The concept and meaning of an employment contract
Before starting any activity, the parties to the employment contract - the employer and the employee - must discuss all working conditions and outline mutual obligations. To do this, they need to enter into an agreement that will reflect all the nuances of their labor relations. This agreement is an employment contract. A more formal concept of an employment contract is reflected in Art. 56 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In order for an agreement between an employer and an employee to have legal force, it must be recorded on paper, where all the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties are indicated. An oral agreement has no legal significance. It follows from this that the concept and meaning of an employment contract is to consolidate the legal positions of the employee and the employer in relation to each other.
Nature of relationships and working conditions
Types of employment contracts according to the nature of the labor relationship are divided into:
- work at the main place where the employee is employed for a long period;
- part-time work, including internal work at the same enterprise in a different position or external work at another enterprise in a similar position;
- temporary or seasonal work, which provides for automatic termination at the end of the stage or the end of the season;
- home work, which involves performing duties remotely and not requiring personal presence at the actual location of the employer;
- a form of labor relations for carrying out the duties of a state or municipal service, where the types of conditions are determined by special internal legislative acts.
A comparative analysis of working conditions divides conditions into normal, harmful on the appropriate scale or dangerous, established by certified commissions, distinguishes work at night and work in northern regions with unfavorable climatic factors.
Download samples by type of contract Sample of an open-ended employment contract (20.4 KiB, 491 hits)
Sample civil contract with an employee (63.0 KiB, 10,026 hits)
Sample of an Individual Entrepreneur Agreement with an employee (25.8 KiB, 3,123 hits)
Sample of a fixed-term employment contract with a probationary period (19.2 KiB, 424 hits)
Sample employment contract (62.0 KiB, 343 hits)
Sample of an Employment Agreement between individuals (23.8 KiB, 656 hits)
Signs (elements) of an employment contract
An employment contract differs from other types of agreements in the following ways:
- it reflects the qualifications, profession, position, specialty in the area of which relations are regulated;
- the obligations assigned to the employee are fulfilled by him personally, while he is subject to routine and discipline, and also participates in the general labor process;
- receipt of remuneration (salary) for work performed is mandatory;
- All rights and obligations of the social sphere stipulated in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, from the moment the employment contract is concluded, become available to the party who acquires the status of “employee”.
Obligations of the employee as a party to the employment contract
The rights and obligations of the employee are listed in Art. 21 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The main obligation, perhaps, can be called the high-quality performance of one’s work as specified in the contract. After all, in fact, this is the purpose for which he is hired. Compliance with labor discipline is also one of the important obligations of an employee. All labor standards specified in the contract are binding.
Any employment contract will also stipulate that the employee must be careful and careful with the employer’s property and material objects. But each employment contract is individual and each of them, in addition to the general conditions discussed above, stipulates the employee’s own special obligations, which are discussed individually.
Obligations of the employer as a party to the employment contract
The employer also has many obligations. Their list is enshrined in Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Let's look at the main ones:
- to achieve a good result, the employer, as a party to the employment contract, must provide the employee with safe and decent working conditions, consumables, equipment - everything that is necessary for effective work;
- he must provide only the work specified in the employment contract and demand a result that does not go beyond the scope of the agreement;
- work performed must be paid on time and in the amount specified in the employment contract;
- in case of damage, including moral damage, the employer must compensate it;
- compliance with the work and rest regime established by law, as well as the implementation of social insurance, are mandatory.
How to draw up an employment contract correctly
The structure and content of the employment contract must correspond to its purpose, i.e., reflect the terms of the relationship between the parties to the contract - the employer and the employee.
It is important to consider that an employment contract may contain mandatory and additional conditions. What is their difference? The presence of mandatory conditions is provided for by law for everyone and is aimed at protecting the labor rights of employees. Additional conditions are voluntary. They appear in the case of special working conditions or when the employer and the employee agree on additional social benefits for the employee or his family at the expense of the employer.
Additional conditions should not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the standards established by labor legislation and other documents containing labor law standards: collective agreement, local regulations.
An employment contract form is available. A new employer can fill out such a form to hire new employees, and an employee can compare it with his current contract to check its legality. Example of a completed employment contract
There are mandatory conditions in the employment contract, but additional ones may also be included.
