Modern market relations, the desire of the employer to most effectively organize their business, minimize costs and maximize profits, force the latter to increasingly attract workers to work outside the established working hours. According to Art. 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the legislator provided for two types of such work: overtime and irregular working hours. It is important for all parties to the labor relationship to understand that this is not the same thing. Let's figure out together what an irregular working day is, how payment for an irregular working day occurs, as well as other nuances.
Working long hours is quite common
The concept of irregular working hours
Current legislation, within the framework of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, defines an irregular working day as a special, special mode of work, according to which individual employees (officials) may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions beyond the duration established for them working hours. We will consider the features of irregular working hours, an employment contract with irregular working hours, with examples and comments later in the article.
It is important to note that such overtime is not paid in excess of the established wage under standard working hours. That is, if an order on irregular working hours has not been issued against you, or an irregular working day is not specified in the employment contract, then overtime will not be compensated.
How is an irregular working day interpreted in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is designed to regulate relations between management and subordinates, pays a lot of attention to establishing standards for time spent at work that are not harmful to health, as well as standards for the time that the body will have enough to recuperate, including irregular working hours.
The length of time an employee must remain within the company while performing his or her job functions is specified in the “Working Hours” section. Within the framework of this concept, as well as the concept of “irregular working hours,” it is recorded how many hours an employee must perform his duties during the day (in some cases, the term “shift” is used instead of a working day). There are also time limits for the work week and year. There is a separate concept of “rest time”. With its help, the duration of daily rest, weekends and vacations is regulated.
Typically, working hours are perceived as a 5-day workday with an 8-hour working day. This is precisely the norm that operates in the vast majority of enterprises and organizations - both public and private. But there is another working mode - irregular working hours (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Irregular working hours are not introduced for the entire enterprise, but only for some individuals who simply need to work beyond the plan. It turns out that the entire company has, for example, a standard 5-day work schedule with work starting at 9 am, while individuals work irregular working hours. Their duties include reporting to work at, say, 6 a.m. or leaving the office after 10 p.m.
For many, long working hours are closely intertwined with the concepts of “overtime” and “overtime.” But at the legislative level they are separated. Irregular working hours are a separate work schedule that allows the employer to employ specific employees outside of their standard schedule.
If an employee does not have an irregular working day, then he can be recruited to work outside of working hours only to perform overtime work. Find out how to properly register and pay for overtime work from the ConsultantPlus Guide. You can get acquainted with the material using a free trial access.
What does the law say about long working hours?
One of the key problems is that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain either norms or criteria for determining the norms of acceptable processing under NSD, thereby creating a situation for potential abuse of administrative resources by the employer.
Also, the legislator does not highlight the grounds on which this regime can be established for employees, leaving the issue to the will of the employer. But the law clearly states the need to make decisions on irregular working hours, taking into account the opinion of the trade union. As we see, weak legislative regulation of certain aspects gives rise to situations of abuse of rights on the part of the employer.

Long working hours can be used as an abuse by employers
Sample employment contract with irregular working hours
An irregular working day in an employment contract - you will find a sample of such a document below - can be reflected if it is introduced for hired employees. It is mandatory to include information about the application of an irregular regime in an employment contract, or the law allows an alternative procedure for its introduction, you will find out by reading the article to the end.
What is an irregular day?
What document is required when establishing an irregular day - additional. agreement on long working hours or a new contract?
Worker's compensation
Contents of the sample contract
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the working day is 8 hours. But sometimes the labor regime changes periodically. What is meant by the term irregular hours in official documents in 2021?
Work in irregular hours differs significantly from the usual work schedule.
Asking is faster than reading! right now through the form (below), and one of our lawyers will call you back to provide a free consultation.
According to the law, the employer must inform the employee in advance about the peculiarities of work activity and, in particular, about the working hours.
This also applies to potential deviations from the standard work shift duration. Moreover, such nuances should be reflected in the employment contract.
In particular, a clause on non-standardization is included in the agreement. An irregular work schedule differs from the generally accepted work pattern in the form of a five- or six-day workweek, when an employee works at strictly established hours.
Important
For an employee, irregularity is expressed in the fact that he can be involved in performing functional duties beyond the duration of a regular shift.
Moreover, consent for processing is not required. There is no special form of employment contract for irregular working hours.
A document is drawn up based on a standard template. But if an employee is given an irregular working day, the employment contract must take into account the peculiarities of the labor regime.
Definitions
An explanation of the designation “irregular working hours” is discussed in Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The term defines a special working regime when individual employees, by order of management, may from time to time be involved in work activities outside the standard working day.
Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the entry of data on irregular days into the contract. This condition is especially important since information about the working hours is included in the section of mandatory information.
This fact is confirmed by Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, concerning the content of the agreement. For comparison, it should be noted that the usual length of a working day is eight hours, excluding break time.
And if an employee is involved in work outside the specified period, then his activity is considered work with a special regime.
The absence of strict limits on the working day qualifies as an irregular working day.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Application for renunciation of inheritance: sample 2021
The law does not contain a closed list of reasons why irregular work hours may be applied.
But it is said that an employee can be involved in work outside of working hours only for objective reasons related to production necessity.

