What are graduated mortgage payments?
Each loan under any repayment system consists of 2 parts: the amount of debt and the interest part. Differentiated (decreasing) payments are a method of loan repayment in which you pay the loan body in equal installments, and interest is charged on the balance of the debt. In the first quarter of the loan term, you will have to make the largest payments, and in the future the amount of monthly payments will decrease.
Few banks offer mortgages with differentiated payments. This is due to the fact that in this case you immediately begin to repay the loan amount. For the bank, this situation is unprofitable, because interest is considered the main source of its income. In case of early repayment, the borrower will be able to save a significant amount of money. More popular banks such as Sberbank, VTB, Otkritie do not have these types of mortgages.
Formula for calculation
You can calculate your mortgage payment yourself using formulas.
Basic payment – C = A/D , where:
- C – monthly repayment amount of the loan body;
- A – the size of the mortgage loan;
- D – mortgage term in months.
The percentage part is calculated using the formula – S=R*L/12 , where:
- S – accrued interest;
- R – debt balance for a given month;
- L – annual interest rate on the mortgage.
R=A-(C*n) , where n is the number of loan payments paid.
Analysis by example
Let's calculate the differentiated mortgage payment if, for example, you decide to take 2,000,000 rubles at 12% per annum for 15 years (or 180 months). The main payment to repay the debt will be: 2,000,000/180 = 11,111.11 rubles.
Now let’s calculate how much you need to deposit into your account every month:
| Month | Calculation | Total amount in rubles |
| 1 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*0))*0,12/12 | 31111,11 |
| 2 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*1))*0,12/12 | 31000 |
| 3 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*2))*0,12/12 | 30888,89 |
| 4 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*3))*0,12/12 | 30777,78 |
| 5 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*4))*0,12/12 | 30666,67 |
| 6 | 11111,11+(2000000-(11111,11*5))*0,12/12 | 30555,56 |
On the websites of banks that provide loans with differentiated payments, you can find a special calculator and do not count everything manually.
Annuity payment and differentiated: the difference
Financial experts agree that if the borrower expects to pay off the loan in a short period of time (up to five years), then it is better to give preference to an annuity. However, there is controversy regarding medium- and long-term loans.
For example, if a borrower takes out a long-term loan, say $100,000 for 10 years with an interest rate on the loan of 10% per annum, then a differentiated payment is more profitable, and significantly. In our conditional example, the interest payment for ten years with differentiated payments will be $50,416.67, and with annuity payments - $58,580.88. Accordingly, the overpayment under the differentiated scheme will be less: by $8,447.53.
But let’s not forget that the example is conditional, and in practice everything does not look so simple. A number of banking experts do not hide that the idea of a significant financial advantage of differentiated payments is largely a marketing myth. The bank will never miss its profit. It is only important for him to convince the borrower that he can really save by choosing one or another payment plan.
“Credits.ru” note: the main thing you need to understand is that the method of calculating interest for both forms of payments is the same. In both cases, interest is calculated on the remaining balance of the debt.
What does annuity payment mean?
With the annuity payment method, you will make equal payments throughout the entire loan term. Stability is great, but in the first months most of the payment will go towards paying interest. By the end of the mortgage term, the situation will change: the principal amount will go to pay off the loan body.
The principle of equal monthly payments is that initially you are forced to pay the bank most of the interest, and only then pay off the principal debt. This is especially true if you decide to pay off your mortgage early.
Formula for calculation
The size of the annuity payment is calculated using a complex formula: Mn = Сз*(Mpc/(1 – (1 + Mpc²))
In this formula:
- MP – the amount of the monthly mortgage payment;
- Сз – loan amount;
- Mpc – interest rate per month;
- Sk – mortgage term in months.
Analysis by example
Calculating equal payments is quite complicated, so let's look at it with an example. Let's take the following parameters:
- mortgage amount – 2,000,000 rubles;
- interest rate – 12% per annum;
- term – 15 years.
Mpc = 12/100/12 = 0.01%.
The calculation of the annuity payment in this case is as follows:
2,000,000*(0.01/(1-(1+0.01)-24)=24003.36 rub.
This is exactly how much money you will have to deposit into your bank account every month.
The ratio of the interest part and the principal debt in the first 5 months can be seen in the table:
| Monthly payment | Interest | Main debt |
| 24003,36 | 20000 | 4003,36 |
| 24003,36 | 19959,97 | 4043,39 |
| 24003,36 | 19919,53 | 4083,83 |
| 24003,36 | 19878,69 | 4124,67 |
| 24003,36 | 19837,65 | 4165,91 |
What does annuity and differentiated payments mean?
Banks use the following loan repayment methods: annuity (classic, rental) and differentiated (commercial, decreasing). The average person cannot understand what they are, but studying their features helps plan your credit load and save money.
