declared invalid by a court only at the request of an interested party. The provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on shared ownership apply to property acquired by persons whose marriage is declared invalid.
The marriage contract concluded by the spouses is declared invalid. The recognition of a marriage as invalid does not affect the rights of children born in such a marriage or within three hundred days from the date of recognition of the marriage as invalid.
Recognition of a marriage as invalid entails annulment of certain other rights of the spouses without an additional decision being made by the court:
- the right to bear the surname adopted during state registration of marriage;
- the right to use the living space of the other spouse when moving into it after marriage;
- rights of inheritance by law after the death of a spouse;
- rights to a survivor's pension.
There are exceptions to these special rules, the purpose of which is to protect the rights of the spouse whose rights were violated during the conclusion of an invalid marriage (the bona fide spouse). The court has the right to recognize the right of a conscientious spouse to receive maintenance from the other spouse; in relation to the division of property acquired jointly, the court has the right to apply the provisions of the Family Code of the Russian Federation regulating the legal regime of property of spouses.
A conscientious spouse has the right to demand compensation for material and moral damage caused to him according to the rules provided for by civil law, by filing a claim for compensation for damage after the marriage is declared invalid. In addition, a conscientious spouse has the right, when a marriage is declared invalid, to retain the surname chosen by him during state registration of the marriage.
The legal significance of the institution of invalidity of marriage in family law is that it makes it possible to terminate the legal relationship between spouses that arose during the state registration of marriage from the moment of marriage, to return the spouses to their original legal status.
Did not find an answer to your question? Ask it to a lawyer by phone!
The law (Article 44 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation) establishes general and special grounds for declaring a marriage contract invalid.
According to paragraph 1 of Article 44 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, a marriage contract may be declared invalid in whole or in part by the court on the grounds provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation for the invalidity of transactions.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 44 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the court may declare a marriage contract invalid in whole or in part at the request of one of the spouses if the terms of the contract place this spouse in an extremely unfavorable position.
That is, this norm establishes special family law grounds for invalidating a marriage contract.
If the spouse challenges the validity of the marriage contract or its terms on the grounds provided for in paragraph 2 of Art.
44 of the RF IC, the statute of limitations should be calculated from the moment when this spouse learned or should have learned that as a result of the implementation of the terms of the marriage contract, he found himself in an extremely unfavorable property situation. This may be recognized as the moment of division of property carried out under the terms of the marriage contract, as a result of which one spouse is completely deprived of the right of ownership of property acquired by the spouses during the marriage.
Article 2 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation determines that family legislation establishes the conditions and procedure for marriage, termination of marriage and recognition of its invalidity, regulates non-property and property relations between family members: spouses, parents and children (adoptive parents and adopted children), and in cases within the limits provided for by family law, between other relatives and other persons, and also determines the forms and procedure for placing children left without parental care into the family.
By virtue of Article 4 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, civil legislation is applied to the property and personal non-property relations between family members that are not regulated by family legislation, as mentioned in Article 2 of this Code.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 9 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, claims arising from family relationships are not subject to limitation, except in cases where the period for protecting the violated right is established by the said Code.
The Family Code of the Russian Federation does not establish a statute of limitations for claims to challenge a marriage contract.
By its legal nature, a marriage contract is a type of bilateral transaction, but it has its own specifics, determined by the basic principles (principles) of family law.
Since the claim of the spouse under paragraph 2 of Article 44 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation for the recognition of a marriage contract as invalid by this Code is not established by the statute of limitations, then to such a claim of the spouse, based on the provisions of Article 4 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, for the purposes of stability and legal certainty of civil transactions, a period of limitation is applied the limitation period provided for in Article 181 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, for requirements to recognize a transaction as invalid.
By virtue of Article 181 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the limitation period for claims to apply the consequences of the invalidity of a void transaction and to recognize such a transaction as invalid (clause 3 of Article 166) is three years. The limitation period for these claims begins from the day when the execution of a void transaction began, and in the event of a claim being brought by a person who is not a party to the transaction, from the day when this person learned or should have known about the beginning of its execution.
In this case, the limitation period for a person who is not a party to the transaction, in any case, cannot exceed ten years from the date of commencement of execution of the transaction.
The limitation period for a claim to declare a voidable transaction invalid and to apply the consequences of its invalidity is one year. The limitation period for the said claim begins from the day the violence or threat under the influence of which the transaction was concluded ceases (clause 1 of Article 179), or from the day when the plaintiff learned or should have learned about other circumstances that are the basis for declaring the transaction invalid.
In accordance with the second paragraph of paragraph 15 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 5, 1998 No. 15 “On the application of legislation by courts when considering cases of divorce,” if the marriage contract changes the statutory regime of joint ownership, then the court, when resolving a dispute about the division of property, spouses must be guided by the terms of such an agreement.
It should be borne in mind that, by virtue of paragraph 3 of Article 42 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the terms of the marriage contract on the regime of joint property, which place one of the spouses in an extremely unfavorable position (for example, one of the spouses is completely deprived of the right of ownership of property acquired by the spouses during the marriage) may be declared invalid by the court at the request of this spouse.
From the foregoing it follows that when a spouse challenges the validity of a marriage contract or its terms on the grounds provided for in paragraph 2 of Article 44 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, the statute of limitations should be calculated from the moment when this spouse learned or should have learned that as a result of the implementation According to the terms of the marriage contract, he found himself in an extremely unfavorable property situation.
This moment may coincide with the division of property carried out under the terms of a marriage contract, as a result of which a situation has arisen indicating that one spouse is completely deprived of the right of ownership of property acquired by the spouses during the marriage.
In family law, there are legal processes that require precise determination of the statute of limitations.