Regulatory regulation
Activities related to the management of solid waste in Russia are regulated by a number of regulations:
- FZ-52;
- FZ-89;
- Government resolutions No. 354, 1156;
- SanPiN 42-128-4690-88;
- Resolution of the State Construction Committee No. 170.
The law defines the responsible persons and the procedure for waste management at all stages from collection to disposal. Terminology updates for 2021 are associated with a change in the principle of classifying waste as a specific type. The term MSW, used until 2021, was used only for waste that was generated as a result of the activities of individuals. The new term MSW also refers to waste from legal entities that has the same characteristics as MSW.
Another important change effective from 2021 is the introduction of regional operators into the waste management chain. Now these companies are responsible for the circulation of all waste in the territory of the federal subject assigned to them.
Regional operators ensure the collection, removal and proper disposal of waste. They can outsource some of their operations, remaining the sole responsible participant for the situation with MSW in the region.
Components of the regulatory framework
Legislative acts, SNiPs, and rules establish standards for storage, methods of collecting MSW, transportation, disposal, and obtaining a license.
- No89-FZ of June 24, 1998 “On production and consumption waste”
- No. 99-FZ dated May 4, 2011 “On licensing of certain types of activities.” Sets when a license must be obtained
- No96-FZ of May 4, 1999 No. 96-FZ “On the protection of atmospheric air”
- No7-FZ dated January 10, 2002 “On Environmental Protection”
- No. 52-FZ of March 30, 1999 No. 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population”
Classification of municipal solid waste
Several types of classification of solid household waste are used, differing in the characteristics by which the division occurs:
- state of aggregation;
- origin and composition;
- Hazard Class;
- duration of use.
The choice of classification method depends on the tasks that are performed by separating waste into classes.
The state of aggregation is taken into account when choosing tools that are used to process waste. For example, separate collection systems often use mesh containers to hold dry and solid residues.
By composition
Taking into account the origin and composition is necessary to determine waste treatment methods: methods of sorting, processing, disposal. Based on the origin and composition in Russia, the Federal Classification Catalog of Waste (FKKO) has been formed. This is a guide to all types of waste, where waste is divided into groups and each type is assigned its own code, displaying the following information:
- group (name of the FKKO block);
- origin and composition;
- state of aggregation and physical form;
- Hazard Class.
Division by composition is most common when organizing a separate waste collection system, in which each type of raw material (waste paper, glass, etc.) is sent to a designated container. A less advanced sorting system is partially beginning to be implemented in Russia: waste is divided into dry (inorganic) and wet (organic and inorganic).
By hazard class
One of the characteristics indicated in the FKKO code is the hazard class. In Russia, there are 5 hazard classes, where the most dangerous is class I, and the safest is class V. This division is necessary to develop safe and rational methods of waste management. Solid household waste includes waste of two hazard classes:
| Hazard Class | Description | Examples of raw materials |
| IV | Garbage with a low degree of danger; if released into the natural environment, it will take at least 3 years to recover | Wood, plastic, rubber |
| V | Virtually harmless waste of natural origin that does not harm the environment | Metals, waste paper, organics |
Other classes of waste are not considered household waste and must be disposed of separately. For example, construction or bulky waste is stored in storage bins or a company is ordered for removal. Batteries and accumulators must be handed over to collection points.
By duration of use
Separation of solid waste by duration of use is necessary to determine the timing of circulation of certain types of waste. There are two groups: short-term and long-term use. Short-term solid waste is generated daily during human activity: food residues, printed publications read, packaging of goods. Durable goods become waste after years of use: car tires, containers, metal and wooden appliances or tools.
The concept of solid waste
The official name for household items and items that we stop using and throw in the trash is municipal solid waste (MSW). This category includes things that have fallen out of use as a result of breakdown, loss of functionality, or become morally or technically obsolete.
Every day, large volumes of materials used as containers and packaging accumulate in landfills, remain in places where city festivals or outdoor picnics are held, and become sources of pollution of the atmosphere, land and water resources. Getting acquainted with some of the figures is impressive and concretizes the scale of the problem.
