Happy owners of garden plots located in picturesque areas often decide to build a residential or garden house on their land.
Some people need a place to relax while gardening, others dream of a cottage where it will be comfortable to stay all year round.
how legal such construction is and what difficulties may be encountered.
Legal norms for the use of garden land
In accordance with the modern classification, there are 2 types of permitted use of land related to gardening:
- Type 1.5 involves conducting activities for the industrial cultivation of perennial crops.
- Type 13.2, in addition to agricultural activities, allows the construction of outbuildings and a garden house on the site.
Thus, only owners of plots with VRI 13.2 “Gardening” .

The category of land is also important: it is better if the plot is located on the territory of populated areas.
Additional information on garden plots located within the boundaries of populated areas can be obtained here.
If the category of land on the gardening plot is agricultural, then it will be very difficult to register there; only a garden house for recreation is allowed to be built there.
Detailed information can be found in the feature article.
What can be built on the land for gardening and vegetable gardening?
On a site intended for gardening , you can build:
- greenhouses;
- barn;
- garage;
- outbuildings for storing equipment and crops.
The construction of a garden house is also allowed, but it cannot serve as a place of permanent residence. Making it residential with the subsequent installation of communication lines is possible only if the structure is not located on agricultural land.
On plots for gardening, the list of permissible buildings is somewhat wider:
- sheds and outbuildings for storing equipment;
- premises for the harvested crop;
- greenhouses;
- bathhouse, toilet;
- other auxiliary structures.
The construction of a residential building on land for gardening is prohibited. This provision does not depend on the category of the site. To construct capital buildings, it is necessary to change the purpose of the allocated land.
Differences in the construction of a building for permanent and seasonal residence
The set of rules SNiP 30-02-97*, regulating garden buildings, highlights the difference between a garden and a residential building, in the possibility of registering residence in the latter.
Garden
Let's take a closer look at the features of a garden house:
- Is a residential property used for recreation
- Living inside it is temporary
- Such a residential building cannot be divided into separate apartments
- Construction is possible without obtaining a permit
A garden house can be considered suitable for living if the following are met:
- fire safety requirements,
- building codes and regulations (intact floors and walls, reliable foundation, protection from melt water),
- sanitary requirements (sufficient insolation, the presence of thermal insulation of walls to maintain optimal temperature inside the building),
- provision of engineering infrastructure (heating, lighting, water supply, sewerage, ventilation).
Residential
A residential building can be used as a permanent residence . Registration is permitted there.
When starting construction, it is necessary to clearly determine whether the building will later be designated as residential. Since the cost of refurbishment of a summer house practically corresponds to the construction of a new residential property.
There are currently several problems:
- many garden plots are not used for their intended purpose,
- owners do not develop plots due to the great difficulties with subsequent registration.

At the same time, there are no restrictions on the category of land.
The law comes into force on January 1, 2019, after which unregistered seasonal country houses are also recognized as garden houses .
Re-registration of documents for constructed objects is carried out at the request of the owner.
The VRIs covered by the law include 13.2 and 13.3. Thus, owners of plots with such permitted use can construct garden and residential buildings.
Bringing the old VRI to the current classification is carried out at the initiative of the owner, but is not mandatory.
Suitability of the house for seasonal living
A garden house must be built in such a way as to provide the possibility of seasonal living (not year-round, when compared with a residential building).
It is forbidden to do this on your own summer cottage
All premises should be divided into residential and household ones. In rooms the minimum ceiling height is 2200 mm, and 2000 mm in auxiliary rooms.
You can arrange a cellar or basement, the height of which is at least 1600 mm. The staircase to the second floor can be made internally or externally (outside the building).
The roof structure must be such that rainwater does not drain onto the neighbors' property.
Is it possible to get a registration?
Current law No. 66-FZ does not provide for temporary or permanent registration in a garden house . However, the decision of the Constitutional Court changed the current situation and made it possible to register through the court.
If registration is necessary, the owner can act in one of two ways:
- Convert a non-residential property to a residential one by contacting the authorized body of the local administration. A redevelopment project will be required, agreed upon by several authorities.
- Recognize the garden house as residential, suitable for living, in court. After a positive decision, registration is possible.
The most popular method is a court decision ; it requires less financial costs and time.