That is, the basis for activities outside the eight-hour working day must be justified. An important nuance is that production necessity is an episodic phenomenon.
If the use of irregular work becomes systematic, the employer faces administrative or financial liability.
Advice
A similar outcome is likely if the employee complains to the labor inspectorate. When the results of the audit confirm the essence of the complaint, all excess hours are recognized as overtime and are subject to additional payment.
It is also necessary to know that activities during irregular working hours require the employee to perform his immediate job responsibilities specified in the job description or contract.
If an employee is assigned to perform other functions, this is considered a violation.
The procedure for introducing a work regime with irregular hours is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.

In particular, important provisions are contained in Article 101 of the Labor Code, dedicated to the work of workers outside the generally accepted working hours.
It is also stated here that the employer has the right to resort to extending working hours occasionally, justifying the need in the form of an oral or written order.
Moreover, this list is developed taking into account the position of a trade union or other body that protects the interests of the work collective.
An employee involved in irregular work must be familiar with the documentation regarding the establishment of a special regime, as well as the benefits and compensation provided.
This norm is determined by Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, the working day can increase in any variation, both before the start of the standard working day and at its end.
note
Moreover, current legislation does not indicate the total duration of additional working hours.
Still looking for an answer? It's easier to ask a lawyer! Write your question using the form (below), and our specialists will quickly prepare the best options for solving your problem and call you back on the day you submit your application. It's free!
A regime with irregular working hours established for a specific employee is certainly reflected in the individual contract.
But when signing such a document, the employer should know that extended working hours are strictly prohibited for certain groups of workers (Article 92, Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), this applies to:
- minor workers;
- persons with disabilities (medical limitations or assigned disability group);
- workers working in hazardous/harmful conditions.
Based on the signed agreement with the presence of a condition on a special labor regime, an order of the appropriate content is issued for the enterprise.
The presence of an official document allows you to attract workers to additional work without issuing other documents. To attract someone to work outside of working hours, a verbal order from the manager is enough.
- List of positions. This document identifies positions for which it is possible to establish an irregular working day. The list is approved by a collective labor agreement or other regulatory act of the organization, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of the company. If the organization does not have a body representing the interests of employees, the list is approved by the employer. In addition, the corresponding lists can be legislated in industry documents.
- Inner order rules. Provisions on irregular working hours can be enshrined in this document, both as an annex to it and in certain of its paragraphs.
- Regulations on irregular working hours. The document sets out the conditions for registration, a list of positions, a list of compensation, as well as restrictions.
The boss needs to know about all the prohibitions and restrictions regarding the inclusion of certain persons in the list, which is stipulated under Art. 97, 99, 101 Labor Code: it is impossible to prescribe such a work schedule to persons who, according to legislative norms, are prohibited from engaging in work.
Definition of valid time
Labor legislation defines working hours as the time during which an employee must perform work duties. Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. The employer is required to record the time actually worked by each employee. There are restrictions on overtime work, which is paid additionally and is often confused with irregular working hours. Irregular working hours should be distinguished from overtime.
For irregular working hours, one wage system is provided. In turn, overtime is paid for as work “above the norm” at a different rate.
Limitations of non-standardization
Unlike overtime, for which the law directly provides restrictions: no more than 120 hours per year and no more than 4 hours in two days, an irregular schedule has no legal limits.
Despite the fact that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain direct restrictions on the establishment of an irregular schedule for certain categories of workers, such a regime is not recommended for the persons listed in Art. 92, h.h. 1.2 tbsp. 94 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This applies, for example, to workers under 18 years of age or disabled workers.