- 350 kg is the amount of waste disposed of in the trash by every Russian resident per year.
- More than 5 million tons is the amount of materials that end up in garbage every month in our country.
- More than 60 million tons is the amount of garbage produced by our fellow citizens per year.
It is impossible to imagine the mountains of garbage that accumulate year after year on the planet, occupying more and more of human living space.
Waste not classified as household waste
Among the waste generated in everyday life, there may be those that do not belong to solid waste. These are all wastes of class I-III, which are characterized by a high degree of danger when released into the environment. The danger lies in chemical, toxic, radiation pollution, which spreads through the air or through soil and groundwater. Most often, such waste arises during construction or industrial activities, but there are examples of household origin:
- electronic equipment;
- thermometers;
- batteries, accumulators;
- chemical oils;
- varnishes and paints;
- cables.
Impact of solid waste on the environment
When handled correctly, solid household waste does not have a serious negative impact on the environment - this is evidenced by the assigned hazard class for the components of solid waste.
A negative impact occurs when the rules for handling household waste are violated, in which different types of waste are mixed, and hazardous substances are introduced. Due to this, landfill gas is formed at landfills - a dangerous heterogeneous substance that is susceptible to fire and explosions.
When burning, toxic fumes can be generated, and the flame can spread to other areas of the landfill.
A high proportion of organic residues in solid waste leads to the formation of areas where rodents accumulate, which are carriers of infections. For this reason, regional operators must ensure timely removal of waste from residential areas.
Basic rules for handling solid waste
Legislatively, the rules for waste management are enshrined in SanPiN 42-128-4690-88, which specifies all the conditions and terms that must be observed when handling solid waste. Management companies provide the required conditions for waste collection, and regional operators handle removal. Requirements for storage areas:
- location – 20-100 meters from the house;
- container volume – 0.8 m3;
- number of containers – no more than 5 per site;
- insulated concrete or asphalt base;
- free access for equipment.
The rules determine the frequency of garbage collection: at temperatures above 5 °C - every day, below 5 °C - every 3 days.
Waste collection and sorting
Several types of containers are used to collect waste: gray and blue, mesh, storage bins. Separation into different containers is necessary for sorting waste: dry inorganic waste goes into blue or mesh, organics and wet inorganic waste go into gray, bulky and construction waste goes into bins. Instead of gray, blue or mesh, there may be one-color bins - this means that a separate waste collection system has not yet been implemented. In such a situation, all solid household waste is thrown into single-color containers.
Removal and transportation of waste
When implementing a waste sorting system, transport with a separated cargo compartment must be used for removal to prevent mixing of solid waste. In the absence of separation, household waste is removed by transport with a common compartment. Additionally, garbage trucks can be equipped with mobile presses to compact solid waste in the vehicle - this allows for efficient use of transport.
It is unacceptable to use transport for the removal of dry inorganic waste if it previously transported organic matter. The condition applies even if the body has been washed. Every time a garbage truck enters a solid waste landfill, it undergoes disinfection treatment to prevent the transfer of infections to places located along the route.
To control movement along an agreed route, all garbage trucks are required to be equipped with the GLONASS system. On average, garbage trucks can hold up to 20 m3 of solid waste.
For the removal of bulky waste, trucks with a platform on which a storage bin is placed are used. The machine is also equipped with loading and unloading devices for performing container operations.
Construction of a landfill
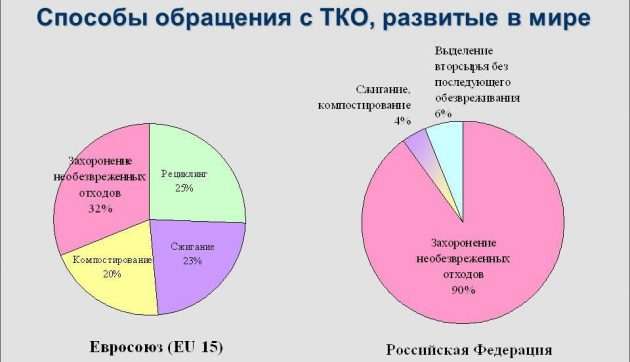
In Russia, almost all municipal solid waste is subject to disposal at landfills.