Mandatory details of the employment contract
In an employment contract, the main place is given to mandatory details. Their presence is required by law. On the part of the employee, the full name, passport data, TIN, information about the address of registration and actual residence, telephone number, and a signature are indicated. From the employer's side - full name, address, bank details, details of the representative who signs the contract, and his signature, seal of the organization. If the employer is an individual entrepreneur, his personal data is indicated and a stamp is affixed if available.
There are positions, professions and specialties for which the law provides for certain compensations, benefits or, conversely, restrictions. This applies primarily to harmful and dangerous working conditions. In the employment contract, the names of these positions, professions or specialties (as well as qualification requirements for them) must be indicated as they are indicated in official directories. Such reference books are approved in accordance with the procedure established by the government of the Russian Federation or the provisions of professional standards.
The text of the contract itself must contain:
- place and date of conclusion;
- an indication of whether the contract is fixed-term or open-ended (in the first case, the date or conditions of its termination);
- work start date;
- the position of the employee, to whom he reports, structural unit;
- working conditions: work is performed at the main place or part-time;
- place of work;
- work and rest schedule;
- job responsibilities;

The contents of the employment contract must fully describe the terms of its validity.
If, when concluding an agreement, any mandatory details were not included in it, then this is not a basis for its recognition as not concluded or its termination. The employment contract must be supplemented with missing information or conditions. In this case, the data is entered directly into the text of the contract, and the conditions are determined by an appendix or a separate agreement of the parties. These documents are drawn up in writing, signed by both parties and are integral parts of the employment contract.
Failure to include in an employment contract any of the mandatory rights or obligations of the employee and employer provided for by law cannot be considered as a waiver of them. The law is higher than the contract, therefore it is binding.
How to correctly indicate the place of work in an employment contract
To correctly determine your place of work, you must indicate:
- name of the division (for example, head office, Tambov branch, steelmaking shop, etc.);
- the exact address of the location of the structural unit (for example, Saratov, Radishcheva St., building 222, office 312).
In addition to the geographical description of the employee’s place of work, the contract should reflect in detail the characteristics of the workplace:
- where it is located - workshop, table, warehouse, for the driver - type of vehicle, etc.;
- how the workplace is equipped - computer, selector, Internet access, working tools, mechanisms, equipment, etc.;
- other details depending on the specifics of the employee’s job responsibilities.
An inaccurate description of the place of work in the contract may lead to the parties avoiding compliance with its terms. And the employee will even be able to take advantage of the opportunity to pause work. If a stationary workplace is not implied (for example, with a promoter, a walking courier, or in other cases of traveling work), this is also indicated in the contract with the most precise wording.

If a person works from home, his residence address is indicated as the place of work
Working hours and rest time
Art. 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for acceptable working hours with the duration of the working week:
- five days with two days off;
- six days with one day off;
- with the provision of days off on a sliding schedule;
- part-time work week.
The most common is a 40-hour work week. As a rule, this is a weekly five working days and two days off - Saturday and Sunday. But organizing a business does not always allow you to comply with such a regime. Standards for working hours and shifts are usually established by internal labor regulations in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other regulations, collective agreements, and agreements. If for one specific employee they differ from the general rules, the working hours are clearly stated in the employment contract.
In any case, the contract must contain a clause on the working hours: duration of daily work, including part-time work (shifts), start and end times of work, break times, number of shifts, alternation of working and non-working days. It is possible to provide for work with irregular working hours for certain categories of workers.
An irregular working day involves the performance of one’s job duties outside the established working hours. This mode of operation is often indicated for top managers.
Shift work may be provided. Often they do, for example, a 12-hour working day with sliding weekends. In such cases, summarized recording of working time is used with the condition that the duration of working time does not exceed that permitted by law for a specified period (month, quarter, etc.).
An employment contract may provide for work with a flexible schedule, reduced working hours with payment in proportion to the time worked. For some employees, due to special circumstances under the employment contract, the working day may be divided into parts.

The employment contract specifies hours of work and rest
The legislation establishes separate standards for the working hours of disabled people. The employment of disabled people of groups 1 and 2 during the week cannot exceed 35 hours per week, for groups 3 - the period specified in the IPR. Disabled people of groups 2 and 3 are entitled to regular leave of at least 30 days, plus unpaid 60 days leave. These conditions are fixed in the employment contract. Disabled people are involved in overtime work only with their written consent. Accordingly, the contract with them cannot contain a clause on irregular working hours.