Irregular schedules are not recommended for minors
Restrictions on the introduction of irregular working hours may be provided for by other regulatory documents. For example, it is impossible to establish an irregular working day for truck drivers.
For citizens who work part-time, an irregular working day can be introduced only if such workers have a part-time working week, but with a full working day (shift) (Part 2 of Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This is most important for people who combine work and study.
Is it necessary to record irregular work hours?
Despite the fact that an employee is not entitled to additional payment for work under irregular working hours, records of irregular working hours must be kept (Part 4 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This can be done in a separate journal, developed, for example, on the basis of the unified form No. T-13 “Working time sheet” (Decree of the State Statistics Committee of January 5, 2004 No. 1).
Attracting to work on holidays and weekends, to work at night
Let us repeat that many employers interpret Art. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in their favor, considering that those who work irregular working hours must work “without days off or holidays.” But this position is wrong. Workers in this regime are subject to all the norms of the Labor Code and can be recruited to work on a non-working holiday or day off only in compliance with the rules established by the code.
This is also important to know:
Overtime work of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2021: how it is paid, should not exceed...
For example, to attract employees with irregular working hours to work on days off, you will have to strictly follow Art. 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and formalize:
- written agreement;
- taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization;
- notification of the right to refuse work on a day off (for disabled people, women with children under three years of age) and familiarize employees with it against signature;
- order to hire someone to work on a day off.
In addition, before issuing an order, you will have to make sure that employees have no medical contraindications for such work.
Finally, work on a day off must be paid according to the rules of Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
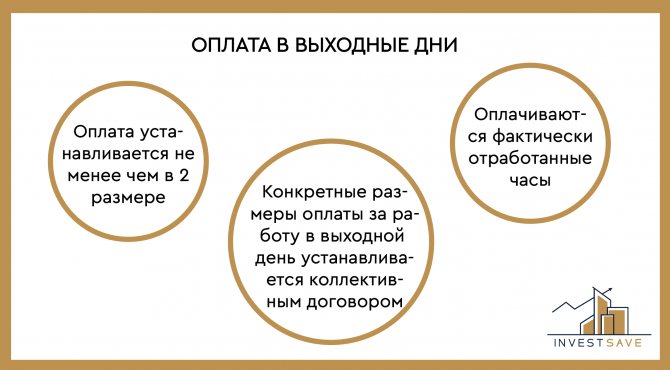
Please note: Work on a weekend or a non-working holiday is paid at least double the amount:
- for piece workers - at no less than double piece rates;
- employees whose work is paid at daily and hourly tariff rates - in the amount of at least double the daily or hourly tariff rate;
- for employees receiving a salary (official salary) - in the amount of at least a single daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work was performed within the monthly working time norm, and in the amount of no less than double the daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work was performed in excess of the monthly working hours.
Like working on weekends, working at night is a deviation from the norm for an employee with irregular working hours. Let us remind you that according to Art. 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the time from 22.00 to 6.00 is considered night time. Accordingly, employment at this time must be properly formalized and paid at an increased rate - at least 20% is added to the salary or tariff rate (Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Part-time and part-time work
According to Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee working part-time can be assigned an irregular day if he is assigned a part-time working week, but with a full working day (shift).
If the employee is assigned a part-time working day, then it is impossible to establish an irregular working day for him. In this case, one of the labor modes completely loses its meaning.
Also, the law does not prohibit the establishment of irregular hours for part-time workers. But there are some peculiarities here:
- If a part-time worker is given a working day of no more than 4 hours, then such a working day is considered incomplete. Therefore, it is impossible to establish an irregular working day;
- If a part-time worker at his main place of work is free from work duties on some days, then he can work a full shift with a part-time workweek. In this case, he will be able to establish an irregular working day (according to Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and, accordingly, compensation in the form of annual paid leave of at least three calendar days.
What is the difference between overtime and irregular working hours?
Irregular working hours means a special working hours regime, which is established for certain categories of workers in the employment contract. The majority of workers are involved in overtime work, but only in cases provided for in Art. 99 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In practice, the use of two different types of work outside the established working hours at the initiative of the employer often leads to the replacement of irregular working hours with overtime work.

Conditions for engaging in overtime work
The only thing common between these varieties is that the work is performed at the initiative of the employer and outside the working hours established for the employee by the relevant regulations or employment contract. The rest has its own characteristics:
- Reinforced in different articles (Article 99 and Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the procedure for application and duration, as well as how overtime is compensated. Meanwhile, the current rules on irregular working hours allow the employer to “disguise” overtime work as one of the working hours, abusing its administrative power in relation to subordinates.
- As another feature, we will consider the procedure for attracting an employee to work outside the established working hours. Thus, engaging an employee to work overtime is permitted only with his written consent. Under NSD, the employer does not have to obtain the consent of either the employee himself or the representative body of employees. This right of the employer is provided for by the provisions of the employment contract. The employee’s refusal, in this case, will be a violation of labor discipline.
- Another difference is the answer to the question of how many hours per week an employer can involve its employee in irregular or overtime work. For an irregular working day, there are no restrictions on its duration; there are no limits for overtime per week, month, or year.
Occasional occurrence of overtime work

