Light work for pregnant women: Labor Code
For pregnant workers, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes certain guarantees regarding their work activities. Depending on the specific working conditions, such employees need to reduce production standards, transfer them to another job, or release them from work completely (Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, pregnant workers are prohibited (Articles 259, 298 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- send on business trips;
- be required to work overtime, on weekends and non-working holidays, as well as at night.
assign to rotational work;
Reduced production standards
If a pregnant woman works at a job for which production standards are established, then these standards should be reduced for her on the basis of a medical report and an application from her. To understand how much to reduce the standards, the employer needs to focus on the “Hygienic recommendations for the rational employment of pregnant women”, approved by the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision and the Ministry of Health back in 1993. They indicate the amount of physical activity acceptable for women during pregnancy (weight of loads that can be lifted , length of path covered per shift, etc.). In this case, the employee’s work schedule may not change, and her work will need to be paid based on average earnings (despite the decrease in production standards).
At the same time, even if the employee does not have a medical report, from which it would follow that she needs to reduce the intensity of work, she has the right to contact her employer with an application to switch to part-time work. And the employer will have to meet her halfway (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Required package of documents
To transfer a worker to an easier type of work, you need to prepare the following package of documents:
- Medical certificate. The worker is obliged to provide it to the employer, and it is the basis for his transfer to an easier job due to pregnancy, guided by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (the conclusion of a gynecologist with the prescribed period of pregnancy).
- A written request from a worker in which he confirms his desire to change his working conditions.
- An additional agreement to the employment contract, the body of which specifies the updated conditions for fulfilling statutory obligations and the period of such transition.
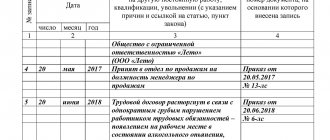
- An order in a standardized form on the transition of a worker to another activity.
- Making an entry in the work book and personal card.
Transfer to another job
An employee working in harmful or dangerous work, in the event of pregnancy, must be transferred to another job, the performance of which does not involve exposure to adverse production factors (Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The transfer must also be completed for a pregnant employee whose current job is not suitable due to personal medical conditions. In this case, a certificate from a medical institution must indicate what working conditions are suitable for her, and the employee must write an application asking for another job.
In such a situation, the employer should familiarize the employee with the vacancies he has available that are suitable for a pregnant woman. And if one of the vacancies suits her, arrange the transfer by concluding an additional agreement to the employment contract. If a pregnant woman’s salary in a new position is higher than her salary in her previous position, then she will have to be paid a new salary. Otherwise, the worker will have to be paid based on her average earnings.
If not a single vacancy suits the employee, then the employer will have to release her from work, retaining both her position and average earnings. It is impossible to dismiss a pregnant employee at the initiative of the employer (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Exceptions are provided for cases of liquidation of the employing organization, as well as the expiration of the employment contract concluded with it.
What else?
It is important that a pregnant woman cannot be fired at the request of the employer, even if she did not inform the employer about her situation when she was hired. If an employee was hired for a specific period, but the employment contract has expired, she only needs to fill out an application directly for the extension of this agreement and, of course, attach a medical report that confirms the presence of pregnancy. Thus, the employer has the right to dismiss an employee only after the end of the period within a week when the employment contract is no longer relevant in relation to her.
Interestingly, there is only one case in which the dismissal of a pregnant woman may be legal. Thus, an employee can be dismissed if the conclusion of an employment contract with her was relevant only for the period of performance of the duties of an employee who was temporarily absent from the workplace. However, in such circumstances, the employer undertakes to offer the pregnant woman all vacancies that are available and suitable for her according to her position. In the absence of such, the dismissal of the employee is permissible.
Light work for pregnant women according to the Labor Code
My friend was working as a cook in a restaurant when she found out she was expecting a child. You understand that work of this kind requires regular standing at the stove, lifting heavy objects, and performing some work that is not suitable for pregnant women. If at the beginning she somehow managed, then gradually the situation got out of control.
This is interesting: Personal medical record and its design
A friend applied to management for an easier job. In response to her appeal, the boss offered to write a statement of her own free will, citing that he had no other vacancies, and the restaurant could not close because of her position.
As a result, she quit, and only then realized that she had done so in vain, because her rights were protected by law.
In today’s article we will talk about how the labor code regulates the problem of light work for pregnant women in 2021 and what an employee should do if she cannot fulfill her duties and there are no available vacancies with acceptable employment conditions.
Is it possible not to transfer to light work?
By law, the director must create comfortable working conditions for pregnant women in accordance with the labor code. Knowing this, every employee is confident that by submitting a certificate from the housing complex, she will work without stress in favorable conditions for as long as she wishes, or will temporarily stop working, receiving a full-size salary while sitting at home. By making such a decision, the company's management is obliged to place a new employee in her place, enter into a fixed-term contract with him, and actually pay for the same functions twice, which is extremely unprofitable for the enterprise.