There are more than 15 thousand testing grounds in the country, which cover an area of more than 40 thousand km2.
Solid waste landfills are designed according to a structure that includes the following elements:
- waste storage areas;
- economic zones;
- auxiliary buildings.
Depending on the equipment, they may contain installations for sorting and compacting waste and collecting landfill gas. On sorting lines, raw materials suitable for secondary processing are separated from the solid waste mass. For example, more than 15% of household waste is glass, which is easier to clean from organic matter than waste paper.
To prevent waste from entering the soil and groundwater, the base of the landfill contains a waterproofing layer of clay. Additionally, a drainage system is being constructed for the controlled removal of generated liquid waste. The operational life of the landfill is no more than 7 years.
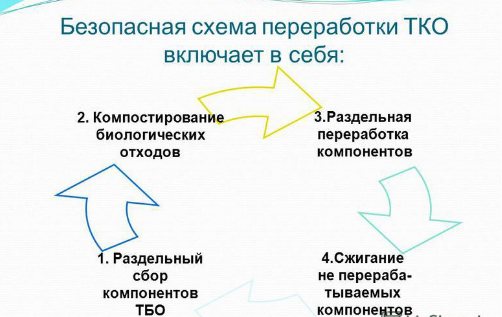
Recycling and disposal of solid waste
Due to the heterogeneous composition of raw materials, recycling of solid waste is complicated, so the disposal method is most often used for disposal. The share of recycling can be increased by introducing a separate waste collection system by material. For example, in developed countries, up to 8 types of waste collection containers are used.
Options for beneficial use of heterogeneous household waste: composting or incineration. Composting is used for organic residues, which, under the influence of biological decomposition processes, form a thick, homogeneous mass. Compost is used as fertilizer. Combustion of solid waste is permissible only if harmful emissions into the air and during energy generation are excluded.
To recycle plastic, metals or glass, they must be cleaned of foreign impurities and dirt after sorting. From secondary raw materials obtained during processing, products are produced that are not inferior in characteristics to the primary ones.
MSW disposal methods
There are several options for getting rid of MSW:
- burial;
- burning;
- composting;
- recycling.
MSW disposal
At first glance, burying solid waste in landfills is the cheapest way, but in practice this is not entirely true.
Landfills for solid waste should be located far from residential, recreational, and water conservation areas; hospitals and parks must not be located near landfills. They occupy vast areas, and if their use is required in the future, a lot of money and time will have to be spent on them so that they can be used for agriculture and residential buildings.
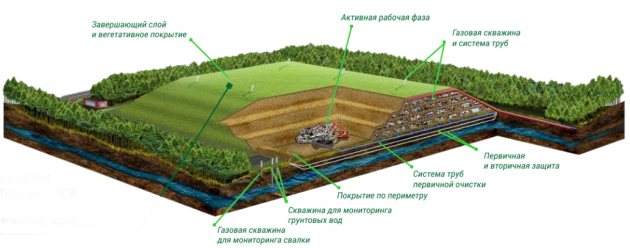
Landfill for solid waste disposal
Landfills cause enormous damage to the soil and air and pollute groundwater. In addition, during the decomposition of waste, gas is released that can ignite. To avoid fire, it must be collected and disposed of.
In addition, the disposal of radioactive and toxic solid waste is prohibited and requires another disposal method.
MSW incineration
The most common method of MSW disposal is incineration. Unlike landfill, which requires a lot of space, after incineration, only ash remains from municipal solid waste.
Another advantage of this method is its low cost. In addition, a side effect of combustion is the release of heat, which can be used for heating and other purposes.
As with landfilling, the main disadvantage of incineration is the harm it causes to the environment. When burned, solid waste releases toxic substances that pollute air and water. But modern waste incinerators are equipped with a cleaning system and do not harm the environment.
Combustion also includes pyrolysis - the decomposition of solid municipal waste under the influence of high temperature in an airless environment. This method is also safe for nature.
