Upon concluding an employment contract, the employee has the right to vacation. Vacation has its own questions regarding the procedure for granting vacation, liability for failure to provide vacation and compensation if vacation is not used. You will receive answers to these questions from our lawyer in this material.
ATTENTION : our labor lawyer will not only explain how to win a labor dispute regarding an employee’s leave, but will also take part in it. Call now!
What and when is leave required according to the labor code?
Chapter 19 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to vacations. According to the provisions of labor legislation, leave may be the following:
- annual basic leave , which is paid by the employer, as a rule, it is 28 days. This leave is provided in accordance with the vacation schedule, in some cases it may be provided not according to the schedule. The initial right to such leave arises after 6 months of work
- Certain categories of workers are provided with annual additional leaves , which are paid. The corresponding leave can be granted together with the main leave or divided into parts with the main leave. Such leave is also indicated in the vacation schedule
- , leave without pay may be granted . In some cases, in order to provide appropriate leave, in addition to the employee’s application, the employer’s consent is required
- maternity leave . Such leave is granted to pregnant women, usually for 140 days, based on an application and provided sick leave. At the same time, a woman can go on vacation later, i.e. it is not necessary that she will take all 140 days
- Holiday to care for the child . After maternity leave, a woman, upon her request, is granted leave to care for a child up to 3 years old. A woman can leave her vacation until her child is 3 years old.
- study leave . As a general rule, if an employee works and studies, the employer is obliged to provide him with paid study leave based on the application and the provided certificate of summons from the educational institution
liability for failure to provide leave to an employee
We draw up a schedule annually. There is an employee who refuses to go to work for two years in a row. In accordance with the Labor Code, “Failure to provide annual payment for two years in a row is prohibited.”
(Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 124. Extension or transfer of annual paid). and for any violation of labor legislation, the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses establishes administrative liability.
What penalties can be applied to an organization for failure to provide vacations to employees?
Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges the employer to comply with laws and other regulatory legal acts, local regulations, the terms of the collective agreement, agreements and employment contracts.
According to Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, failure to provide annual payment for two years in a row is prohibited. In addition, it is prohibited to refuse to provide annual paid leave to employees under the age of eighteen and to employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions.
What penalties and fines, according to tax and labor legislation, does an organization face if it spends vacations at its own expense? Doesn’t he take annual paid vacations? And it doesn’t accrue vacation pay? What does it violate in this case and what consequences will it have for the organization?
What penalties and fines, according to tax and labor legislation, does an organization face if it spends vacations at its own expense?
Doesn’t he do annual paid ones? And it doesn’t accrue vacation pay? What does it violate in this case and what consequences will it have for the organization?
In this situation, the organization violates labor laws.
For such violations, the legislation provides for a fine of 30,000 rubles for organizations.
Vacation not taken
Answer: According to Art. 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee must be paid annually. In accordance with Art.
123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the priority for granting paid vacations is determined annually in accordance with the vacation schedule approved by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization no later than two weeks before the start of the calendar year.
Failure to provide leave
Hello, Sergey Borisovich! Upon dismissal, the employee has the right upon dismissal or monetary compensation for unused (Article 127 of the Labor Code).
Upon dismissal, the employee is paid monetary compensation for all unused wages.
Upon written request from the employee, unused vacations may be granted to him with subsequent dismissal (except for cases of dismissal for guilty actions).
Responsibility for failure to provide annual leave in Ukraine
Failure to provide employees with leave is a gross violation of labor laws. The Ministry of Labor, in a letter dated June 17, 2011 No. 190/13/116-11, recalled that statutes of limitations do not apply to the employee’s right.
Therefore, if an employee was not provided with annual leave (main and additional), as well as leave for employees with children, for, say, 4 years, then upon dismissal the employer must pay compensation for all days unused for 4 years.
Is it possible to change the vacation schedule?