Therefore, if the director doubts the advisability of transferring to light work, and has good reasons for this, he has the right to check the conditions and mode of work before agreeing to this step. The reason for refusal may be the absence of specific circumstances, namely:
- no need to lift heavy loads;
- is not involved in monotonous conveyor-type work;
- the duties are so simple that they do not cause physical strain or stress;
- contact with harmful and toxic substances is not expected.
Computer work is considered a sufficiently compelling reason for refusal to provide the most lightweight functions. Many subordinates who are expecting a child present as an argument the assertion that spending a long time in front of a monitor is a dangerous factor. However, the degree of harm can be determined by the results of medical examinations. In addition, modern technology is recognized as secure, since liquid crystal displays are used everywhere. This conclusion is confirmed by Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 15-1/OOG-3481 dated September 27, 2016. It states that all PCs that have compliance certificates are considered safe. To avoid conflict, the employer has the right to propose drawing up a new work contract for working remotely. Registration will take some time, but the woman will be able to be in any place convenient for her, even at home.
What rules apply in such circumstances?
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, pregnancy is not a disease, but a natural state of a woman, therefore, the expectant mother will not be able to receive complete liberation. On the other hand, bearing a child is a responsible undertaking that requires attentiveness and care for one’s own condition on the part of the young woman.
It is difficult to determine the moment when a pregnant employee begins to think about vacation, since each woman has her own physiological mechanism. Some suffer from toxicosis in the early stages, while others feel unwell in the middle of pregnancy.
The most unfavorable period for employment is the third trimester, as it becomes difficult for a woman to move and perform her duties. In addition, all the employee’s thoughts are focused on the birth of the baby, and on work.
In addition to the above points, there is another important factor, the influence of which can be completely avoided. According to the law, if working conditions at an enterprise are difficult or difficult, the employee has the right to switch to lighter work.
What employment conditions are considered harmful?
The rights of pregnant women at work are clearly defined in labor standards. Whether the conditions of employment are harmful in a particular situation is determined by the outcome of these provisions and standards. Even simple and habitual activities can have a negative impact on the condition of mother and baby.
It should be said about actions:
- lifting weights from the floor, as well as above shoulder level;
- during monotonous work, when a woman takes a working position. During pregnancy, you should not focus on the abdomen and chest, and also often squat or kneel;
- conducting activities in the presence of radiation or electromagnetic radiation, constant vibration or in a noisy room;
- contact with toxic compounds;
- constant tension on the muscles of the abdomen and legs;
- work that is accompanied by serious mental stress.
The group of hazardous jobs includes duties that require constant sitting at a desk and computer. To avoid negative effects on the fetus, women turn to the management of the enterprise to provide easier employment conditions.
“Easy work” according to labor standards
The rights and interests of such citizens are protected at different levels. The most detail on this topic is written in Art. 93 and Art. 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Since not all employers treat such workers with understanding, but, on the contrary, force the woman to submit a resignation letter, expectant mothers should read the provisions of these articles in advance and be guided by them after presenting demands at the place of work.
According to paragraphs of Art. 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, female workers have the right to count on the following preferences regarding the conditions of their employment:
- reduction in output or service volume;
- moving to another position where there is no negative influence of external factors;
- guarantee of average earnings, regardless of employment conditions.
Article 93 states that an employee can work according to the main schedule or according to another schedule. Upon request, the employer must provide the employee with the opportunity to perform her duties within the framework of an incomplete week and days. In this case, the payment is retained. It is all the described points that determine the meaning of “easy work” for pregnant women.
In addition to the Labor Code, all legal relations arising between a citizen and an employer are regulated by a special document - SanPiN. We are talking about a register of sanitary standards and rules that quite clearly define the conditions of employment of citizens at the enterprise and how harmful they can be for the expectant mother.
All of the above points are decisive for the organization of work of such workers. For violation of standards and general regulations, the company will face significant penalties.
Rights and obligations
As it turned out, the main responsibility of the employer regarding the issue under consideration is the transfer of pregnant women to another job, subject to their provision of appropriate medical indications. Then, when the employer is not able to immediately provide a pregnant woman with favorable working conditions, and he needs a certain period of time to resolve this situation, the employee, one way or another, should be released from work for this time. In this case, the employer undertakes to pay for absolutely all days of her absence.
In addition, the relevant production standards assume that a pregnant woman is entitled to full leave, subject to payment on an annual basis. It is interesting to add that here it does not matter at all how long a woman has worked in a particular company. Thus, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with such leave directly upon her application, or before or after maternity leave.
Considering light work for pregnant women, the Labor Code assumes that the employer is obliged to ensure compliance with sanitation standards in the workplace of a pregnant woman. In addition, the law guarantees its retention for an employee in a position. Why? The fact is that the employer is not given the right to terminate the employment relationship with her on his own initiative. If the period of the employment contract ends, then directly at the request of the employee, the employer undertakes to extend this agreement.

Light Labor Law for Pregnant Women

Legislation protects pregnant women at work. They, like all other citizens, have the right to work, which cannot be limited due to pregnancy. However, pregnant women are entitled to light work, and in some legal cases the employer has the right to restrict a woman's access to work (if it may be dangerous to her health). In other cases, a woman herself has the right to decide whether to use benefits at work or not. Let's find out what rights pregnant women have at work.