Savicheva Olga
Corporate accountant, practicing economist
Ask a Question
The problem in interpreting the concept of “episodicity” still creates great difficulties in practice. The concept of “episodicity” can be characterized as an accident, suddenness, which is similar to the grounds for attracting overtime work in emergency circumstances. As a consequence, the same reasons make it easy to replace overtime during overtime work with irregular working hours. In practice, it is difficult to determine the degree of episodic or systematic involvement, and any assessment of the circumstances inevitably becomes subjective, since there are no criteria established by law. In case of abuse of the right, the court may recognize overtime during irregular working hours as a cover for overtime work, which is paid additionally (see Letter of Rostrud dated June 7, 2008 No. 1316-6-1).
What does irregular working hours mean for an employee and an employer?
Before agreeing to an irregular work schedule, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with what awaits a citizen and what an employer can count on after signing an employment agreement with such a norm.
For the employee this will mean the following:
- Consent to a delay (early exit) will be asked at the workplace only once - at the time of signing the employment contract. Further, the worker will be obliged to carry out the orders of his immediate supervisor;
- An employee will not be able to refuse to do work after the end of the working day. This will be equated to a violation of labor discipline, with the application of disciplinary sanctions provided for by law. It is important to understand here that attraction should be episodic. Otherwise, it is easy to prove that this is overtime work;
- In the employment contract, it is advisable to outline the scope of “activities outside the schedule.” For example, indicate that the functions are performed outside the main working hours, but no more than 2 hours before its start or end;
- such activity should be periodic (for example, once a week or once a month when reporting is required). If such work is on a permanent basis, the employee has the right to demand a change in the schedule with payment for the time actually worked;
- working under conditions of an extended period means performing a larger volume of the same type of functions. This cannot be regarded as an assignment of other duties that go beyond the scope of the employment contract (work instructions);
- as compensation for this regime, a minimum of 3 days of additional leave is required (mandatory). Based on the terms of the employment agreement or collective agreement, additional payments may also be applied, allowances may be established, and bonuses may be paid.
Registration of irregular working hours
Employers are wondering: how to establish such a work schedule? Let's figure it out:
- Simply familiarizing an employee with a local regulatory legal act, a list of positions, where it will be indicated that he is entitled to NSD is not enough and is unlawful. Such orders should not be carried out verbally either.
- It is necessary to establish a list of positions for which irregular work hours will be established. The list can be drawn up in a separate document, introduced by order, or specified in a collective labor agreement. Also, if desired, you can develop a Regulation on irregular working hours, which will describe in detail the features and guarantees.
Documentation of conditions
When hiring an employee, it is necessary to familiarize him with the collective agreement, internal labor regulations and other local regulations in force in the organization and relating to his labor function. After this, an employment contract is concluded with the employee, which includes a condition for working on irregular working hours. By signing it, the employee agrees with the nature of the work, which involves overtime.
This is also important to know:
Pre-holiday day according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: which days are considered holidays
Sample employment contract

Sample order

Registration of attraction to work beyond normal working hours
To establish an irregular working hours regime in an organization, you need to perform the following steps:
- justify the introduction of the regime;
- determine a list of employee positions;
- fix the regime and list of positions in the local act;
- include conditions on long working hours, guarantees and compensation in the employee’s employment contract;
- approve the Regulations on irregular working hours;
- draw up separate orders for each position or employee who will have to switch to such a regime, and familiarize each employee with them.