Remember, debt repayment methods directly affect the amount of interest payments. Lenders rely on them when creating a payment schedule. When familiarizing the client with the conditions, each bank informs him about how repayment will occur.
But no one among the bankers will tell what their difference is and what method is beneficial for the debtor, since they are pursuing their own interests. But first things first. An annuity payment is the repayment of debt in equal installments over the entire loan term. In this case, the principal amount of the debt is not repaid, because An annuity scheme involves repaying mostly interest rather than the loan body itself. The review clearly describes the situation with the annuity system.
“For 1.5 years, I regularly transferred 50 thousand rubles to the bank every month for a mortgage. I decided to find out how long it would take to repay the loan, and gasped. It turns out that during all this time the amount of my principal debt decreased by only 60 thousand rubles. the rest of the money went to pay off interest.”
Sergey
This scheme is characterized by small payments. And this is beneficial for the client, because... You don’t have to cut your expenses too much. But if you expect an early return, the savings will be insignificant. The advantage of the annuity system is convenience, since payments are fixed. There is a difference here, because with a differentiated scheme you will have to find out its size with each mandatory payment.
A differentiated repayment system is a loan payment with large amounts at the first stage and a gradual decrease in monthly installments. The first payments are large, since interest is accrued not on the entire debt, but on its balance. Therefore, it is in the borrower’s interests to deposit large amounts first so that the balance of the debt decreases along with differentiated payments. Not everyone can handle this method of fulfilling their obligations under a contract, which is why it is not in demand.
Which type of payment is more profitable?
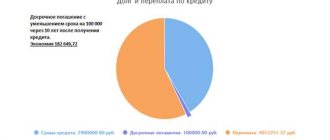
What is more profitable: annuity or differentiated payments? For a mortgage of 2,000,000 rubles. at 12% per annum for 15 years, when repaid with annuity payments, the overpayment will be 2,320,605 rubles, and with differentiated payments - 1,810,000 rubles. At first glance, the benefits are obvious. The difference in the cost of loans is 510,605 rubles.
However, you need to think about whether it is worth paying such large down payments? Income may drop sharply, and then repaying the loan will become an acute problem. The same initial monthly payment as with the annuity repayment method is only possible if the mortgage term is significantly increased. In addition, only a few banks are ready to offer loans with differentiated payments, for example, Rosselkhozbank and Gazprombank.
What's better?
Most borrowers are only concerned about the approval of the application and do not ask themselves which scheme is more profitable for them. And because of this, they can seriously miscalculate.
The method for calculating the monthly tranche depends on both the loan term and the amount. For people who plan to bear mortgage bondage for 15 years or more, it is more profitable to find a banking product with a differentiated debt repayment system. In this case, the overpayment will be much less. If desired, the client can deposit an amount to pay off the debt, and he will benefit both at the beginning and at the end of the period.
Those who take out a home loan for a short period benefit from annuities. The borrower pays the same amount monthly, while his solvency does not change (except in emergency situations: loss of job, etc.). Early repayment is economically justified only in the first years of lending.
So, recommendations on which payments are more profitable: annuity or differentiated depend on the loan term, the borrower’s solvency and his focus on early repayment.
Nowadays the differentiated scheme is practically not used. It can be found at monopoly banks: Sberbank, Gazprombank and VTB 24. However, they do not advertise it much.
The difference between the schemes for depositing money on a mortgage loan
The annuity payment can be calculated using the formula:
Payment ann. = Mortgage amount * (Rm + [Rm / ((1 + Rm)^Month – 1)]),
Where:
- Prm – Annual mortgage rate divided by 12.
- Months – the number of months for which the mortgage was taken out.
Calculating a differentiated payment is very simple (we wrote about the calculation of such a payment and which banks offer such loans here). Divide the principal debt by the number of months the mortgage is taken out. This will give you the amount of your principal repayment. This component of the mortgage payment does not change throughout the entire term. Payment of interest for using money will be different every month. It can be calculated using the formula:
Interest = Mortgage balance * Annual rate / 365 * Number of days in month
Payment diff. = Monthly principal payment + Interest
The annuity payment is always less than the graduated payment at the beginning of the mortgage period, so the mortgage amount may be larger.
The same monthly payment is possible only if the payment of the principal debt is increased gradually. Thus, with annuity payments, the principal debt is paid more slowly than with differentiated payments and the overpayment is correspondingly higher. You can learn more about how to make early repayment of a mortgage using annuity payments and whether it is worth doing this in our article.
When a significant amount of money appears, it becomes possible to reduce payments and the mortgage term. It is more profitable for banks to reduce mortgage payments. The longer the borrower remains a client of the bank, the more of its services the bank will be able to offer the client.