Translation processing
When preparing a translation, it is necessary to take into account some points established by law that determine the period of a certificate for light work:
- While managers decide on the issue of transferring workers to light work due to a medical certificate, their average earnings are retained. In addition, a person may not do work to the extent that he did before if his health condition does not allow him to do so.
- Pregnant women must be transferred before the end of their pregnancy. The average earnings she received in her previous position are retained for the entire period.
- If it is necessary to transfer due to an injury at work or the presence of an illness considered to be occupational, the employee’s average earnings are retained until his recovery or loss of professional capacity is determined.
- If an employee needs to transfer to light work for a period of up to 4 months, and he does not agree with the options offered to him, or the employer cannot offer him the appropriate options, then he terminates the employment agreement. In this case, the employee is given a benefit equal to his average salary for two weeks.
- If an employee needs to transfer to light work for more than 4 months, and the person does not agree with the options offered to him, or the employer is unable to offer opportunities for transfer, then the agreement is terminated.
REFERENCE! In this case, the employee receives a benefit equal to his average earnings for two weeks.
- The employee returns to his old workplace after the transfer period specified in the additional agreement to the contract.
- If the period specified in the additional agreement expires, the period specified in the additional agreement becomes invalid, and the employee continues to work in a new place.
Rights of pregnant women at work
So, what can a pregnant employee demand:
- According to the application, the woman must be provided with light work. To do this, she needs to attach a medical report to the request. It can be obtained at a antenatal clinic or clinic. The conclusion usually lists all the harmful working conditions from which the employee must be protected. However, her earnings should remain the same. If a worker is not immediately allowed to do light work due to the employer’s actions, she has the right not to go to work under normal conditions until she starts light work, while still receiving average earnings for the days missed. The right to this is regulated by Articles 224 and 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- An employee has the right to work part-time or a week. In this case, wages are calculated for hours actually worked. (Article 93 of the Labor Code).
- Working at night and during the day is prohibited. Even overtime delays of a couple of hours are not acceptable. (Articles 96, 99, 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- You cannot involve her in work on weekends and holidays (Article 259 of the Labor Code).
- You cannot send her on business trips (Article 259 of the Labor Code).
- She is prohibited from working on a rotational basis (Article 299 of the Labor Code).
- Early leave. Typically, leave is granted annually, but to receive it you must work for at least six months. The rule does not apply to pregnant women; you can go on vacation at any time. Also, you can arrange it immediately before going on maternity leave, then you can extend the time you stay at home before giving birth and better prepare for it.
- An employee cannot be transferred to another position without her consent.
- A woman has the right to regularly visit doctors and examinations, for this she must be freely given time off from work. But the Labor Code does not regulate this issue in detail. It does not stipulate what specific documents a woman must bring, or how long or how often she can attend medical examinations. These issues are regulated by the labor inspectorate. In order to exercise this right, you must notify the employer in writing in advance about the date of the leave, and then provide supporting documents from a medical institution.
- Additional breaks during the working day.
This is interesting: Where to get a compulsory medical insurance policy
General working conditions
It is important to note that if a pregnant woman performs piecework work, production standards are reduced by forty percent. It is important to add that in such circumstances, the payment for light work due to the special position of an employee of a particular company is not reduced.
By the way, if a representative of the fair sex works at an agricultural enterprise, then she, one way or another, should be relieved of duties in livestock and crop production. Moreover, the above rule begins to apply immediately from the moment of medical confirmation of pregnancy.
It is interesting to know that office working conditions presuppose that a woman in a position has the right not to work with computer equipment. If it is impossible to ensure such a condition, then it is necessary to reduce working time to three hours a day. By the way, for pregnant employees of self-respecting companies, as a rule, a corrugated footrest is provided, as well as a chair that fully meets certain parameters. Among them are a rotating mechanism, the presence of a headrest, armrests, and a high backrest, which must be adjustable in terms of height.

Maternity leave and sick leave
A woman is entitled to leave, which gives her the opportunity to calmly prepare for childbirth and spend time in the maternity hospital - at 30 weeks of pregnancy under normal conditions and at 28 weeks with a multiple pregnancy . To receive it, you need to apply for sick leave at the antenatal clinic. The duration of this sick leave is regulated by Art. 255 TK and can range from 70 to 194 days, depending on the condition of the woman and the number of children. During this period, the woman receives 100 percent income from work (the same salary as if she continued to work - the average daily income is multiplied by the number of days).
The father of an unborn child also has such a benefit - he can receive his annual paid leave precisely while his wife is on leave under the BiR. To do this, he must write a statement. He also has the right to unpaid leave for family reasons, which will be 14 days (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
For this reason, it is completely unprofitable for many well-paid employees to be on maternity leave . The solution may be a nanny or the help of relatives - the law does not limit the right of any close relative to go on maternity leave instead of a working mother. This could be dad, grandpa or grandma (but only one relative). For example, this is beneficial if a relative’s salary is much lower. To register, the relative must provide an application and a certificate stating that the mother did not formalize such a right.