To establish an irregular regime, it is necessary to formalize such a regime in local acts
If a special work regime is established for an employee who is already working, then he must also be familiarized with the list of positions and the procedure for attracting work in irregular hours. In addition, an additional agreement to the employment contract must be concluded with him, which will change the working hours and establish compensation.
The agreement must contain the following information:
- date, number and place of detention;
- name of company;
- position and full name employee;
- details of the employment contract to which changes are made;
- new terms included in the contract.
Next, the employer must issue an order establishing a special regime for specific employees. The document is drawn up in any form, but it must indicate the date, number, place of publication, name of the organization, from what date and to whom an irregular schedule is established, and the number of days of additional leave. Once all the documents are completed, the employer, if necessary, has the right to give orders to the employee that it is necessary to stay late and finish the work.
Commentary on Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
An irregular working day is a special work regime, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the normal working hours. The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is established by a collective agreement, agreement or internal labor regulations of the organization.
The peculiarity of the considered working hours is that the employee is subject to the general working hours of the organization, but may stay at work at the request of the employer to perform his job duties beyond the normal work shift or be called to work before the start of the working day.
It should be noted that employees can be involved in working with irregular working hours only to perform their labor functions, which they must perform under the employment contract. Consequently, an employee cannot be obligated to perform any other types of work, including outside the normal working hours.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that irregular working hours are established only for individual employees included in a special list (it is attached to the collective agreement or internal regulations in force in the organization). This list can also be established in industry, regional and other agreements.
Irregular working hours may be used for administrative, managerial, technical and business personnel; persons whose work cannot be counted in time; persons who allocate time at their own discretion; persons whose working time, due to the nature of the work, is divided into parts of indefinite duration.
It should be noted that, when applying the rules of Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must not obtain the consent of either the employee himself or the representative body of employees to attract (on days of production necessity) employees to work beyond the established working hours. This right of the employer is already provided for in the terms of the employment contract. The employee does not have the right to refuse to perform such work. Otherwise, there is a gross violation of labor discipline. Note that this article contains a definition of irregular working hours, which states that in accordance with this mode of work, employees may be involved in performing their labor functions outside the working hours established for a given employee.
The establishment of irregular working hours does not mean that these workers are not subject to the basic norms of labor legislation on working hours and rest periods. Therefore, recruitment to work outside the established working hours cannot be systematic.
Since working with irregular working hours involves certain overtime in excess of normal working hours, the Code, as compensation, provides that employees with irregular working hours are provided with annual additional paid leave, the duration of which is determined by the collective agreement or internal labor regulations. In the event that such leave (at least three calendar days) is not provided, overtime in excess of normal working hours is compensated with the written consent of the employee as overtime work (Article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
How is an employee compensated for working irregular hours?
Employees who work within such a work schedule are provided with annual additional paid leave, the duration of which is determined by the collective labor agreement or other local regulatory legal acts of the company. The duration of such leave cannot be less than 3 days (Article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is best to formalize this feature of working conditions in the provisions of the employment contract. If at the time of its conclusion it was not yet known about the possibility of recruitment, everything can be formalized by an additional agreement to the employment contract, or an order.

Compensation for irregular work is additional vacation days
Compensation for working irregular hours
As we found out, overtime during the named work mode is not paid. However, legislators did not leave such workers without compensation.
Article 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that employees with irregular working hours are provided with annual additional paid leave, the duration of which is determined by a collective agreement or internal labor regulations and cannot be less than three calendar days. This leave can be added to the annual main paid leave or taken separately.
Please note: The right to additional paid leave does not depend on whether the employee works overtime or goes home on time. If the employment contract reflects the condition of irregular working hours, then it will not be possible to avoid the provision of additional days of rest.
Sometimes employees, believing that they have worked a lot (for example, worked outside working hours every day for a month), ask the employer for an additional paid day off. Their desire is understandable - they thought that they would overwork sometimes, but the employer involved them in such work all the time. But overtime hours during irregular working hours are not equal to overtime hours during overtime work, in which an employee has the right to choose additional rest time instead of increased pay (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Since the law provides for only one type of compensation - additional leave, the employer is not obliged to satisfy such a request,
Table of advantages and disadvantages of irregular working hours for the employee and the employer
| Benefits for the employee | Disadvantages for the employee |
| Additional guarantees - at least 3 calendar days to the main vacation. | You cannot object and refuse to work beyond the norm. |
| It is likely that the attraction will be minimal. | If hired, time is not paid in addition to wages. |
| Independence of the right to guarantees from the volume of involvement in work beyond the norm. | The problem of abuse of rights on the part of the employer may arise if the involvement in work is not occasional, but regular. |
| The law does not establish a maximum amount of overtime for an employee. | |
| Benefits for the employer | Disadvantages for the employer |
| Not paid above salary - savings. | It is not possible to regularly engage in work beyond the established time. |
| The employee cannot refuse; if he refuses, he can be subject to disciplinary action. | It is necessary to take into account the characteristics of individual categories of workers. |
| The law does not establish a maximum amount of overtime for an employee. |
Table of advantages and disadvantages of irregular working hours
Sometimes employers interpret the condition of non-working hours in such a way that an employee can be engaged both on a day off and on a holiday. But this is an erroneous interpretation of the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, to attract employees with irregular working hours to work on days off, you will have to strictly follow Art. 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which means to formalize:
- written agreement;
- taking into account the opinion of the trade union;
- notification of the right to refuse work on a day off (for disabled people, women with children under three years of age) and familiarize employees with it against signature;
- order to engage in work duties on a day off.
In addition, before issuing an order, you will have to make sure that employees have no medical contraindications for such work. Finally, work on a day off must be paid according to the rules of Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Features of payment on weekends and holidays
What does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation say about irregular working hours?
The concept of irregular working hours is enshrined in Article 101 of the Labor Code. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this is a schedule option when some specialists from time to time perform their duties before or after their shift. For example, a manager has a standard schedule of 8:30 a.m. to 5:30 p.m., but his contract specifies an irregular schedule. The boss has the right to detain him for a meeting with clients after 17:30 or, conversely, call him before 8:30. But not every day, but “episodically”, irregularly.
The boss does not have the authority to force an employee to work overtime every day. It will be lawful to call him only when it is objectively impossible to do without his participation. It is categorically impossible, referring to the definition of “irregular,” to force a person to spend 2-3 extra hours at work every day.
In addition, the Labor Code requires that a corresponding clause be included in the employment contract, and that an organization must issue a special order listing all positions with such a working day. Without this, it will not be possible to assign overtime to an employee: there is a risk that he will complain to the labor inspectorate or directly to the court.