Interest is paid on the outstanding balance. The longer the client is a debtor, the more interest the bank will receive. Reducing payments reduces the risk of paying off your mortgage. It is more profitable for the borrower to shorten the mortgage term. Quicker relief from the burdens of a mortgage, less overpayment.
In the first half of the term, the borrower pays most of the interest to the lending institution. It is during this period that it is most beneficial for him to change the mortgage agreement. At the end of the term, interest is minimal and it will not be possible to significantly reduce the overpayment.
Read the mortgage agreement carefully before signing. The agreement may stipulate conditions under which changing the terms of the agreement is disadvantageous to the borrowers.
What is the difference between an annuity payment and a differentiated one?
First of all, we strongly recommend that you read our publications on annuity payments and differentiated payments. We are sure that you will find detailed answers to many questions in them. Briefly, the main differences between these payments can be formulated as follows:
Annuity payment
- These are monthly loan payments that are made in equal amounts.
According to the annuity scheme, a payment schedule will be calculated for you so that you will pay the same amount every month to repay the loan. Moreover, at the initial stage, most of the payment will go to repay interest, and a smaller part will go to repay the loan body. Towards the end of the loan period, interest will make up a smaller share of the annuity payment amount, and most of it will be used to repay the loan body.
Differentiated payment
– these are constantly decreasing monthly loan payments.
If the entire loan term is conditionally divided into four equal parts, then the first part accounts for the largest payments, and the last – the smallest. The size of payments in the middle of the loan term is approximately the same as with the annuity method of loan repayment. The differentiated payment consists of the amount used to repay the loan body (it is the same in all payments) and interest payments on the loan (they are constantly decreasing).
That's all the differences! It remains to find out which payments are more profitable.
Which payment is more profitable - annuity or differentiated?
Both debt schemes for settlements with the bank have both their advantages and disadvantages. In order to make the optimal choice, it is necessary to be guided by the principle of specific benefit; what exactly will be more convenient for the payer based on the specifics of the situation - regular contributions or work to reduce it. Some will be willing to pay large amounts at the first stage of repayment, while others would prefer that these amounts be smaller, but with a larger total.
If the main goal is to overpay the company as little as possible, then the choice should be made in favor of differentiated payments. When the client’s solvency is not too high and stable, it is better to give preference to the annuity option, which is less burdensome at the beginning. In addition, the time factor must be taken into account. If you need money very urgently, then the second scheme is the best way to apply for a loan.
And one more nuance that experts recommend paying attention to when choosing a payment method. Now almost every financial organization on its website offers online calculations of differentiated repayments, so that the potential client can make all the calculations himself and see the economic benefits. But the downside is that this service can only be called accurate with a big stretch. In practice, the payment schedule includes other amounts, and they are much higher. This is especially noticeable with long-term loans against the background of making large regular payments - for example, with a mortgage. In addition, additional services – insurance, commissions – may not be included in the formula. The costs for them are quite high and will place an additional burden on a person who did not count on it at all.
Differentiated payment
This is a calculation scheme where the monthly loan repayment amount gradually decreases towards the end of the loan period.
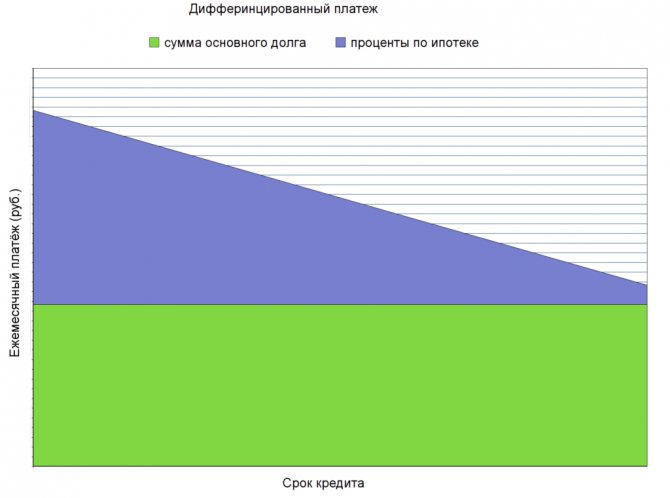
With a differentiated loan repayment scheme, the monthly payment is calculated as the amount of the principal debt divided by months in equal parts, plus interest accrued monthly on the remaining debt. Naturally, the size of the debt decreases towards the end of the loan term, hence the reduction in the monthly payment. Thus, the first payments will be larger than the last ones.
Schedule
The principle of a differentiated method of loan repayment is most easily represented in the form of a graph.
Calculation formula
The part of the monthly payment used to repay the principal debt is calculated as follows: you need to divide the amount of the principal debt by the loan term in months.
B is the part of the monthly payment to repay the principal debt, S is the amount of the principal debt, N is the loan term in months.