- sanitary,
- construction,
- firefighters
standards.
If the garden house is the only available place for permanent residence, the likelihood of a positive court decision increases.
The package of documents attached to the claim for filing a lawsuit includes:
- The conclusion of an expert organization on the compliance of the object with SNiPs, issued on the basis of title documents and a technical passport.
- Conclusion of the SES on the compliance of the facility with sanitary standards. If the authority does not issue the required certificate, it can be replaced with a similar expert opinion.
- Conclusion of OGPN on compliance with fire safety standards or a similar conclusion of a third-party organization.
- A document confirming the actual residence of a citizen in a garden house, for example, a certificate from the chairman of the SNT.
After a positive court decision is made, you must obtain a mailing address . To do this, contact the local administration.
If the plot is located within the boundaries of a populated area, then assigning an address does not cause difficulties. If the plot is located at a short distance, the owner can initiate its inclusion within the boundaries of the locality. This decision is made at the local leadership level.
It is also possible to obtain an address without including the plot of land in the boundaries of the settlement, but the procedure is more complicated. The postal address of such houses will coincide with the address of the site on which it is located.
After assigning a postal address, the owner initiates cadastral changes and receives a new technical passport for the garden house as a residential property.
Construction of what objects is allowed on land plots
Not all plots of land originally intended for gardening are allowed to erect residential buildings. If the premises are nevertheless built, you may encounter significant problems when registering the property. Land provided for gardening or horticulture is initially considered agricultural land. Exceptions are permitted. Sometimes land is included in settlement plots. The category directly affects whether the construction of a residential building is permissible.
If the land plot is intended for agricultural activities and is located within the boundaries of a populated area, only the following structures can be built on it:
- sheds and garages;
- baths and greenhouses;
- garden houses not intended for permanent residence;
- other outbuildings.
At the same time, there is no provision in the current legislation prohibiting construction on land plots intended for vegetable gardening or horticulture. Therefore, performing actions is not considered a violation, but it will not be possible to permanently reside in such a structure on an official basis.
Video
Permission to build a residential building

Based on the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (subclause 1, clause 17), it is not required for construction on garden plots.
In order to avoid problems with neighbors during the construction of objects, it is necessary to take into account the rules for the location of buildings from borders, roads, and other objects according to SNiPs.
If it is planned to build an object, subsequently registered as an individual residential property, then the owner can obtain permission in a simplified manner in accordance with the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (Part 9, Article 51).
To do this, he needs to contact the body authorized in the field of urban planning and submit the following documents:
- of a legal nature,
- urban plan,
- plot layout diagram with the designated location of the facility under construction.
The obtained permission will be submitted to the court.
Construction rules
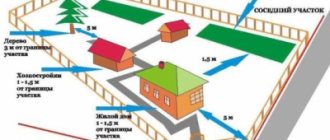
In accordance with construction standards, the construction of buildings on a garden plot must be carried out according to the following rules :
- from the house to the boundary line with the neighbor there must be at least three meters, the calculation is carried out from the nearest wall or part of the house protruding by 50 cm or more;
- buildings for animals must be located four meters from the border;
- other outbuildings - no less than a meter from the neighbor’s property.
The location of the outdoor toilet is highlighted separately :
- from the house or cellar - at least 12 meters;
- from a bathhouse, shower or well - from 8 meters.
These standards apply to both buildings within the same site and neighboring buildings. Failure to comply with regulations may result in a requirement to demolish the structure.
At the same time, pay attention to local regulations. Gardening partnerships may have their own building rules. In some cases, they allow a slight reduction in the established parameters.
It is emphasized that the total number of buildings and garden paths should not occupy an area of more than 25% of the entire territory of the site. Accordingly, gardening should be carried out on the remaining land.
Advantages and disadvantages

It is important to weigh the pros and cons, especially if you have no previous experience of living in a private home and caring for it.
What benefits does the owner receive when building a house on garden land:
- The plot is already owned or is much cheaper than for individual housing construction.
- Low payments for the use of utility infrastructure.
- No noisy neighbors or freeways outside your windows.
- Your own home is built in accordance with personal concepts of beauty, including exterior and interior decoration. Compliance with building codes is mandatory.
- The progress and speed of construction depends on your desire and financial capabilities.
- Favorable environmental conditions: clean air, water, land, natural sounds of wildlife around.
What are the main disadvantages of living on a garden plot:
- Building a house that meets all requirements and standards is expensive.
- SNT members pay considerable annual fees, which go towards maintaining infrastructure facilities.
- Low transport accessibility. Public transport outside the city runs on schedule, with large intervals. This leads to the need for each family member to have their own car.
- The infrastructure is poorly developed. Troubleshooting (broken wires, broken water tower) takes a lot of time.
- The peculiarities of the winter climate with heavy snow drifts impose restrictions on physical activity.
- Maintaining your home during the cold winter months requires significant effort.
- Registration in a garden house is possible only through the court.
- The arrangement of social and transport infrastructure, even for garden villages located within the boundaries of a populated area, is carried out at the expense of the owner-gardeners. The new law No. 217-FZ provides for co-financing programs for such expenses, but it is not yet known whether there will be funds for them in the regional budgets.
In some cases, the owner may initiate changes to the VRI of his plot. More details about the procedure can be found in a special article.
Read more about the main differences between garden land and individual housing construction in a separate article.