During irregular working hours, overtime is sporadic
Features for the employee
So, when concluding an employment contract, you found out that the regime will involve overtime. How will his work schedule be structured and what legal provisions do he need to know in order to prevent his rights from being violated?
Firstly, if irregular working hours are written into the employment contract, the employer will not take written consent from the employee for any overtime. The citizen had already agreed to each excess when he signed the contract.
Secondly, you cannot refuse to work overtime . This is tantamount to a refusal to perform official duties at normal times and is fraught with dismissal. If in a particular case it is impossible to stay/come for overtime, you need to make special arrangements with the manager and provide supporting documents. For example, a medical certificate.
Third, “irregular” does not mean “endless” or “24/7.” In most cases, the working week of such employees has a standard duration of 40 hours, and only in rare, occasional situations can it be extended by 5-6 hours in total. Each processing is justified by objective necessity. There is no compelling reason to work urgently - the citizen goes home.
Fourthly, compensation is due for an irregular schedule. Money can act in this capacity, but more often it can be time off or vacation (for example, 3 additional days per year).
Features for the employer
An irregular work schedule mainly imposes obligations on the citizen, but also a lot on the management. So that all overtime is considered legal, and subordinates do not rush to complain to the labor inspectorate, they first issue an order, where:
- publish a list of positions with an alternative schedule;
- describe the potential time frame for overtime (indicate that there is an obligation to perform functions on weekends and holidays as directed by management).
When the contract is signed, the boss has the right to involve employees in work, referring to a separate schedule, but only sometimes and for objective reasons. You cannot force an employee to be on site on Saturday if the work he needs to do is “waiting” until the start of the new week.
Another important feature is that during processing, the employee does not take on any additional functions. He performs only his direct duties. Example: if at 19:00 a delivery of raw materials to a warehouse is expected, which must be immediately accepted, not only the loaders remain, but also the storekeeper who will monitor the unloading and draw up all related documents. You cannot delegate this task to movers.
When working part-time
A part-time worker is allowed to establish an irregular schedule only when he has a shift schedule at his main place of work and works part-time for 8 hours. In all other cases, the part-time worker does not work more than 4 hours and is not involved in overtime.
Payment for irregular working hours to a part-time employee is regulated on the same basis as payment to other employees. All circumstances are recorded in the employment contract.

Irregular working hours are stipulated in the employment contract
Court decisions on disputes related to irregular working hours
Currently, labor disputes are quite common. Often, both parties to an employment contract violate labor laws. Let's look at some court decisions regarding irregular working hours.
Solution 1
An employee who refuses to perform work in this mode cannot be brought to disciplinary liability if the employment contract provides for a condition for working on irregular working hours, but the position is not indicated in the corresponding list.
Citizen S. filed a lawsuit against Romashka LLC to declare illegal and cancel the orders imposing disciplinary sanctions and collecting compensation for moral damages for refusal to perform work outside of their working hours. The defendant referred to the fact that the plaintiff’s employment contract stipulated a condition regarding the establishment of her irregular working hours. However, the court, having examined the evidence presented by the defendant, indicated that the defendant did not submit in the case materials either a collective agreement, agreements, or a local regulatory legal act, in accordance with the provisions of Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation containing a list of positions for employees of Romashka LLC with irregular working hours , which includes the position of the plaintiff.
Consequently, the plaintiff, in accordance with Art. 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation could not be attracted by the employer to work outside the working hours, and therefore decided to recognize the orders of Romashka LLC to announce S.’s reprimand as illegal.
Solution 2
Another example from judicial practice. A taxi driver from Samara went to court to recover unpaid wages for overtime work. The employer objected because the driver signed an employment contract with irregular working hours, which included a corresponding clause. This means that the delay cannot be considered processing.
But the court said that an employee can sometimes be delayed for irregular hours, but the driver did this all the time. This means that this is already overtime work. The court ordered the employer to pay the driver wages for overtime work and compensation for moral damage.