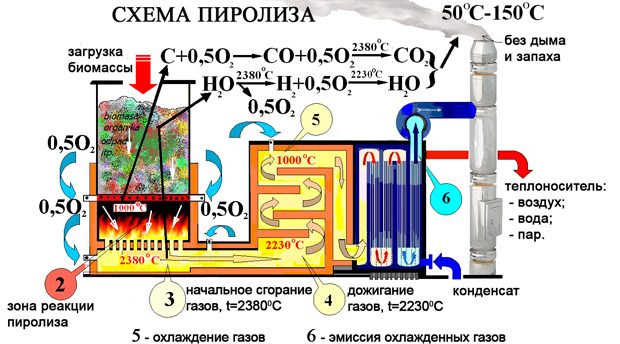
MSW pyrolysis scheme
Composting MSW
Composting is the decomposition of municipal waste by microorganisms. Only organic types of waste can be disposed of in this way. As a result of this processing, compost is obtained - a natural fertilizer, which is subsequently used in agriculture.

Composting MSW
This method is simple and cheap, but its implementation requires waste sorting. The only drawback is the unpleasant odor released as a result of rotting.
MSW recycling
MSW includes a large amount of waste that can be reused:
- Ferrous and non-ferrous metals are sent to foundries for subsequent smelting;
- plastic , if it is not very dirty, and there are no strict requirements for the material obtained after processing;
- glass , which after recycling can be used in construction;
- waste paper from which paper is made;
- wood , which may later be useful in construction;
- consumer electronics , from whose electronic boards the sorted metal is sent for recycling;
- petroleum products : asphalt or bitumen.
Each type of waste has its own processing technology. Using recycled materials in production saves natural resources.
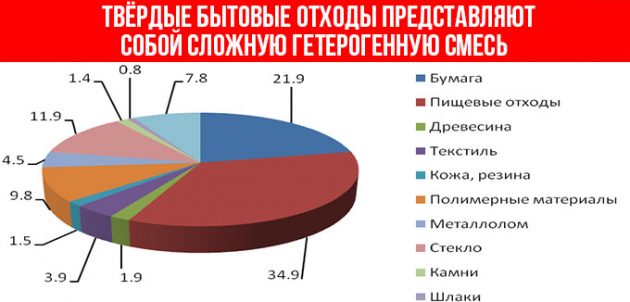
Classification of MSW and their processing, expressed as a percentage
Passport for solid waste
Each enterprise is required to keep records of all waste generated as a result of its activities. For class I-IV waste, a passport must be issued in the prescribed form. To do this, companies analyze all sources of waste generation, determine the hazard class, and coordinate the results with Rosprirodnadzor. All data on the organization’s regular waste circulation is entered into the solid waste management log, where the following data is indicated: amount of waste, dates of actions taken with it (and links to acts), responsible persons.
Current situation with household waste in Russia
In Russia, only in 2021 a primitive solid waste collection system began to be introduced. Despite this, more than 95% of waste is still sent to landfills - more than 65 million tons of waste per year. The introduction of a full-fledged system for separate waste collection should occur in conjunction with the legislative establishment of responsibilities for its recycling.
The first type of waste that is planned to be completely used without destruction is the remains of woodworking production.
The implementation of updated standards is delayed due to the unwillingness of manufacturers to include all generated waste in the production chain. It will take at least another 10 years to create a system for processing the remaining types.
Organization of collection and removal of solid waste
Local authorities use three methods for collecting and removing solid waste:
- a containerless method of MSW removal is carried out directly from residents, when a garbage truck travels along an established route, and people themselves fill the body.
- non-replaceable containers - collected solid waste is poured into a waste collection machine, the containers remain at the collection sites.
- replaceable containers – collected waste; a specialized waste collection organization picks up the container, leaving a new, empty one at the container site.
In the Russian Federation, two methods of collecting solid waste are used:
- unsorted - waste is collected in one container and sent to a landfill;
- selective collection of waste waste - waste is separated by type in places of accumulation.