Remuneration and bonuses
According to Art. 129 of the Labor Code, payment to employees under an employment contract can be established in the form of time-based payment at monthly salaries, daily or hourly tariff rates. Depending on the profession, the contract may provide for piecework payment. It does not depend on the length of time worked, but on the number of products manufactured, work performed, etc. Payment can consist of several types. For example, this is a basic salary, to which a percentage of products sold or the amount of concluded contracts is added daily. If working conditions require regional allowances or coefficients, this should be reflected in the contract.
Bonus terms are not a mandatory clause of the contract. But if the job involves regularly receiving bonuses, it is better to record this in writing. This approach will avoid disputes and misunderstandings.
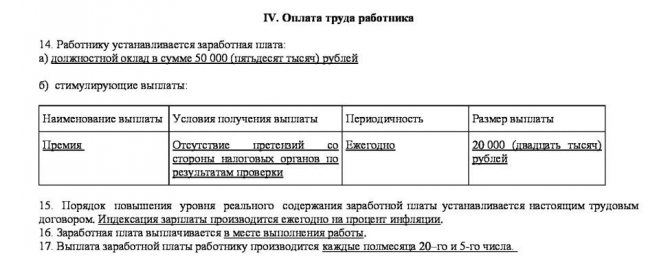
The employment contract must specify the amount and terms of payment of wages.
For example, a sales manager is promised a monthly bonus of 10,000 rubles if the plan is fulfilled. This condition is written down in the contract, since otherwise the employee will not be sure that he will receive this money. This means there will be no clear motivation. Another option: the company received a large contract, management decided to financially reward the department that worked on it. Here the bonus can be issued by a separate order; the law does not prohibit this. But it is impossible to foresee such a situation in advance, which means there is no point in stipulating it in employee contracts.
The employer has the right to involve employees in overtime work and call them on weekends. Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the rules of compensation and increased coefficients in such cases. The terms of the employment contract may include payment for overtime hours, but it cannot be less than what is established by law. And the employee has the right to increased pay or time off, even if the contract does not say this.
Video: the latest innovations in drawing up an employment contract
Responsibility for errors in the employment contract
For errors in an employment contract, the Code of Administrative Offenses provides for considerable fines, both for the company as a legal entity and for the director. Such punishments are provided for in Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
The fines are as follows:
- If the contract does not indicate a place of work with a full address (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the company will be fined 50 thousand rubles.
- If the class of working conditions is not determined, the fine will be 80 thousand rubles. (under Part 3 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code). The employer is obliged to conduct a special assessment and determine the class of working conditions: optimal, acceptable, dangerous, harmful. Working conditions indicating the date of the special assessment must be specified in the employment contract (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- If a fixed-term contract is drawn up without specifying the reason for temporary employment (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), you can receive a fine of 30 thousand rubles. under Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code.
- If the employer has chosen a shift work schedule, but is not specified in the employment contract indicating the duration of the working day (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), including indicating a schedule with sliding days off, then he faces a fine of 30 thousand rubles. under Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code.
- An agreement without a signature is practically not considered a document. The employee not only signs two copies of the contract, but also confirms receipt of the employment contract with a signature on the employer’s copy (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If this requirement is not met, the manager will be fined 1.5 thousand rubles. under Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If the contract does not specify labor functions and payment conditions, this is also a violation for which a fine is imposed.
Labor functions and contract
The labor function of an employee is his immediate responsibilities, described in more detail. They are usually reflected separately in the employee’s job description, but can also be included directly in the employment contract itself.
Labor relations are individualized for a specific employee, depending on the position he occupies and the tasks assigned to him. In this case, the employment contract specifies the specific type of work performed, the scope of job responsibilities, and the limits of emerging responsibilities. If the work assigned to an employee involves the provision of various benefits, compensation and payments established by law, then it is necessary to indicate his position in the labor functions.
Classification and types of employment contracts
There are several reasons for dividing employment agreements. In particular, the following agreements can be distinguished based on their duration: for a definite and indefinite period. The significance from a practical point of view lies in the provision and formation of primary authority. It consists of constant work and receiving income for performing labor functions. Fixed-term agreements can be divided into separate types of contracts.