Labor disputes are often resolved in courts
List of positions for workers with irregular working hours
The circle of people who can work irregular working hours is established almost arbitrarily at the local level. There is no single list of positions with irregular working hours in the legislation. Only isolated recommendations can be found on this issue.
Thus, in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On approval of the rules for providing annual additional leave to employees with irregular working hours” dated December 11, 2002 No. 884, it is proposed to include the following positions in the list:
- Management team. For example, a CEO can easily work long hours.
- Maintenance personnel. The same service technician can come to work early during irregular working hours to check the equipment.
- Housekeeping staff. Having the caretaker come out to work irregular working hours can make the work of the entire staff easier.
- Employees whose time spent at work cannot be counted. A realtor can organize property showings during irregular working hours.
- Employees who have an obligation to work a certain amount of time, but the period when this must be done is not specified. These include people in creative professions, for whom long working hours are quite normal.
So employers have some freedom in choosing positions with irregular working hours. In private structures, irregular working hours are established almost entirely at the request of management. The main thing is that the list of positions is fixed in writing.
FAQ
Having understood the theory and examined practical examples, identifying the advantages and disadvantages of establishing irregular working hours and its differences from overtime work, we will answer the most frequently asked questions.
What is better: regular or irregular working hours?
This question cannot be answered unambiguously. Not only the legal, but also the human factor of your boss will be key. On the one hand, if the employment contract provides for an irregular work schedule, you have the right to additional days of vacation, which is good news, provided that there is a possibility that you will not be involved in working outside the standard schedule at all.
That is, it is better for the employer to provide for irregular working hours in the terms of the employment contract, and the employee should not categorically evaluate this fact. The main feature and difference from overtime work (overtime) is that irregular working hours are episodic, that is, they cannot be permanent, and may not be applied at all by the employer in practice. But if you still like certainty and tranquility, a normal working day and a standard 28 days of vacation per year are for you, but no one can guarantee the absence of overtime.

Working long hours has its benefits
Is it possible to take a vacation with irregular working hours?
Yes, the condition of an irregular work schedule in no case cancels the right to annual paid leave. Moreover, for employees hired within the framework of such a schedule, additional guarantees are established regarding the duration of vacation. Additionally, such employees are entitled to at least 3 calendar days per year.
Since the law does not establish a mandatory requirement for the number of undivided days of additional leave when dividing it into parts, as in relation to the main annual leave (Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the employee has the right to divide additional leave for an irregular working day according to the schedule at his own discretion.
How work is controlled under NSD
Control over the quality and quantity of work during an irregular work schedule on the part of the employer is no different from standard conditions. However, it is important for accounting departments to correctly keep records of overtime in order to avoid problems with regulatory authorities, as well as confusion with the concept of overtime work.