Changes may be made to the vacation schedule in individual cases, since changes in personnel composition are not excluded during the year; some circumstances may also change for employees due to which they will not be able to go on vacation as scheduled, etc.
When are changes to the schedule required?
- If, with the consent of the employee, his vacation is postponed to another time
- If an employee is recalled from vacation
- When replacing part of the vacation with monetary compensation
When new employees are hired after the schedule is approved, changes to the schedule may or may not be made.
In general, if any changes occur in vacations, it is better to include them in the vacation schedule. Another question is that not all employers even draw up schedules, since they do not conduct personnel records as such or draw up schedules formally.
USEFUL : any labor disputes are best resolved after consultation with our labor lawyer in Yekaterinburg
Failure to provide leave to an employee
Answer to the question:
Labor legislation prohibits failure to provide annual paid leave for two years in a row (Part 4 of Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, for failure to provide leave, regardless of the reasons, the employer may be held administratively liable on the basis of clause 1 of Article 5.27 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, we recommend providing the employee with accrued vacation time.
Please note that if the duration of an employee’s vacation does not exceed 28 calendar days, the employer does not have the right to replace it with monetary compensation.
Compensation can be paid (1) only for part of the vacation exceeding 28 calendar days per working year; (2) only at the request of the employee; (3) if there is no prohibition on replacing vacation with compensation (More on this: In what cases can vacation be replaced with monetary compensation).
In practice, the following methods are used to correct this situation.
1. The employment contract with the employee is terminated and upon dismissal he is paid compensation for all unused vacations. The next day, a new employment contract is concluded with the employee. Of course, this happens in agreement with the employee.
2. The employee is granted short-term vacations including days off, for example, from Friday to Monday inclusive. In such a situation, the employee will eventually use all accumulated vacation time.
In this case, not so much working time will be used, and the employee will receive vacation pay.
Note that taking vacation only on weekends also occurs, but the legality of this method can be argued.
Note:
The vacation schedule is mandatory for both the employee and the employer; failure to comply with the employer’s order to provide vacation can be regarded as a violation of labor discipline on the part of the employee and the employee may be held liable.
If an employee goes to work without authorization during the period of granted leave, do not pay for the specified days (see Is it necessary to compensate for work on a weekend or holiday if the employee went to work on his own initiative).
When issuing an order to provide scheduled leave, you can instruct the security service not to allow the employee into the employer’s building during the period of his leave.
This will also eliminate disputes regarding payment for days worked without permission during the vacation period.
Details in the materials of the Personnel System:
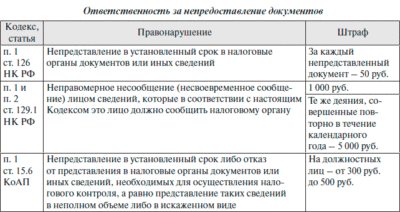
Situation: What liability is provided for failure to provide leave to employees
Administrative liability may be applied for failure to provide leave:
- a fine of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. – for the organization;
- a fine of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles. – for officials of the organization (for example, a manager).
How to challenge a vacation schedule?
An employee may be put on vacation in the vacation schedule when he does not want to go on vacation or cannot due to certain circumstances, for example, because he wants to go on vacation with his spouse or he has the right to choose when it is convenient for him to go on vacation, but he is not deprived of rights.
You can challenge the vacation schedule to the labor dispute commission or to the court.
The employee must file a claim in court, formulating his demands, for example, to recognize the vacation schedule as illegal, properly justifying his position.
The court will consider the case in the manner of claim proceedings with hearing both sides, examining evidence in the case and making a decision on the merits of the dispute. If the court comes to the conclusion that the schedule was drawn up in violation, it will accordingly recognize it as illegal in part, since the employee can only apply for the protection of his rights and not agree with the vacation schedule insofar as it concerns his rights.
USEFUL : our lawyer will help you draw up a statement of claim for the protection of labor rights: professionally, profitably and on time
Complaint regarding employee leave issues
If an employee does not agree with any of the employer’s decisions regarding his leave, he has the right to write a complaint on these issues to the labor dispute commission, the labor inspectorate, or the prosecutor’s office.