The debt balance for the current month is calculated as follows: the part of the monthly payment going to repay the principal debt must be multiplied by the number of months already paid. And subtract what you received from the original principal.
B is the part of the monthly payment to repay the principal debt, S is the amount of the principal debt, Sn is the balance of the principal debt in the month, n is the number of elapsed months.
To calculate the interest accrued on the debt balance, you need to multiply the principal balance in the current month by the monthly interest rate (annual divided by 12 months).
p – accrued interest per month, Sn – outstanding principal balance per month, P – annual interest rate.
Thus, the monthly payment under a differentiated repayment scheme can be calculated using the following formula:
- Dn - differentiated monthly payment
- p — accrued interest per month
- Sn - balance of principal debt in the month
- P—annual interest rate
- B – part of the monthly payment to repay the principal debt
- S – initial amount of principal debt
- N – loan term in months
- n – number of months passed
Table
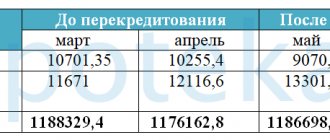
As an example of a differentiated scheme, we present in the table the calculation of payments on a loan of 500 thousand rubles for a period of one year at 14% per annum.
| № | We eat. payment | Basic duty | Interest | Ost. debt |
| 1 | 47 500.00 | 41 666.67 | 5 833.33 | 458 333.33 |
| 2 | 47 013.89 | 41 666.67 | 5 347.22 | 416 666.67 |
| 3 | 46 527.78 | 41 666.67 | 4 861.11 | 375 000.00 |
| 4 | 46 041.67 | 41 666.67 | 4 375.00 | 333 333.33 |
| 5 | 45 555.56 | 41 666.67 | 3 888.89 | 291 666.67 |
| 6 | 45 069.44 | 41 666.67 | 3 402.78 | 250 000.00 |
| 7 | 44 583.33 | 41 666.67 | 2 916.67 | 208 333.33 |
| 8 | 44 097.22 | 41 666.67 | 2 430.56 | 166 666.67 |
| 9 | 43 611.11 | 41 666.67 | 1 944.44 | 125 000.00 |
| 10 | 43 125.00 | 41 666.67 | 1 458.33 | 83 333.33 |
| 11 | 42 638.89 | 41 666.67 | 972.22 | 41 666.67 |
| 12 | 42 152.78 | 41 666.67 | 486.11 | 0.00 |
| Overpayment on interest: RUB 37,916.67. | ||||
| Total loan cost: RUB 537,916.67. | ||||
pros
- The payment amount decreases every month, the credit load decreases
- Significant savings on interest payments for using a loan
Minuses
- The first large payments can be quite a serious burden on the borrower's budget
- Banks impose more stringent requirements on borrowers applying for a differentiated payment scheme.
Advantages and disadvantages of the options under study
Advantages of annuity payment:
- Simplicity, due to which there is no risk of accidental underpayment; it is easier to avoid fines since the amount is fixed.
- Uniform financial burden, no unaffordable initial payments, the ability to plan a budget during the loan term.
- More lenient requirements for a citizen who wants to take out a mortgage loan: there is no need to thoroughly check the financial situation, as with another payment scheme. Consequently, the loan approval rate is much higher.
- In accordance with Russian legislation, mortgage interest is returned through personal income tax (a type of direct taxes calculated from the income of individuals minus expenses), thus, annuity payments are more profitable when providing tax deductions: when making annuity payments in the first few years, such payments exceed the amount of the principal debt.
- Widespread in Russian banks, the ability to choose from a variety of offers.
Disadvantages of an annuity:
- If the interest rate exceeds the principal amount of the debt within half of the term, this is why this type of payment is more profitable for financial institutions: the bank will receive a profit quickly.
- A complex formula for calculating debt according to such a scheme will cause difficulties for a person without the appropriate education, and there will be a need to use online calculators.
- The overpayment is greater than with differentiated payments; it is inappropriate to repay the loan in advance: the funds spent on interest payments are not returned.
Advantages of differentiated payment:
- Overpayment on the loan is minimized: this scheme is much more profitable for the borrower than other types of payments.
- A uniform reduction in financial burden allows the payer to feel calmer.
- Most borrowers can easily calculate monthly payments; they do not have to resort to the help of third-party services.
Disadvantages of differentiated type:
- The risk of making an error caused by the difference between payments, which may lead to the payment of fines.
- There is a meager list of banks offering this loan repayment scheme: clients are forced to choose only from 2 organizations.
- Relatively high initial payments, which leads to a strict selection of those wishing to receive a mortgage: credit history and income are thoroughly checked.
- The maximum loan amount is less than with annuity payments. This is due to the impressive size of the first payment, which must be consistent with the borrower’s income.