Working on an irregular schedule requires additional accounting from the accounting and HR departments
What to do if your employer forces you to switch to irregular working hours
Based on the fundamental principle of freedom of contract, the parties have the right to agree and adjust the terms of contracts at their own discretion. This also applies to an employment contract. The employer has the right to include a condition on an irregular schedule, and the employee has the right to refuse to enter into an employment contract with irregular working hours if the conditions do not suit him and choose another employer or renegotiate the conditions with the first one.
However, you should not be critical of this feature, as we said earlier - an irregular schedule may not be implemented in practice, while the employee will have guarantees.
If you have already concluded an employment contract and the employer insists on irregular working hours, it is important that this is documented, since such overtime is not paid like overtime, which means you may be left without any compensation or guarantees. It is important to check their availability when concluding an additional agreement to the employment contract.
General concepts
Article number 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the manager the right to provide employees with a certain amount of work that exceeds the existing generally accepted norm.
These works must be performed during hours that are not specified in the employment contract. It is also worth noting that the legislation of the Russian Federation took care of individuals working overtime, providing them with the opportunity for additional rest.
In this case, the employee is entitled to leave not at his own expense, but paid by the employer. You can read about this in Article 119 of the Labor Code. If you have additional questions, please review articles numbered 97, 116 and 126.
An irregular working day is a specific schedule according to which individuals periodically work extra time (in excess of the established standard working hours) in order to cope with the required amount of work on time.
The main characteristics of an irregular working day include the following:
- Such a schedule can be established only for a certain category of individuals holding certain job positions.
- A slightly longer working day than existing standards should be introduced only when there is an urgent need for it.
- This mode is usually used for individuals engaged in such types of work, the performance of which cannot be accurately recorded using time.
- An irregular schedule is best suited for those employees who have expressed a desire to independently manage their working time.
- Any types of work that require seasonal performance, as well as the relevance of which depends on the time of day, and work that does not have clearly established time boundaries, are considered irregular.
We recommend that you pay attention to Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which displays the main points and rules that require mandatory compliance when concluding an employment contract.
If a document is drawn up without taking into account the requirements of Article 57, then it will automatically not have legal force. And in an agreement that has no legal value, it makes no sense to stipulate any conditions, including those regarding irregular working hours.
You can find a sample employment contract with irregular working hours here.
An irregular working day in an employment contract is a schedule that allows individuals to work beyond the norm established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This need is justified by production needs, when it is necessary to perform a larger amount of work.
Irregular work includes any activity that does not have a clearly defined time frame. The subtleties of drawing up an employment agreement are determined by Article No. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An agreement that violates the provisions of this article is automatically considered illegitimate.
In this case, there is no need to introduce irregular working hours, since the employment contract (a sample is presented below) simply will not have legal force.
Legal basis
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation implies a certain algorithm for fixing irregular days in an employment contract. This form of work must be indicated in accordance with the following rules:
- The employment agreement form must include a list of specialties that provide the opportunity to work on an irregular schedule.
- The contract clause on irregular working hours must be drawn up in accordance with all the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Any discrepancies that violate the employee’s rights to work and rest will be considered illegitimate.
- The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the duration of an employee’s shift.
- Russian legislation also does not provide for the payment of compensation or additional vacation days for work on a non-fixed schedule.
- A subordinate can perform exclusively those functions that relate to his profession.
The contract can be supplemented with other data, but the provisions listed above must be mandatory in the contract.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee of any organization can work no more than 40 hours in one week. With a five-day work week, a person can work a maximum of eight hours per day in one day.
However, the employer has a way to go beyond the time frames established by law - to organize a non-fixed schedule with working days. The whole process is regulated by Article No. 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In order for an employee to work beyond his standard shift, an appropriate clause on the form of the labor process must be added to an employment contract with irregular working hours.
note
In the agreement that was signed between the employee and the employer, it is necessary to indicate the mode of attracting the employee.
For example, the contract can indicate “the employee is involved in the performance of official duties occasionally.”
As mentioned, the extra-standard work week is not limited to a certain time frame. However, the contract must contain information on such aspects as:
- number of shifts during one month;
- the number of hours that the employee must work overtime;
- work and rest schedule.
Important! The Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines a list of categories of employees who are prohibited from engaging in irregular work.
These include:
- pregnant employees;
- employees who are under 18 years of age;
- persons with disabilities;
- people of retirement age;
- mothers of many children;
- employees who undergo training on the evening shift.
After introducing the above-normal form of work and making appropriate changes to the contract, the employer issues a decree that must contain a specific list of positions. Later, the employer undertakes to familiarize employees with the details of the new working regime.

There is a unified sample employment contract with irregular working hours. It consists of the following parts:
- “Hat” (the name of the organization and working hours are indicated on the left, and the initials of the manager on the right).
- Part 1 includes general provisions that explain the essence of this form of labor, as well as its regulatory framework.
- Part 2 consists of a list of individuals for whom the terms of the agreement become relevant after entry into force.
- Part 3 contains compensation provisions.
- The final provisions of the document include a list of all administrative persons with whom the excess schedule was agreed upon.
Contract clauses
Generally speaking, an agreement with a non-fixed working day must necessarily contain the following provisions:
- date of the contract;
- Full name of the employee and employer;
- information about the position and place of work;
- rights and obligations of both parties;
- functions of the parties;
- insurance guarantees;
- personal information of the employee and employer.
The employer must notify the employee about how irregular working hours should be stipulated in the employment contract. This can only be done in a new contract when there is a production need. Russian legislation provides that an employee does not have the right to refuse to work on an extra-standard schedule, therefore the agreement is unilateral.
The subordinate undertakes to fulfill his obligations, which are specified in the contract with non-standard working hours. Involving a subordinate in excess work will be considered a direct violation of the law on the part of the administrative apparatus of the enterprise.
It is worth noting that an individual can work on an irregular schedule only in certain cases when production requires it. The Labor Code does not provide for regular performance of labor functions under such conditions. Also, the manager is not obligated to pay additional financial compensation, however, he can provide it to an individual.
Peculiarities of specifying irregular working hours in an employment contract Link to main publication
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: One-time employment contract with an individual
Results
The issue of establishing and applying irregular working hours is relevant today for both employers and employees. Some want to save money, while others, on the contrary, want to receive additional guarantees or compensation.
In practice, both employees and employers incorrectly interpret and do not distinguish between the concepts of “irregular hours,” “overtime,” “overtime,” “additional work,” and so on. There are often cases of abuse of rights on the part of employers, in order to save money, when, with an established irregular working day, an employee is involved in working beyond the norm not occasionally, but systematically. Such circumstances are qualified as overtime work, which is subject to additional payment. Therefore, it is important for an employee to know his rights in order to stop their violation or protect them in a timely manner, and for an employer to avoid problems with regulatory authorities.