When preparing a complaint, the applicant must indicate how his rights are violated by the employer and how they are violated.
A complaint may be investigated and a decision may be made based on the results of the inspection.
If it is established that the employer has violated labor legislation in matters of providing leave to an employee, the employer will be held administratively liable.
Employer's liability for failure to provide leave
Every employer may be held liable for failure to provide leave if the employee's rights have been violated. Such situations include:
- Refusal of the administration of a company or enterprise to follow the established schedule.
- The employee has not taken vacation for 2 years in a row.
- Refusal to grant leave to Chernobyl victims, minors, pregnant women and other categories of citizens.
- Lack of vacation for persons working in harmful and dangerous conditions.
For such violations, the employer is held administratively liable.
Penalty for failure to provide vacation as scheduled
Failure to provide leave as scheduled is a violation of labor legislation, for which administrative liability is provided under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
When committing the corresponding offense for the first time, the person will be held accountable under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation with the imposition of punishment in the form of a warning or a fine in the following amounts:
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs – from 1,000 rubles to 5,000 rubles
- for legal entities – from 30,000 rubles to 50,000 rubles
- For committing a repeated offense, the fines under Part 2 will be:
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs – from 10,000 rubles to 20,000 rubles
- for legal entities – from 50,000 rubles. up to 70,000 rubles
To avoid a fine for failure to provide vacation as scheduled, it should be rescheduled by agreeing with the employee and by making changes to the vacation schedule. Under certain conditions, vacation may be transferred to another year. At the same time, we should not forget that it is impossible not to provide an employee with leave for more than 2 years in a row and for certain categories of employees.
You can appeal the fine in court. To do this, it is necessary to prepare a complaint against the decision of the labor inspectorate on bringing to administrative responsibility and submit it to the court. Next, take part in the consideration of the complaint, voicing its arguments and wait for the court’s decision.
The grounds for appeal can be very different, including the expiration of the statute of limitations for bringing to justice, the absence of an offense, the insignificance of the committed act.
You can, of course, try to reduce the fine, however, it is unlikely that the labor inspectorate or court will impose a fine lower than that provided for by the sanctions of this article, since the procedure for imposing a fine less than the minimum is regulated by Part 2.2., 3.2. Art. 4.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. According to the provisions of this article, a fine below the minimum can be imposed on citizens if the minimum fine for citizens is at least 10 thousand rubles, for officials - at least 50 thousand rubles, for legal entities - at least 100 thousand rubles. Thus, only citizens have a chance to reduce the fine if they are brought to justice under Part 2 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Penalty table
How will they be punished for failure to provide a worker with vacation rights for more than two years in a row, what are the consequences of not having a vacation schedule or not paying vacation pay? The amount of the sanction is specified in Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which provides for punishment for any violation of labor legislation.
| Nature of the violation | Responsibility measures |
| Failure to provide leave | Legal entity: 30,000-50,000 rubles, for a repeat - 50,000-70,000 rubles. Official: 1000-5000 rubles, for repeated - 10,000-20,000 rubles, possible disqualification for officials for a period of 1 to 3 years. |
| Responsibility of the employer for the lack of a vacation schedule | The first time a warning is possible. The fines are the same as above. A micro-enterprise has the right not to have a schedule (the order of rest is established by agreements). |
| Failure to adhere to schedule | The same fines + compensation for moral damage (by agreement with the employee). |
| Non-payment of holiday pay | Administrative fines:
Criminal punishment for a manager: up to 120,000 rubles. - for partial non-payment; up to 500,000 rub. - for complete non-payment. |
As you can see, the amount of the fine for the lack of a vacation schedule is established by the Code of Administrative Offenses the same as for other violations relating to the rights of employees. The exception is non-payment of vacation pay: here the penalties are noticeably higher.