These include:
- absolute certainty of the period (when an elective position is established);
- relative certainty of deadlines (this applies to persons who enter a position in a company to carry out specific work);
- conditional (such acts are concluded with a person who will work in a specific position for a certain period).
Types and forms of employment contracts
As a general rule, employment contracts are concluded in writing and in a number of copies equal to the number of parties. As a rule, there are only two of them – the employer and the employee. Each copy must be certified at the end with the signatures of all parties and comes into force from the date of its signing.
According to their types, contracts are divided into:
- fixed-term, which are concluded for a certain period, but not more than five years:
- unlimited, their validity period is not specified.
In turn, fixed-term contracts are also subdivided. They can be concluded for a period of:
- until the completion of certain work;
- before the expiration of a specific date;
- for the period of replacement of an absent person.
Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties entails the termination of the legalized relationship between the employer and the employee.
What are the terms of an employment contract?

An employment contract can be either indefinite or fixed-term. The commencement of an employment contract is usually stated in the part called “Basic/General Provisions” in the line: the employee must begin performing his job duties on (date). Important: the date indicated in the header of the contract is not the date of commencement of duties. This is the date of drawing up and registration of the employment contract. For example: the contract was drawn up on November 25, 2019, but the employee must begin performing his job duties on November 30, 2019.
We’ve sorted out the start date, now let’s move on to the expiration of the employment contract. So, according to the general rules, an employment contract is concluded for an indefinite period. If the contract does not specify a term, it is considered unlimited.
A fixed-term employment contract can be concluded for a maximum of 5 years. No later than three days before the expiration of a fixed-term employment contract, the employer is obliged to notify the employee in writing of the termination of this contract.
Important: in order to conclude a fixed-term contract, the employer must have a basis. If it does not exist, then if a labor dispute arises, you have the right to demand the conclusion of an agreement for an indefinite period.
A fixed-term employment contract is concluded in the following cases: 1. If the main employee is absent, in particular, on vacation, or on sick leave, or on a long business trip, but his job is retained. (there will be a separate post about the wording of the term in the contract) 2. For the duration of temporary work. Up to two months maximum. 3. For the duration of seasonal work. 4. In case the future employee will work abroad. 5. To carry out work that goes beyond the normal activities of the employer (for example, installation or some kind of reconstruction). This requires appropriate grounds and documentation with deadlines to support it. 6. In the event that an organization is created with a clearly defined deadline for performing certain work. 7. For the duration of certain work, in the event that the completion date cannot be determined by a specific date. 8. If the work takes place in the form of an internship. 9. For work related to elected bodies or an elective position 10. If a person is sent from the employment service to perform public works or work of a temporary nature 11. In case of performing alternative civil service.
Also, a fixed-term employment contract can be concluded by agreement of the parties in the cases provided for in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
An employment contract with a foreign citizen is also concluded for an indefinite period. Here it is already necessary to track the period of honey. policy, patent and other documents of a foreign citizen, so that if they are not provided, the employment contract can be terminated. But you cannot enter into an agreement in advance for the duration of, for example, the validity of a patent!
If a fixed-term employment contract was concluded, but neither the employer nor the employee demanded termination of the contract before the end of its validity period, and the employee continues to perform his job duties, then the contract is considered unlimited.
Know your rights!
Sincerely,
Rasskazova Anastasia Grigorievna
Specialist in the field of labor relations and personnel records management "FLC GROUP"
Always in touch, FLC_GROUP
If you liked the article, like and subscribe to us on social networks!
Thank you for your attention! FLC GROUP "FIRST LAW BOARD"
The difference between an employment contract and a civil law one
The main difference between an employment contract and a civil contract is that the first is regulated by the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the second by the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. On the basis of an employment contract, the employee performs work only personally, without the right of delegation, whereas in a civil agreement there is the possibility of transferring part of the work to a third party.
The purpose of a civil law contract is to achieve a specific result, while under an employment contract the main thing is the labor process itself, the performance of a certain labor function.
According to the employment contract, remuneration is made systematically, according to the established salary and at least every half month. In a civil agreement, payment is specifically stipulated and can be a lump sum upon completion of work or achievement of a specific result.










